137884__BrianBares-EmergingManagers-Handout
advertisement

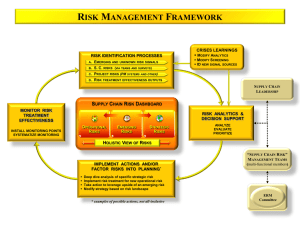
Emerging Managers Formation and Evaluation Brian T. Bares, CFA 1 EMERGING MANAGER INTRODUCTION 2 EMERGING MANAGER FORMATION 3 EVALUATING EMERGING MANAGERS 4 WHAT NEEDS TO CHANGE What is an EM? • Emerging Managers are: – Small (low levels of AUM) – Young (less than 5 years old) – Owner/Operators AUM Typical Manager Lifecycle Time Why Emerging Managers? Better Performance Supporting Comments “Hedge Funds under three years of age tend to perform better than do older hedge funds without necessarily adding to the volatility of returns.” - Lazard Asset Mgmt Study Supporting Comments “The annualized returns of Emerging Managers stood at 9.49% compared with 7.61% for bigger peers.” -Neuberger Berman 2011 strategy outlook Supporting Comments “Between 1996 and 2008, funds with less than $100mm delivered 13% annually compared with 10% for funds over $500mm.” - PerTrac Financial Solutions Study Why Better Performance? • • • • • • Freed of legacy positions Freedom to be more concentrated Incentive fees Flexibility with lower AUM Niche/innovative strategies Focused and dedicated talent 1 EMERGING MANAGER INTRODUCTION 2 EMERGING MANAGER FORMATION 3 EVALUATING EMERGING MANAGERS 4 WHAT NEEDS TO CHANGE What Does It Take? Breakeven Insufficient Recurring Fees Sufficient Recurring Fees What Does it Really Take? Client’s Interests Manager’s Interests Optimal AUM Fundraising Optimal Asset Bloat Investment Return Optimal AUM AUM EM’s Time Choices Research Fundraising Paradox of Investor Demands Marketing & Fundraising Breakeven Sufficient Recurring Fees EMs Need to Market • Target a receptive niche • Be proactive in raising your profile • Market even at optimal AUM Figure Out Your “Fit” Real Assets Public & Hedge 1 2 3 4 Private Equity Fixed Income Examples Long/Short Equity Global Macro Event Driven One-on-Ones are Critical Our Story Direct Investors Family Offices Endowments Foundations High Net Worth Fund of Funds Seeders Emerging Manager Strategic HNW Seed Programs Specialists Outsourcing Fundraising • Third Party Marketers • Can Be Expensive • EM must still “close” • Personality must fit • Prime Broker/Capital Introduction • Wholesale Relationships Remember: Institutions rarely invest without meeting the investment decision makers Insourcing Fundraising • Inside Salesperson • Captive 3rd-party marketing • Closer to the investment process • Expensive Investors will still require one-on-ones with the decision makers Databases Database entry is time consuming but worthwhile BarclayHedge Consultants Lipper Morningstar eVestment Informa Manager New Manager Formation Registration Service Providers 1 2 Emerging Manager Hire Team 3 4 Initial Funding Low Barriers to Entry Startup Example $21,195.14 Typical Expenses 20% Compensation Infrastructure HR Client Development Other Income 40% 60% 80% 100% 50% 18% 13% 3% 8% 7% Source: Charles Schwab & Co. Helpful Hints • Carving out from an existing firm – Existing track record – Expertise – Relationships • Initial Accounts or Partners – Breakeven is an easier hurdle – Existing investors make it easy to attract more investors 1 EMERGING MANAGER INTRODUCTION 2 EMERGING MANAGER FORMATION 3 EVALUATING EMERGING MANAGERS 4 WHAT NEEDS TO CHANGE The Check Boxes Prospective Institutions May Require: A Multi-Year Track Record A Limit on % of Strategy/Fund Assets Expensive Infrastructure Transparency Prior History of Investment Team Institutional Hurdles Fewer/Better Check Boxes • Investors with EM-friendly Due Diligence: – – – – – High Net-Worth Individuals Family Offices Specialty Fund of Funds Some Foundations and Endowments Specialty Institutions Due Diligence for EMs • The Key Determinants for Success: – People – Philosophy – Process – Historical Performance (if relevant) People • Key Members of the team: – – – – – – – History Personality How they work together Drive and motivation Intelligence Investment Skill Integrity Philosophy • Value vs. Growth • Efficient vs. Inefficient • Macro Process • Source of your investment edge • Is it repeatable? Performance The Potential for Outperformance is Everything One-on-One Meetings • Nearly all Prospective Investors Require One-on-Ones • Meetings Usually Cover: – – – – – History of the Firm Bios on Key Team Members Investment Approach Sample Ideas/Investments Strategy/Fund Structure Emerging Manager Fees • They are dependent on: – Niche – Optimal Asset Base – Return Potential • EMs should not need to excessively discount if capacity is limited Chicken and Egg Problem Emerging Managers Institutional Due Diligence AUM Hurdles Agency Issues Agency Issues Institutions want to avoid being: • More than 10% of strategy AUM • Alone in their allocation Social Proof • Wrong about their decision Maverick Risk Agency Issues 1 EMERGING MANAGER INTRODUCTION 2 EMERGING MANAGER FORMATION 3 EVALUATING EMERGING MANAGERS 4 WHAT NEEDS TO CHANGE Due Diligence Must… • Remove Barriers to EM Allocations – Length of performance track record – AUM restrictions • Focus on Qualitative Due Diligence – People – Philosophy – Process • Be Proactive and Constructive The Big Get Bigger Market Share By AUM 2001 75% Top 30 Firms 2009 Top 18 Firms 25% $95B to $1.6T $215B to $3.3T All Other Firms All Other Firms Source: Northern Trust Global Advisors Benefits of More EMs • • • • • Less “too big to fail” More experimentation Better institutional performance More diversity More industry jobs In Summary • To BE an Emerging Manager – – – – Be an entrepreneur Get to know your prospective clients Have a strategy that fits Work your ass off • To HIRE an Emerging Manager – Get rid of the impediments for funding – Seek out People, Philosophy, Process – Work your ass off Thank You Brian T. Bares, CFA