1330-Michelle
advertisement

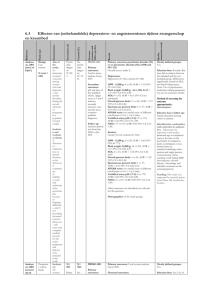
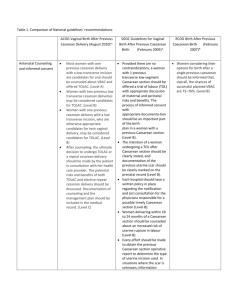
Women’s health in pregnancy and postpartum Michelle Wise BSc MD FRCSC MSc Senior Lecturer, Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, U of A Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist, National Women’s Health, ADHB Outline • • • • • • Iodine supplements in pregnancy Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy First trimester screening Gestational weight gain Planning a VBAC Postnatal contraception Iodine supplement • Essential for normal brain development • Moderate iodine deficiency and goitre found in 12/170 pregnant women nationwide (Pettigrew et al. 2006) • Iodine levels of breast-fed infants < half that of formula-fed infants (Skeaff 2005) • Choose iodised table salt at home Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy • Don’t forget vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) First Trimester Screening (FTS) • Offered routinely to all pregnant women regardless of age • Combines: – Maternal age – Nuchal translucency at 11 - 13+6 weeks – PAPP-A and free βhCG at 9 – 13+6 weeks Maternal Serum Screening, by age Ontario Women’s Health Equity Report 2010 FTS • 85-90% of Down syndrome pregnancies are detected using FTS, compared to: – 50% with age alone – 75% with MSS • 5% of screening results will be “↑ risk” – To be followed by discussion of options for diagnostic testing and clinical management • 98% of “↑ risk” babies will be unaffected RANZCOG “A Decision Aid: Testing in pregnancy for fetal abnormalities” FTS • If twins, need to know chorionicity to correct MoM values of blood tests • Additional factors that modify aneuploidy risk assessment: – Previous pregnancy w T21 or T18 – Assisted reproduction – Maternal weight Obesity in Pregnancy Obesity in pregnancy – Set goals for gestational weight gain – Early diabetes testing • add HbA1c and fasting 2h OGTT to booking bloods to exclude T2DM – Measure weight at each visit – Monitor for maternal and fetal complications • GDM, HTN, stillbirth, C/S, PPH) – Timely referral Centre for Maternal and Child Enquiries 2010: Guideline on management of women with obesity in pregnancy Gestational weight gain BMI Institute of Medicine 2009 guidelines Normal 11-16 kg 25-29 7-11 kg 30 or more < 9 kg Limited or no weight gain in obese women is associated with improved pregnancy outcomes Planning a VBAC • What is the risk of uterine rupture in women having attempt at Vaginal Birth After Caesarean (VBAC) Risk of uterine rupture with VBAC attempt • Bujold et al. 2002 – 1,527 women w 1 prev C/S having TOL – Cohort study with chart review • Bujold et al. 2010 – 1,768 women w 1 prev C/S having TOL – Cohort study with chart review Inter-delivery interval, months Inter-delivery interval, months Planning VBAC • 2o analyses from two large multicentre studies further support ↑ risk for rupture with shorter inter-pregnancy intervals • Conclusion: important to counsel and provide effective contraception post-caesarean Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM) • 98% effective during first 6 months if all 3 criteria met: – Menses have not returned – Exclusive breastfeeding – Baby feeding during the night (< 6 hrs) • When to start COC LAM Interagency Working Group www.irh.org Planning VBAC For more information: • • • • • • • www.ranzcog.edu.au www.rcog.org.uk www.healthed.govt.nz www.consensus.nih.gov/2010/vbac.htm www.nationalwomenshealth.adhb.govt.nz Or contact me m.wise@auckland.ac.nz Or attend: – Update in Women’s Health for Primary Care (12 November 2011) – Postgraduate diploma in Obstetrics and Medical Gynaecology