NUR 113: SKILL 21-4 INSTILLING
EYE & EAR MEDICATIONS
SKILL 21-4: INSTILLING EYE & EAR MEDICATIONS-INTRODUCTION
Common eye (ophthalmic) medications are in the form of drops and
ointments, including over-the counter preparations such as artificial tears
and vasoconstrictors (e.g., Visine and Murine).
However, many patients receive prescribed ophthalmic drugs for eye
conditions such as glaucoma, infection, and following cataract extraction.
In addition, there is a third type of delivery system, the intraocular disk.
Medications delivered by disk resemble a contact lens; but the disk is
placed in the conjunctival sac, not on the cornea, and it remains in place for
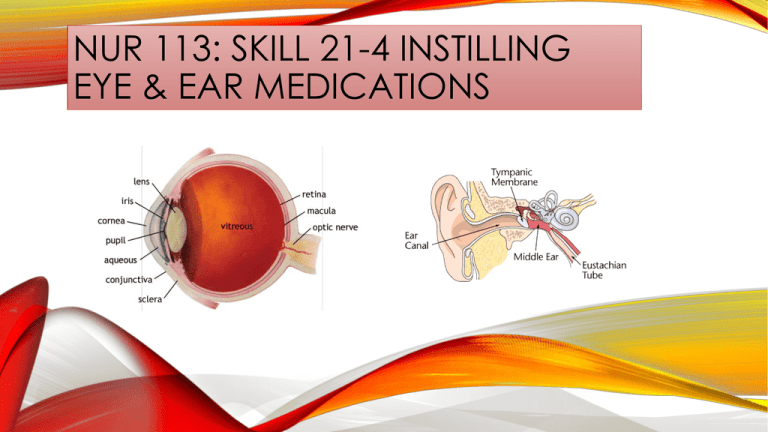
up to 1 week. The eye is the most sensitive organ to which you apply
medications.
The cornea is richly supplied with sensitive nerve fibers. Care must be
taken to prevent instilling medication directly onto the cornea. The
conjunctival sac is much less sensitive and thus a more appropriate site for
medication instillation.
Any patient receiving topical eye medications should learn correct selfadministration of the medication, especially patients with glaucoma, who
must often undergo life long medication administration for control for the
disease.
ASSESSMENT
1. Check accuracy and completeness of each
medication administration record (MAR) with
health care provider’s medication order. Check
patient’s name, drug name and dosage route
(eye{s} or ear{s}) and time for administration.
2. Review pertinent information related to
medication, including action, purpose, normal
dose and route, side effects, time of onset and
peak action, and nursing implications.
3.Assess condition of external eye or ear
structures (see chapter 6). This may be done just
before drug instillation (if drainage is present,
apply clean gloves).
ASSESSMENT – CONT’D
4. Determine whether patient has any symptoms of
eye or ear discomfort or visual or hearing
impairment.
5. Assess patient’s medical history, history of
allergies (including latex), and medication history.
6. Assess patient’s level of consciousness (LOC)
and ability to follow directions.
7. Assess patient’s knowledge regarding drug
therapy and desire to self-administer medication.
8. Assess patient’s ability to manipulate and hold
dropper or ocular disk.
PLANNING
1. Expected outcomes following completion of
procedure:
Patient experiences desired effect of medication
Patient denies discomfort
Patient experiences no side effects, and symptoms
(e.g., irritation) are relieved.
Patient is able to discuss information about
medication and technique correctly.
Patient demonstrates self-instillation of eye-drops.
2. Explain procedure to the patient
Demonstrates learning
Relieves anxiety and promotes patient
participation.
IMPLEMENTATION
1. Prepare medications for instillation. Check label of medication
against MAR 2 times. Preparations usually involves taking eyedrops/eardrops out of refrigerator and rewarming to room temperature
before administering to patient. Check expiration date on container.
2. Take medication(s) to patient at correct time (see agency policy).
Medications that require exact timing include stat, first-time or
loading doses, and one time doses.
Give time-critical scheduled medications (e.g., antibiotics,
anticoagulants, insulin, anticonvulsants, immunosuppressive
agents) at exact time ordered (no later than 30 minutes before or
after scheduled dose).
Give non-time-critical scheduled medications within a range of 1
or 2 hours of scheduled dose.
During administration, apply six rights of medication
administration:
6 RIGHTS OF MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION
IMPLEMENTATION – CONT’D
3. Perform hand hygiene
4. Identify patient using two identifiers.
5. At patient’s bedside again compare MAR or computer
printout with names of medications on medication labels
and patient name. Ask patient if they have any allergies.
6. Discuss purpose of each medication, action, and
possible adverse effects. Allow patient to ask any
questions about the drugs. Patients who self-instill
medications may be allowed to give drops under nurse’s
supervision (check agency policy). Tell patients receiving
eye-drops (mydriatics) that vision will be blurred
temporarily and sensitivity to light may occur.
IMPLEMENTATION – CONT’D
7. INSTILL EYE MEDICATIONS:
A. Apply clean gloves. Ask patient to lie supine or sit back in chair
with head slightly hyperextended, looking up.
B. If drainage or crusting is present along eyelid margins or inner
canthus, gently wash away. Soak any dried crusts with warm, damp
washcloth or cotton ball over eye for several minutes. Always wipe
clean from inner to outer canthus. Remove gloves and perform hand
hygiene.
C. Explain there might be a temporary burning sensation from the
drops – the corneas are highly sensitive.
D. INSTILL EYEDROPS:
1. Apply clean gloves. Hold cotton ball or clean tissue in non-dominant
hand on patient’s cheekbone just below lower eyelid.
2. With tissue or cotton resting below lower lid, gently press downward
with thumb or forefinger against bony orbit, exposing conjunctival sac.
Never press directly against patient’s eyeball.
CONJUNCTIVAL SAC
IMPLEMENTATION – CONT’D
Instill Eye-drops – cont’d
3. Ask patient to look at the ceiling. Rest dominant hand on
patient’s forehead; hold filled medication eyedropper
approximately 1 to 2 cm (1/2 to ¼ inch) above conjunctival
sac.
4. Drop prescribed number of drops into conjunctival sac.
5. If patient blinks or closes eye, causing drops to land on
outer lid margins, repeat procedure.
6. When administering drops that may cause systemic
effects, apply gentle pressure to patient’s nasolacrimal duct
with clean tissue for 30 to 60 seconds over each eye, one at a
time. Avoid pressure directly against patient’s eyeball.
7. After instilling drops, ask patient to close eyes gently.
IMPLEMENTATION – CONT’D
E.
Instill Eye Ointment:
1. Holding applicator above lower lid margin, apply
thin ribbon of ointment evenly along inner edge of
lower eyelid on conjunctiva from inner to outer
canthus.
2. Have patient close eye and rub lid lightly in circular
motion with cotton ball if not contraindicated. Avoid
placing pressure directly against patient’s eyeball.
3. If excess medication is on eyelid, gently wipe it
from inner to outer canthus.
4. If patient needs an eye patch, apply clean one by
placing it over affected eye so entire eye is covered.
Tape securely without applying pressure to the eye
A clean eye patch reduces the risk of infection.
IMPLEMENTATION – CONT’D
F. Apply
Intraocular Disk:
1. Open package containing disk. Gently press your
fingertip against disk so it adheres to your finger. It
may be necessary to moisten gloved finger with
sterile saline. Position convex side of disk on your
fingertip.
2. With your other hand gently pull patient’s lower
eyelid away from eye. Ask patient to look up.
3. Place disk in conjunctival sac so it floats on sclera
between iris and lower eyelid.
4. Pull patient’s lower eyelid out and over disk. You
should not be able to see disk at this time. Repeat if
you can see the disk.
IMPLEMENTATION – CONT’D
8. After administering eye medications
remove and dispose of gloves and soiled
supplies, perform hand hygiene.
9. Remove intraocular disk.
A. Perform hand hygiene and apply
clean gloves. Gently pull downward
on lower eyelid using your nondominant hand.
B. Using forefinger and thumb of
your dominant hand, pinch disk and
lift it out of patient’s eye.
C. Remove and dispose of gloves,
perform hand hygiene.
IMPLEMENTATON – CONT’D
10. Instill
Eardrops:
A. Perform hand hygiene. Apply clean gloves
(only if drainage is present).
B. Warm medication to room temperature by
running war water over bottle (make sure not to
damage label or allow water to enter bottle).
C. Position patient on side (if not
contraindicated) with ear to be treated facing up,
or patient may sit in chair or at bedside. Stabilize
patient’s head with his or her own hand.
D. Straighten ear can by pulling pina up and back
to 10 o’clock position (adult or child older than
age 3) or down and back to 6 to 9 o’clock
position (child under 3).
IMPLEMENTATION – CONT’D
E. If cerumen or drainage occludes outermost
portion of ear canal, wipe out gently with cottontipped applicator. Take care not to force cerumen
into canal.
F. Instill prescribed drops holding dropper 1 cm
(1/2 inch) above ear canal.
G. Ask patient to remain in side-lying position for
a few minutes. Apply gentle message or pressure
to tragus of ear with finger.
H. If ordered, gently insert portion of cotton ball
into outermost part of canal. Do not press cotton
into canal.
I. Remove cotton after 15 minutes. Help patient to
comfortable position after drops are absorbed.
J. Dispose of soiled supplies in proper receptacle,
remove and dispose of gloves, and perform hand
hygiene.
EVALUATION
1. Observe response to medication by
assessing visual or hearing changes,
asking if symptoms are relieved, and
noting any side effects or discomfort felt.
2. Ask patient to discuss purpose of drug,
action, side effects, and technique of
administration.
3. Have patient or family caregiver
demonstrate self-administration of next
dose.
UNEXPECTED OUTCOMES
1. Patient complains of burning or pain or experiences local
side effects (e.g., headache, bloodshot eyes, local eye
irritation). Drug concentration and patient’s sensitivity
both influence chances of side effects developing.
2. Patient experiences systemic effects from drops (e.g.,
increased heart rate and blood pressure from
epinephrine, decreased heart rate and blood pressure
from timolol).
3. Ear canal remains inflamed, swollen, tender to palpation.
Drainage is present.
4. Patient’s hearing acuity continues to be reduced.
5. Patient is unable to explain drug information or steps for
taking eye-drops / eardrops and/or has trouble manipulating
dropper
RECORDING & REPORTING
Record drug, concentration, dose or strength, number of drops,
site of application (left, right, or both eye/ear), and time of
administration on MAR immediately after administration, not
before. Include initials or signature. Record patient teaching
and validation of understanding in nurse’s notes and EHR.
Record objective data related to tissues involved (e.g., redness,
drainage, irritation), any subjective data (e.g., pain, itching,
altered vision or hearing), and patient’s response to
medications. Note any side effects experienced in nurses’ notes
and EHR.
Report adverse effects/patient response and/or withheld drugs
to nurse in charge or health care provider. Depending on
medication, immediate health care provider notification may be
required.
END OF SKILL
The book has provided videos for you and the links are as follows:
FOR THE EAR-DROP VIDEO:
http://booksite.Elsevier.com/Perry-Potter/ClinicalSkills/video26.php
Elsevier: Perry-Potter: Clinical Nursing Skills and
Techniques, 8e-21.5 Administering Ear Drops.
FOR THE EYE-DROP VIDEO:
http://booksite.Elsevier.com/Perry-Potter/ClinicalSkills/video25.php
Elsevier: Perry-Potter: Clinical Nursing Skills and
Techniques. 8e-21.4 Administering Eye Medications.