Nuclear Chemistry 2 - radioactive decay
advertisement
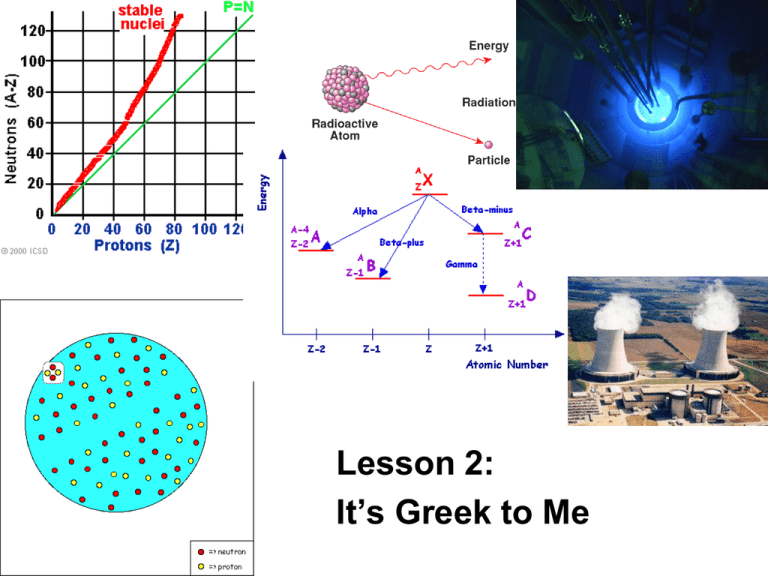
Lesson 2: It’s Greek to Me ChemCatalyst Uranium-238 is used in nuclear reactors to generate electricity. In the nuclear reactor, uranium-238 changes to lead209. • How can atoms of uranium-238 change into atoms of lead-209? • The nuclear reaction is initiated by 1 colliding the uranium-238 with 0 n . What do you think this symbol represents? The Big Question • What changes in the nucleus during radioactive decay? • Goal - Predict the result of radioactive decay of an atom. Notes • A nuclear reaction happens when the nucleus of an atom is unstable and spontaneously decays emitting particles. • There are two types of nuclear decay, alpha and beta. Depending on the type of decay either an alpha particle or beta particle is emitted. • Chemists use equations like the following one to represent nuclear reactions. 47 Ca 20 238 U 92 g g + 47 Sc 21 + 234 Th 90 A more detailed map Activity Purpose: This activity introduces you to two common forms of nuclear decay. It’s Greek to me… Parent isotope Particle emitted Daughter Change isotope in atomic # # of protons lost or gained # of neutrons lost or gained Change in mass number Alpha or beta decay? Making Sense • Give a specific example of how a chemist might make gold using alpha decay. Be specific about which isotope of gold is made. • Give a specific example of how a chemist might make gold using beta decay. Be specific about which isotope of gold is made. • Would the isotopes of gold prepared by alpha and beta decay be located in the band of stability? Notes • Alpha (α) decay and beta (β)decay are two forms of nuclear decay. • During alpha decay, a nucleus is splitting into two smaller elements, one of which is always a helium atom. • Chemists use the symbol α (Greek letter) to represent an alpha particle. U He Th U Th 238 92 238 92 4 2 234 90 234 90 • During beta decay a neutron inside the nucleus of an atom emits an electron. –This electron is a part of nuclear decay and therefore comes from the nucleus. • Sometimes a neutron can be split into an electron and a proton. • Removal of an electron from a neutron changes the neutron into a proton 0 1 n e p 1 0 1 1 n p 1 0 1 1 140 56 Ba 140 57 La (cont.) • The process of splitting a large nucleus into smaller ones is called nuclear fission. • Besides alpha and beta particles, many radioactive nuclei release energy in the form of gamma rays ( rays). (cont.) (cont.) • The release of a ray does not change the mass number or the atomic number – a ray has no mass. • radiation by itself does not change the identity of the atom. –But ray emission usually occurs whenever there is alpha or beta emission. Nuclear fission Sometimes you can get an atom to split by bombarding it with neutrons U n Kr 238 92 1 0 91 2 142 90 Ba 5 n 1 0 Can we use nuclear chemistry to make gold? • What isotope would you want to start with if you were to make gold using alpha decay? Why? • What isotope of gold would you make? • Is this isotope stable? • What element would you want to start with if you were to make gold using beta decay? Explain • Is this isotope stable? • Do you think chemists use nuclear decay to make gold? Why or why not? Check-In • What products do you expect if an atom of actinium-227 –undergoes alpha decay? – Write equation – Is the formed atom stable? –undergoes beta decay? – Write equation – Is the formed atom stable? Wrap-Up • When changes occur in the nucleus of an atom it is called a _____ reaction. • When an α particle is emitted from an atom, the nucleus loses two _____ and two ______. An α particle is the same as a _____ atom. • When a β particle is emitted from an atom, the nucleus gains a(n) _____ and loses a(n) _____. A β particle is the same as a(n) ______.