HF302 Apr 7 - freville-at
advertisement

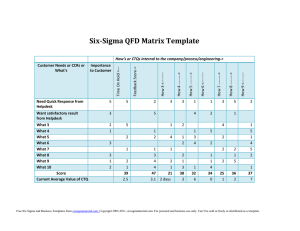
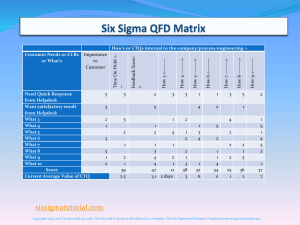
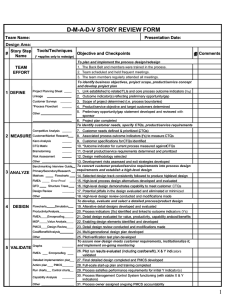
April 7 This Friday: One hour of presentations (not panel) in lieu of this class. Turn in short commentary for grade. HFAP Program: http://hfapconference.com/ Questions about design project? Data collection? http://www.nationaldefensemagazine.org/blog/Documents /20120119%20JCIDS%20Process%20Flow%2024x60%20rev %201%200.pdf (Joint Capabilities Integration Development System – JCIDS) Quiz Review Back to the House of Quality Examples Fatigue and Circadian Rhythms Strategies for Grounding Your Design in Research Trade-Off Analysis House of Quality But first… https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mnUEDA6drB 8 - The University of Colorado’s “Energy Efficient Engineers”, 2012 House of Quality Example Customer Requirements Light weight Easy to use Reliable Target Values Customer Importance 50 30 20 Aluminum Parts Steel Parts 5 2 4 330 Auto Focus Auto Exposure 8 7 8 5 3 260 340 270 Variant of House of Quality House Of Quality Tradeoff Matrix Importance Product characteristics Customer requirements Relationship matrix Technical assessment and target values Competitive assessment Source: Hauser, J.R., & Clausing, D. (1988). The House of Quality. Harvard Business Review, MayJune, 2-14. Retreived from www.csuchico.ed u/~jtrailer/HOQ.p df. Cascade the Houses to “derive your requirements”: Functional CTQs House of Quality (QFD Matrix 2) Technical CTQs House of Quality (QFD Matrix 3) System CTQs Operational Characteristics Design Characteristics (QFD Matrix 1) Design Characteristics Functional Requirements House of Quality Functional Requirements Process Requirements Customer CTQs Customer Requirements Process Requirements House of Quality (QFD Matrix 4) Control CTQs CTQ = Critical-To-Quality 9 Two Reasons You May Feel Sleepy Melatonin Factoids The Hormone Melatonin Adenosine http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/a/a_11/a_11_m/a_11_m_cyc/a_11_m_cyc.html http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/i/i_03/i_03_m/i_03_m_par/i_03_m_par_cafeine.html Stress Effects on Cognition How does fatigue affect performance? The Yerkes-Dodson Law High & low stress/arousal can lead to impaired performance by reducing resource availability Novice or Expert or Stress Effects on Cognition If your attention is reduced, information processing in cognitive capacity will suffer. The Yerkes-Dodson Law: Tunneling & lapsing can occur here Fatigue Effects on Cognition attentional lapses some slowing of information processing Attention & working memory are compromised. Reduced Attentional Resources Cause… Lapses in attention Slowing of information processing Information not processed as ‘deeply’ Attentional narrowing/tunneling “Satisficing” Task shedding Reliance on automated performance Reliance on schemas/templates Stress Effects on Cognition High Arousal or Preoccupation Reduced attentional capacity Attentional tunneling Perceptual Working memory Reduced working memory capacity Less effective memory storage & recall Compromised: Attention, Working Memory, Retrieval from Long Term Memory Hancock & Warm’s Model of Stress Effects on Performance Stress is operationalized as level of arousal A - physiological function B - behavior/performance C - subjective comfort D - normative zone Hancock, P.A. & Szalma, J.L. (2006). Stress and Neuroergonomics. In: R. Parasuraman and M. Rizzo (Eds.),