Wollman: OASIS Blue: SmartGrid Standards: NIST SGIP
advertisement

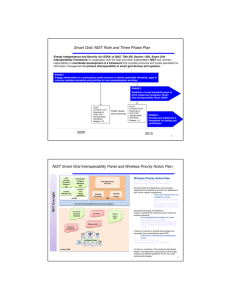
Accelerating Standards for the Smart Grid David Wollman National Institute of Standards and Technology david.wollman@nist.gov 301-975-2433 http://www.nist.gov/smartgrid/ May 27, 2010 1 Key elements for success to accelerate standards National Smart Grid policy framework Visible and committed leadership from the top NIST Three Phase Plan NIST Framework and Roadmap Smart Grid Interoperability Panel Strong active coordination President Obama, Secretary of Energy Chu, Secretary of Commerce Locke, … Planning and engagement of the broad Smart Grid community 2007 Energy Independence and Security Act, Title VIII defined agency roles NIST leadership, honest broker/convener Federal and State Agencies/Commissions Standards Developing Organizations International Coordination Technical driving forces within Standards Organizations Motivated technical experts with sufficient dedicated time and connections National Institute of Standards and Technology Role: Coordination of Interoperability Standards in United States Department of Energy (DOE) lead agency for U.S. Government Smart Grid effort $3.4 billion of ARRA-funded Smart Grid Investment Grants; R&D portfolio Smart Grid Task Force – DOE, NIST, FERC, FCC, EPA, ITA, DHS, … NIST coordinates and accelerates development of standards by private sector SDOs Federal Energy Regulatory Commission initiates rulemaking when consensus State Public Utilities Commissions (California, Texas, Ohio, …) International … and more Global Consortia Regional/National … and more NIST Three Phase Plan for Smart Grid Interoperability PHASE 1 Identify NIST an roleinitial set of existing consensus standards and develop a roadmap to fill gaps PHASE 2 Establish Smart Grid Interoperability Panel (SGIP) public-private forum with governance for ongoing efforts Summer 2009 workshops Draft Framework Sept 2009 PHASE 3 Conformity Framework (includes Testing and Certification) Smart Grid Interoperability Panel established Nov 2009 NIST Interoperability Framework 1.0 Released Jan 2010 2009 SGIP/GB meetings 2010 SGIP & Governing Board Connectivity Week May 2010 today George Arnold, NIST - National Coordinator for Smart Grid Interoperability NIST Framework and Roadmap, Release 1.0 Revised version January 2010 Public comments reviewed and addressed Smart Grid Vision / Model 75 key standards identified IEC, IEEE, … 16 Priority Action Plans to fill gaps (one completed) Includes cyber security strategy http://www.nist.gov/smartgrid/ Companion document NISTIR 7628 Conceptual Model Priority Action Plans address standards gaps and issues Priority Action Plans Priority Action Plans Smart meter upgradeability standard (PAP 00, completed by NEMA in 2009) Guidelines for use of IP protocol suite in the Smart Grid (PAP 01) Standard meter data profiles (PAP 05) Guidelines for the use of wireless communications (PAP 02) Develop common specification for price and product definition (PAP 03) Develop common scheduling communication for energy transactions (PAP 04) Standard demand response signals (PAP 09) Customer energy use information (PAP10) Energy storage interconnection guidelines (PAP 07) Interoperability standards to support plug-in electric vehicles (PAP 11) Wind Interconnection Standards (PAP 16) Harmonize power line carrier standards for appliance communications in home (PAP15) Develop common information model (CIM) for distribution grid management (PAP 08) DNP3 Mapping to IEC 61850 Objects (PAP12) Transmission and distribution power systems model mapping (PAP 14) Harmonization of IEEE C37.118 with IEC 61850 and Precision Time Synchronization (PAP 13) Smart Grid Interoperability Panel and Governing Board Public-private partnership, started in Nov. 2009 Over 570 organizations, over 1500 representatives Supports NIST in coordinating standards Governing Board elected SGIP Chair elected Committees established, SGIP meetings ongoing Electronic collaboration tools, newsletters / communications Project management office Open, transparent process International participation welcome Stakeholder Category Members (22) including utilities, suppliers, IT developers Smart Grid Identified Standards One Organization, One Vote Priority Action Plans (Over570; 450; over over 1500 persons (Over persons participating from participating including including from international international organizations) organizations) Use Cases At large Members (3) Ex Officio (non-voting) Members SGIPGB Requirements Standing Committees Working Groups (Architecture, Conformance and Security) Standards Descriptions (DEWG, PAP, Other) Conceptual Model SGIP Smart Smart Grid Grid Interoperability Interoperability Panel Panel and and Governing Governing Board Board Products (IKB) http://www.nist.gov/smartgrid/ International Smart Grid Coordination Increasing number of bilateral discussions and interactions with China, Japan, Korea, Australia, India, Brazil, France, Germany, … US-EU Energy Council Close coordination with International Standards Developing Organizations (SDOs) through NIST process Example: International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) work coordinated through IEC-Strategic Group 3 NIST Liaison with IEC, joint meeting Nov 2009 & May 2010 Open, transparent process with international participation Web links and contacts Main web portal: www.nist.gov/smartgrid Twiki: http://collaborate.nist.gov/twikisggrid/bin/view/SmartGrid/WebHome SGIP: http://collaborate.nist.gov/twiki-sggrid/bin/view/SmartGrid/SGIP Contacts: George Arnold, National Coordinator for Smart Grid Interoperability, george.arnold@nist.gov, 301-975-5627 David Wollman, Leader, Electrical Metrology Groups and Smart Grid Team-Standards, david.wollman@nist.gov, 301-975-2433