Ch. 7 part 2 (PM and Osmosis)
advertisement
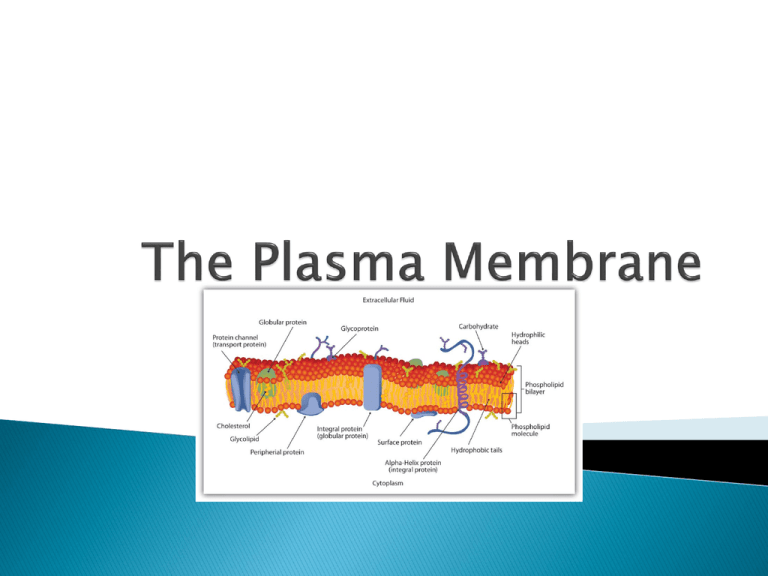
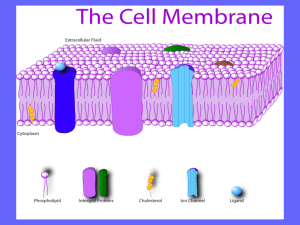
What is the cytoplasm? ◦ Cyto = “cell” ◦ Plasma= “liquid substance of the cell” Cytoplasm? ◦ Clear, gelatinous fluid inside the cell What contains it? ◦ Plasma Membrane Do all cells have this? ◦ YES! Cells need an inside & an outside… ◦ separate cell from its environment ◦ cell membrane is the boundary IN OUT food - sugars - proteins - fats salts O2 H2O waste - ammonia - salts - CO2 - H2O products - proteins cell needs materials in & products or waste out 4 Why have a plasma membrane? ◦ Allow nutrients to move in and out of the cell How does it control how much goes in and out? ◦ Selective permeability Per= “through” Meare= “ to glide” Therefore, what does it mean? What’s the point for allowing materials in and out of the cell? HOMEOSTASIS!!!!! How do you build a barrier that keeps the watery contents of the cell separate from the watery environment? FATS LIPIDS Remember: oil & water don’t mix!! What substance do you know that doesn’t mix with water? 7 Membrane is made of special kind of lipid ◦ phospholipids ◦ “split personality” “attracted to water” Membrane is a double layer ◦ phospholipid bilayer phosphate inside cell lipid outside cell “repelled by water” 8 Cell membrane controls what gets in or out Need to allow some materials — but not all — to pass through the membrane ◦ semi-permeable only some material can get in or out So what needs to get across the membrane? sugar lipids aa O2 H 2O salt waste 9 What molecules can get through the cell membrane directly? ◦ fats and oils can pass directly through inside cell waste outside cell lipid sugar aa salt H2O but… what about other stuff? 10 Need to make “doors” through membrane ◦ protein channels allow substances in & out specific channels allow specific material in & out H2O channel, salt channel, sugar channel, etc. inside cell waste salt H 2O aa sugar outside cell 11 Channels are made of proteins ◦ proteins both “like” water & “like” lipids bi-lipid membrane protein channels in bi-lipid membrane 12 Proteins act as doors in the membrane ◦ channels to move specific molecules through cell membrane HIGH LOW 13 Embedded all the way through the bilayer Allow ions to pass through the membrane Integral Proteins Bond to only one side of the membrane Attach to or near integral proteins Help with ion identification Peripheral Proteins Cell signaling Maintains membrane fluidity Secures Proteins Cholesterol Lipid or Protein with a carbohydrate attached Provide energy Cellular recognition Glycolipid and Glycoprotein Why do molecules move through membrane if you give them a channel? HIGH ? LOW ? 16 Diffusion ◦ move from HIGH to LOW concentration 17