coordinate covalent
advertisement

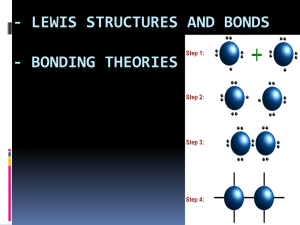
Aim: What are coordinate covalent bonds? DO NOW: FINISH THE WORKSHEET FROM YESTERDAY. IF YOU HAVE FINISHED WALK AROUND AND HELP OTHERS. Coordinate Covalent Bonds • A coordinate bond (also called a dative covalent bond) is a covalent bond (a shared pair of electrons) in which both electrons come from the same atom. • A coordinate covalent bond is usually shown with an arrow. Coordinate Covalent Bond • When one atom donates both electrons in a covalent bond. • Carbon monoxide • CO C O Coordinate Covalent Bond When one atom donates both electrons in a covalent bond. Carbon monoxide CO C O Coordinate Covalent Bond When one atom donates both electrons in a covalent bond. Carbon monoxide CO C O General Rules 1. Select the central atom (atom in the middle); the least electronegative atom (H and halogens will not be central atoms) 2. Count the total number of valence electrons there should be. 3. Put one bond between each atom. Put the rest of the valence electrons on the outer atoms. 4. Check if every atom fulfills octet. If not move paired electrons to fulfill octet. 5. Recount the number of total shared valence electrons. Example 2 • N2O Polyatomic Ions • A polyatomic ion is a tightly bound group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge and behave as a unit. • A group of atoms that are covalently bound and as a whole have a charge. Which compound contains both ionic and covalent bonds? 1. 2. 3. 4. HBr CBr4 NaBr NaOH Practice 1. Draw the electron dot structure for the polyatomic boron tetrafluoride anion (BF4-) Practice 2. Draw the electron dot structure for the hydrogen carbonate ion (HCO3-). Carbon is the central atom, and hydrogen is attached to oxygen in this polyatomic anion. Exceptions to Octet Rule • The octet rule cannot be satisfied whose total number of valence electrons is an odd number. There are also molecules in which an atom has fewer, or more, than a complete octet in the valence electrons. Example 1 • Boron has a tendency to form compounds in which it has an incomplete octet. For example BF3 Example 2 • Atoms of elements in the third or higher periods can exceed their octet as they have d orbitals available for bonding. For example SF6 • http://www.kentchemistry.com/links/bonding/covalentlewisdot.htm