Flexible assembly methods
Consortium meeting in Madrid 2013-11-21
Alexandre Mathern, NCC
Carlos Hermosilla Carrasco, ACC
Low-disturbance sustainable urban construction
Content
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Technical solutions for flexible on-site assembly
ICT solutions
SWOT analysis
Requirements and most critical issues for the assembly process
Procedures for on-site assembly
Low-disturbance sustainable urban construction
2
Innovative technical solutions
•
Solutions for flexible on-site assembly:
–
–
–
–
•
Prefabicated elements
Connections
Installation methods
Processes
Criteria:
– On-site construction time
– On-site construction activities
– Indicators defined in WP6
Low-disturbance sustainable urban construction
3
ICT solutions and robotics
•
ICT solutions that can support the assembly
process were identified.
•
The following areas are covered:
– Resources/persons management
e.g.: real time location system, laser scanning, etc.
– Assembly support
e.g.: distance sensors, rotary gripper for crane, etc.
– Construction safety
e.g.: RFID systems, radar/video systems, etc.
– Information and communications
e.g.: light boards, RFID tags for messages/alarms
– Protection of the environment
e.g.: noise or dust measurement instruments, etc.
Low-disturbance sustainable urban construction
4
SWOT analysis
Strengths
Weaknesses
What are the good characteristics of this technique?
What are the bad characteristics of this technique?
Cost of construction
Cost of maintenance and operation
Whole life cost
Quality / Defects
Whole life performance
Time of construction
Impact on traffic
Health and safety of workers
Health & safety of users and residents
Use of reused/recycled material
Waste generation
GHG emissions
Energy use
Noise generation
Dust generation
Vibration generation
Organisation on-site
Security
Etc.
Opportunities
Threats
What circumstances could promote the diffusion of this
technique in the construction industry?
What circumstances could hinder the diffusion of this
technique in the construction industry?
Political orientations
Societal evolutions
Procurement
Regulations
Funding possibilities
Economic landscape
Economic driver
Experience and knowledge
Innovation / technological driver
Business opportunities
Competition / Alternative solutions
Customer needs
Low-disturbance sustainable urban construction
Standardization
Workforce (skills, wages...)
Potential impact on image
Insurance
Supply chain
Etc.
5
Strategies based on SWOT analyses
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Standardization
Development of design codes
Material durability and means to improve material
Recycling/reuse of new materials
Information on the technology
Demonstration projects
LCC analysis in the procurement stage
Life cycle assessment methods
Procedures for the application of ICT solutions
Training / Education of workers
Material safety data sheets for handling of new materials and precautions
to be taken in case of injuries
Development of manufacturing companies to develop competitiveness
Low-disturbance sustainable urban construction
6
Critical issues for assembly
Procedure optimization starting point
critical issue analysis
Dimensions
Design and manufacture of prefabricated elements
Shape
Mass and center of gravity
Manoeuvrability and manipulation
Transport of prefabricated elements
Preassembly
Element identification
Dimensional tolerances
Element protection during transport
Preparation of construction site
Oversized and overweight elements
Delays due to transport
Storage
Storage location
Equipment parking space
Supports and bearings
Geodesic service placement
Lighting
Temporary structures
Placement of prefabricated elements
Safety and preventive analysis
Order and organization
Element integrity
Assembly
Required equipment
Joints
Placement procedure
Tolerances
Location errors
Safety
Mechanical fasteners
Adhesives
Welding
Verification
Post-assembly
Facility removal
Low-disturbance sustainable urban construction
Joint assembly equipment
Prefabricated elements
Joints
7
Building and assembly procedures
Procedures developed:
• Storage
• Logistics
• Health and safety
• Site operation
• Traffic
• Cooperation and division of duties
• Assembly
• Ordering
• Construction support systems
• Crisis and life hazard situations
Low-disturbance sustainable urban construction
8
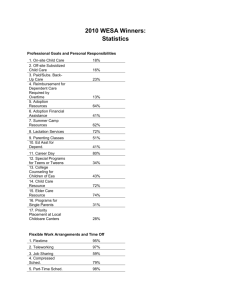
On-site Assembly Methods
Case 1: new bridge over existing avenue
RFID auto-acess for ICTenhanced transport
Night lighting
ICT-assisted crane
Reduced and optimized
storage space
Auto-warning on out of
service scaffolding
Parking area with
maintenance zone and
fuel tank
Limited traffic affection
Provisional crossing for
workers
Reduced foundation due
to lightweight structure
Low-disturbance sustainable urban construction
Pantura connections
speed up building process
Automatic turnstiles
register workers
9
On-site Assembly Methods
Case 2: walkway over motorway refurbishment in enclosed space
Concrete slab between rail
and motorway hosts site
facilities and night
illumination
FRP ready-to-go closed
section for fast assembly
Light boards, cones and
concrete barriers channel
traffic arround the site
Traffic disturbance reduced
to a minimum
Low-disturbance sustainable urban construction
10
On-site Assembly Methods
Case 3: bridge over canal widening in old city center
Anchored barges host
heavy machinery
Noisy jobs are monitored
with detectors and stopped
during the night
Components are brought
in by ship
Site facilities are deployed
on the canal embankment
FRP-concrete combination results in lighter
decks while keeping section ultimate capacity
Waste from old deck demolition is recovered in barges
under the bridge and transported for recycling
Low-disturbance sustainable urban construction
11
Pantura WP:
WP 4
PP title:
T4.3 - Presentation
Madrid
Date:
21 November 2013
Author(s):
Alexandre Mathern
(NCC)
Carlos Hermosilla
(ACC)
The Pantura project is co-financed by the European Commission with contract No.: 265172.
© Copyright © 2011-2013. All rights reserved.
All rights reserved. Any duplication or use of objects such as diagrams in other electronic or
printed publications is not permitted without the author's agreement.
Low-disturbance sustainable urban construction
12