Trichinella spiralis
advertisement

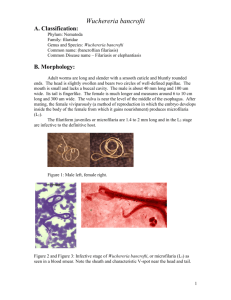
Review of intestinal helminths Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworm) 似蚓蛔线虫(蛔虫) Trichuris trichiura (whipworm) 毛首鞭形线虫 (鞭虫) Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) 蠕形住肠线虫(蛲虫) Ancylostoma duodenale Necator americanus (hookworms) 钩虫 Tissue-blood dwelling nematodes Trichinella spiralis 旋毛形线虫 Wuchereria bancrofti 班氏吴策线虫 Onchocerca volvulus 旋盘尾丝虫 --Filaria 丝虫 The history of Trichinella spiralis In year 1835,Young Jim Paget, a first year medical student at London Hospital Medical School, rushed into the autopsy room. The 51 yr-old Italian bricklayer who had died of tuberculosis, and that they were now dissecting, also had "sandy diaphragm," a condition that dulled even the sharpest of scalpels. Well, anyway, when they had all cleared the room, Jim quietly stole back in and removed a small bit of muscle tissue from the diaphragm. He was more than curious as to the nature of "sandy diaphragm". He first examined it with his trusty hand lens he carried for just such a situation. He thought he saw small worms coiled up inside each nodule. Upon even higher magnification, the presence of coiled worms was revealed. (From www.trichinella.org) Trichinella spiralis Jim Paget Worms in the “sandy diaphragm” Trichinella spiralis Trichina worms were observed in pork in 1846 by Joseph Leidy. He saved hundreds of lives by recommending cooking pork at a high enough temperature to kill the organism. Life cycle work out in1850’s By Rudolph Virchow. Trichinella control Rudolf Virchow (Germany) suggested mandatory diagnosis of all meat at the slaughterhouses in 1877 This has greatly reduced trichinellosis as human health Problem. Trichinella spiralis - cause 旋毛虫病 trichinosis, trichiniasis, or trichinelliasis Worldwide Distribution Parasitic zoonosis Food borne parasitosis Distribution of Trichinella spiralis Trichinosis is most common in temperate and arctic climates - high prevalence in pork-eating areas of the world. arctic temperate Adults of Trichinella spiralis Adults : small, 1.5~4 mm Larva: females give birth to larva ( Eggs: hatch in uterus 子宫) 特点:直接产幼虫 stichosome 成虫形态在诊断 上无意义! 杆状体 Hatched Larva Encysted larva 幼虫囊包-- infective stage 0.25~0.5mm × 0.21~0.42mm Lemon shape 1~2 larva in the cyst Life cycle Adult female in mucosa of small intestine Trichina cysts in skeletal muscle骨骼肌 Pathogenisis 3 stages : 1. Invasion – 1 week first symptoms appear 12 hours to 2 days following ingestion of trichina cysts Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache with slight fever 2. migration of larvae – 2 week to 2 months penetration and encystment in skeletal muscles 骨骼肌 2. migration of larvae – 2 week to 2 months Weakness, Headache and dizziness 头昏, Fever,chills and sweating, Myalgia 肌痛 perorbital edema splinter hemorrhages (under finger nails) Eosinophilia 嗜酸性细胞增多 Deaths are rare and due to myocarditis 心肌炎, encephalitis 脑炎 and pneumonia肺炎 3.calcification (if one survives stage2!) - occurs several months after infection - calcium is deposited around the cysts - Larva eventually die in a year or longer In human infections, 5 larvae/gram body weight are fatal. Diagnosis 1. Muscle biopsy : trichina cysts can be seen with microscope Muscle samples were squeezed between two glass plates 肌肉压片 2. ELISA to identify Trichinella antibodies Others?: Epidemiology 1. Cosmopolitan distribution 2. Source of infection is pork or pork products infection is most frequents among ethnic groups disposed to eat raw or poorly cooked pork products Treatment of Trichinella spiralis Drugs: Mebendazole(甲苯哒唑) Albendazole(阿苯哒唑,丙硫咪唑) Others: Prevention of Trichinella spiralis 1. Thorough cooking (temperature above 58o C) microwave cooking of pork roasts and chops (with bone) is NOT effective in killing trichina 2. freezing for 20 days will kill temperate climate strain - freezing is NOT effective against the arctic strain - smoking, salting, and drying pork, bear or other meat will NOT kill trichina larvae Prevention of Trichinella spiralis 3. - Do not feed pork scraps in garbage to pigs - eliminate rats in areas where pigs are kept Tissue-blood dwelling nemotodes Filaria -cause filariasis Four important filarial worms parasitic in humans are: Wuchereria bancrofti 班氏吴策线虫 Onchocerca volvulus 旋盘尾丝虫 Brugia malayi 马来布鲁线虫 Loa loa 罗阿罗阿线虫 W. bancrofti is strictly a human pathogen and is distributed in tropical areas worldwide More than 80 million were affected Orient, South Pacific, and Southern Asia to India – overlaps with Wuchereria bancrofti - but does not occur in Africa or South America B. malayi infects a number of wild and domestic animals Morphology--Adults of Wuchereria bancrofti Adults occur in the lymphatic vessels (Adult B. malayi are only half the size of W. bancrofti ) filariform larva 丝状蚴 Microfilariae of Wuchereria bancrofti Microfilariae are seen in blood smears and are DIAGNOSTIC worms are 230-320 µm long Morphological differences of microfilariae of Wuchereria bancrofti and Brugia malayi Wuchereria bancrofti Length (µm) Appearance 体态 244-296× 5.3-5.7 graceful sweeping curves Cephalic space length equals width 头隙 Body nuclei well defined, discrete, 体核 round, uniform sized Tail 尾核 no terminal nuclei Brugia malayi 177-230× 5 -6 Irregular kinky curves length twice width blurred, intermingled nuclei crowded together two terminal nuclei Filariform larve-infective stage Microfilariae of Wuchereria bancrofti Nocturnal periodicity of microfilariae 夜现周期性 Pathology of Wuchereria bancrofti Incubation period no symptoms 3 clinical phases: 1. microfilaremia - no symptoms or mild symptoms 微丝蚴血症 Acute allergic inflammatory phase a. lymphadenitis, lymphangitis 淋巴结炎 淋巴管炎 Acute allergic inflammatory phase b. filarial fever 丝虫热 c. funiculitis, orchitis, epididymitis 精索炎, 睾丸炎,附睾炎 3. chronic Obstructive phase a. Elephantiasis 象皮肿 The disfigured legs of lymphatic filariasis patients waiting for medical attention b. chyluria 乳糜尿 c. hydrocele testis 鞘膜积液 Brugia malayi 马来丝虫 Adults live in lymphatic vessels and cause elephantiasis in arm and leg. Difference between W.r and B.m? —— discuss later Diagnosis Identifying microfilaria in blood or other fluid direct blood films concentrations of blood specimens and urine specimens Identifying adults Serologic testing Epidemilogy 1. World Wide distribution 2. Source of infection: patients and infected patients 3. Transmission: by mosquitto Brugia malayi Wuchereria bancrofti Treatment of Wuchereria bancrofti Drugs : hetrazan 海群生 are somewhat effective kill microfilariae and adults with careful administration Global Programme to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis 6 mg/kg diethylcarbamazine citrate (DEC) + 400 mg albendazole; 150 µg/kg ivermectin + 400 mg albendazole (in the case of coendemicity with onchocerciasis) A third option is to follow a treatment regimen using DEC-fortified cooking salt daily for a period of 12 months. Drug Year of registration Indication Praziquantel 1980 Schistosomiasis Mefloquine 1984 Malaria Ivermectin 1987 Onchocerciasis Halofantrine 1988 Malaria Eflornithine 1991 African Tryp. Liposomal amphotericin B 1994 Leishmaniasis (Kala azar) Partners Bayer Hoffman La Roche, WRAIR Merck Smith Kline Beecham, WRAIR Marion Merrel Dow NeXstar Artemether 1997 Malaria Rhone Poulenc Rorer, Kunming Artemetherumefantrine 1999 Malaria Novartis Artemotil (beta-arteether) 2000 Malaria Artecef, WRAIR, Dutch Min. Dev. Miltefosine 2002 Leishmaniasis (Kala azar) Chlorproguanildapsone 2003 Malaria Zentaris, Indian CMR Glaxo Smith Kline, DFID others: Pressure bandages on enlarged limbs forces lymph out. 弹力绷带捆绑 Surgery can be used to remove elephantoid tissue if muscle involvement is minimal. 外科手术 Onchocerca volvulus 旋盘尾丝虫 Causative agent of onchocerciasis (river blindness) 90 million, 17.6 million, 326 thousand Adults of Onchocerca volvulus Skin nodule Microscopic section showing adults and scar tissue reaction Microfilariae of Onchocerca volvulus Unsheathed microfilariae occur in the skin, never the bloodsteam Simulium 蚋 Pathogenisis of adults Nodules (about ½ -1 inch in diameter) are most common in Africa Nodules in Central & South America. Nodules are relatively benign Pathogenisis of Microfilariae Microfilariae in the skin - itching is so severe some people have committed suicide Microfilariae in skin - in parts of Africa, the skin of the scrotum 阴囊 and inguinal area 腹股沟 loses its elasticity 2. Microfilariae invade the eye (occur as microfilariae die in the eye) Microfilariae invade the eye In many parts of Africa, the sighted young are responsible for leading the older blind adults. Diagnosis of Onchocerca volvulus Examination of microfilariae or adult in skin nodule, eye etc. TREATMENT of Onchocerca volvulus 1. Drugs Ivermectin (150mg/kg ) Every 6-12month 2. excise of skin nodule etc Onchocerca volvulus PREVENTION – blackflies control Loa loa Vector : chrysops 斑虻 about 2 million “眼虫” adults occasionally migrate through the eye Calabar swelling 卡拉巴丝虫性肿 块 Microfilariaes present during the daytime Pathogenesis of Loa loa Adults cause Calabar swellings. Eye swells when worms migrate through. Diagnosis and control of Loa Loa Diagnosis: Control: drugs are not so effective for adults surgical removal of worms 讨论课要求 1. 以2~3人组成小组,以小组为单位计分,要求小组成 员分工合作完成 2. 每组同学自由讲解时间控制在12分钟,留3分钟提问 和讨论 3. 每位同学必须至少参加一次讨论 4. 每位同学还必须完成一次课后作业(另行布置) 5. 班长负责协调统计 人体寄生虫学讨论课 讨论主题:总论、线虫 1. 人群土源性线虫的感染率是衡量一个国家或地区整 体发展水平和文明程度的重要指标,如果你是某农 村疾控中心的人员,你在控制土源性线虫感染方面 有哪些具体的措施? 2. 淋巴丝虫病是WHO要求全球范围内限期消除的寄生 虫病,请从生物学及社会学等因素分析人类提出 该目标的依据及具体的措施? 3. 当前哪些因素导致新现和再现寄生虫病的上升, 请举例说明。 补充: 1. 人体寄生虫学研究发展史。 2. 人类能最终消灭人体寄生虫病吗,谈谈你的观点。 3. 寄生虫对人类社会的贡献。 4. 各国(地区)人体寄生虫流行及防治介绍