here

Test 1 solution sketches
Note for multiple-choice questions: Choose the closest answer
PV of Perpetuity
Alma receives $1,000 annually forever.
The stated annual discount rate is 7%, compounded every 6 months.
Determine the present value given the following assumptions.
PV of Perpetuity
Alma receives the first payment three months from today. Subsequent payments are made yearly.
EAR = (1.035) 2 - 1 = 7.1225%
PV = 1000/.071225 * (1.071225) 3/4 =
$14,783.53
PV of Perpetuity
Alma receives $500 every six months, starting today.
PV = 500 + 500/.035 = $14,785.71
Internal Rate of Return
Joey invests $50,000 today. In return he receives $800 one year from now, followed by a payment 10% higher the next year. These yearly payments continue forever, with each payment
10% higher than the previous payment.
What is the internal rate of return of this investment?
Internal Rate of Return
50,000 = 800 / (IRR - .1)
50000*IRR – 5000 = 800
50000*IRR = 5800
IRR = 0.116 or 11.6%
Choosing Investments
Ryan’s Carnivals has exactly $100,000. Ryan must invest one or more of the following three options. The effective annual discount rate is 15%.
Investment I: He invests $60,000 today and receives $92,000 two years from today
Investment II: He invests $51,000 today and receives $80,000 one year from today
Investment III: He invests $X today and receives
$(1.25*X) one year from today
Choosing Investments
X can be any non-negative amount that Ryan wants. Which investments should Ryan invest positive amounts of money in?
Must invest in III since exactly $100K must be invested today and I and II total to more than
$100K
Choosing Investments
III only: NPV = 100000(1.25)/1.15 –
100000 = 8,700
I and III: NPV = 92000/(1.15
2 ) – 60000
+ 40000(1.25)/1.15 – 40000 = 13,043
II and III: NPV = 80000/1.15 – 51000
+ 49000(1.25)/1.15 – 49000 = 22,826
Choose II and III
Yield to Maturity
Roberto buys a zero-coupon bond with a face value of $5,000. The face value will be paid in 7 years. The current price of the bond is $2,500. What is the yield to maturity (expressed as an effective annual rate)?
2500 = 5000/(1+r) 7
(1+r) 7 = 2 r = 10.41%
Compounding interest
Jerry makes a $1,000,000 investment that will earn 12% per year. However, he does not know if his interest is being compounded yearly or monthly. How much more will he earn in interest over the next two years if interest is compounded monthly (versus yearly)?
Compounding interest
Interest if monthly:
1,000,000*(1.01
24 – 1) = 269,735
Interest if annually:
1,000,000*(1.12
2 – 1) = 254,400
Difference = $15,335
Firm Value
Shannon has made a major scientific breakthrough that will lead to increased profits for her company as follows:
$500,000 one year from today
$200,000 two years from today
Each subsequent year: 5% lower than the previous year
These extra profits will be received by the firm forever.
Firm Value
How much does this breakthrough increase the firm’s current value if the effective annual discount rate is 8%?
(In $1000s):
500/1.08+[200/(.08-(-.05))]*1/1.08=1,887
Increases the firm’s value by $1.887 million
Nominal Payments
Byron is set to receive a real payment of $50,000 (in today’s dollars) five years from now. Inflation will be 6% for the first three years, and 8% per year thereafter. The nominal payment five years from now will be ____.
50,000 * (1.06) 3 (1.08) 2 = $69,460
Yield to Maturity
A bond with a face value of $1,000 is currently selling for $800. Annual coupon payments of $50 are to be paid later today and one year from today. The bond matures in one year. What is the yield to maturity (expressed as an effective annual rate)?
800 = 50 + 50/(1+r) + 1000/(1+r)
750 = 1050/(1+r) r = 1050/750 – 1 = 0.4 or 40%
Payback periods
Ali bought a new Green Pimus Hybrid vehicle today for $30,000. He will receive $4,500 in benefits each year, forever, starting one year from today.
Assuming an effective annual discount rate of 10%, in how many years will the net present value of the investment turn from negative to positive.
Payback periods
30000 = 4500/.10 * (1 – 1/(1.1) T )
2/3 = 1 – 1/(1.1) T
(1.1) T = 3
T = ln(3)/ln(1.1) = 11.53 ≈ 12 years
Or we could just guess and check some numbers to see what the best answer is (I will start with 10 since it is in the middle)…
Payback periods
Let T=10:
4500/.1 * [1 – 1/1.1
10 ] = 27,650.56
Must be more than 10
Let T=12:
4500/.1 * [1 – 1/1.1
12 ] = 30,661.61
Retirement Planning
Booker is planning his retirement. He will make a single deposit 5 years from now so that he is able to withdraw $300,000 per year in the future, starting 20 years from today and ending
40 years from today. How much must the deposit be so that the account balance will be
$0 after the final withdrawal? Assume a SAIR of
9%, compounded monthly.
Retirement Planning
EAIR = (1 + .09/12) 12 = 1.0938069
PV of withdrawals (in $1000s):
300/.09381*[1 – 1/(1.09381) 21 ]* 1/1.09381
19
= 493.56
PV of deposit (in $1000s): 493.56
Amount of deposit in 5 years (in $1000s):
493.56(1.0938069) 5 = 772.75
Equivalent Annual Cost
Gareth buys the Hamburger Broiler
3000 machine for $5,000 today. The machine lasts for 14 years, and has maintenance costs of $600 each three times: in 5 years, 9 years, and 12 years.
The effective annual discount rate is
9%. What is the equivalent annual cost of this machine?
Equivalent Annual Cost
PV of costs:
5000 + 600/(1.09) 5 + 600/(1.09) 9 +
600/(1.09) 12 = $5,879.54
EAC:
5879.54 = EAC/.09 * [1 – 1/(1.09) 14 ]
5879.54 = 7.78615 * EAC
EAC = $755.13
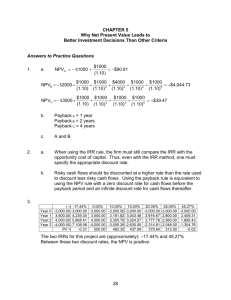
Internal Rate of Return
Diane must choose between two mutually exclusive investments, A or B.
If she invests in A, she pays $600 today and receives $720 one year from now.
If she invests in B, she pays $2,000 today and receives $2,200 one year from now.
Diane’s effective annual discount rate is 5%
Assume that any remaining money is invested in something that has a NPV of 0
Parts (a) and (b)
What is the internal rate of return for
Investment A?
600 * (1 + IRR) =
720
1 + IRR = 1.2
IRR = .2 = 20%
What is the internal rate of return for
Investment B?
2000 * (1 + IRR) =
2200
1 + IRR = 1.1
IRR = .1 = 10%
Part (c)
Which investment should Diane choose?
NPV
A
NPV
B
= 720/1.05 – 600 = 85.71
= 2200/1.05 – 2000 = 95.24
Choose B due to higher NPV