Finite Element Analysis FEA
advertisement

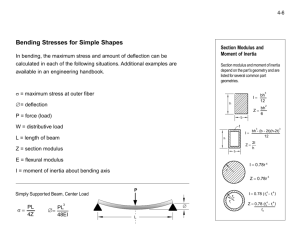
Finite Element Analysis FEA An Introduction to Application Brian Maynard Outline • • • • • • Terminology Overview WHO USES IT! Why is this useful for YOU? What type of analysis is it capable of? What industries is it used in? Some Terminology • Mesh- splitting a model up into small pieces (elements) that make analysis possible (in this case tetrahedral meshing) • Element- base unit that is created by the mesh (the tetrahedrons) • Node- on the surface of the element (green), where the analysis takes place (I,J,K,L,M,N,O,P) • Loads- physical forces acting through the nodes FEA in a Nutshell • Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is used for finding numerical solutions for complicated geometries by dividing the pieces of the geometry into small elements and then coming up with approximate solutions to PDEs at the nodes. This is an iterative process. These solutions are then integrated along the whole geometry to come up with a steady state solution that may evolve with time. A model is solved when all local nodes retain a certain degree of accuracy after a certain iteration. For more on theory see: http://www.comlab.ox.ac.uk/kathryn.gillow/femtutorial.pdf Next 3 slides are taken from Kathryn Gillows talk After creating a geometry and defining the material properties, one must MESH! This is done in the top figure. Meshing can be done in a variety of ways, it is good practice to create smaller element sizes (finer meshing) in areas of greater complexity. This ensures greater accuracy in analysis. After meshing, you want to put some boundary conditions on your model (add loads). Then you are ready to solve your complicated problem FEA style! Here we see a cylindrical magnetic shield modeled. APPLICATIONS! • The applications of this type of analysis is boundless in industry and engineering fields ranging from automotive crash analysis to calculating thermo-mechanical deformation in a pipe to calculating forces in nasal respiration. The types of loads applied to the model can be mixtures of mechanical, electrical, thermal, gravitational, inertial, etc… making its applicability and usefulness obvious for anyone in engineering. Is FEA Used for Research in Our Group? • Well, Zhou and I use it! It helps Zhou figure out charge collecting characteristics of pixels, and it helps me figure out if our pixel VELO is going to experience thermal runaway (an effect brought on by the irradiated silicon’s leakage current). This in turn acts as an exponentially temperature dependent heat source, which under insufficient cooling and/or high power chip, can cause some serious damage to the detector! YIKES! Other people? • It is also used for medical imaging research by another group (Lipson) here at SU in collaboration with SUNY Upstate Medical (Department of Radiology). • FEA is also used in other major experiments at CERN for thermal analysis of the detector (ATLAS, CMS, ALICE) (below is the ATLAS thermal modeling) A Quick Walkthrough • We want to see what the thermal profile of a piece of aluminum with three 1 W heaters placed on it is. The cooling will be applied to areas A and B. The first step is to create the geometry and to set the material properties. Both are given at the right. B A Material Aluminum Glue Heater κ (W/mK) 200 1 150 Pick a Mesh and Mesh • Does this figure display my meshed model? How can you tell? What do the elements look like? Why are the elements smaller by the base of the heaters? How was the pizza? The Solution • Here is the complete nodal solution of all the input heat loads and cooling. Piece of pizza! er… I mean cake! Should YOU Use FEA? • You must first talk with your advisor to make sure that FEA is right for you. Using FEA for an extended period of time may cause successful research, contact your advisor immediately. FEA should not be used with alcohol and may cause undesirable results. Contacting your advisor when under the influence is ill advised. For more information on FEA, search the web or ask questions to people who have used FEA. Some Useful References • Schaum's Outline of Finite Element Analysis • http://www.comlab.ox.ac.uk/kathryn.gillow/ femtutorial.pdf