Validation (Part 6)
advertisement
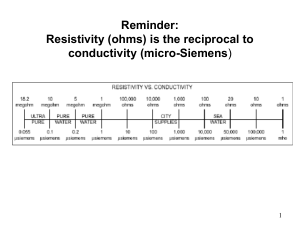
Supplementary Training Modules on Good Manufacturing Practice Validation WHO Technical Report Series, No. 937, 2006. Annex 4. Validation | Slide 1 of 27 August 2006 Validation Part 1. General overview on qualification and validation Part 2. Qualification of HVAC and water systems Part 3. Cleaning validation Part 4. Analytical method validation Part 5. Computerized system validation Part 6. Qualification of systems and equipment Part 7. Non sterile product process validation Validation | Slide 2 of 27 August 2006 Supplementary Training Modules on Good Manufacturing Practice Qualification of systems and equipment Part 6 WHO Technical Report Series, No. 937, 2006. Annex 4. Appendix 6. Validation | Slide 3 of 27 August 2006 Validation Objectives To discuss the principles of qualification of systems and equipment, with specific focus on: The different stages of qualification Requalification and Qualification of “in use” systems and equipment Validation | Slide 4 of 27 August 2006 Validation Principle Systems and equipment: Appropriately designed, located, installed, operated and maintained Critical systems and equipment – should be qualified May include, where appropriate: – Water purification systems, air-handling systems, autoclaves, coating machines Continued suitable performance needed – Why? To ensure batch-to-batch consistency 1.1 – 1.3 Validation | Slide 5 of 27 August 2006 Validation Scope Guidelines describe the general aspects of qualification for systems and equipment Normally qualification would be applicable to critical systems and equipment whose performance may have an impact on the quality of the product 2.1 – 2.2 Validation | Slide 6 of 27 August 2006 Validation General Qualification policy for systems and equipment To include instruments used in production and quality control New systems and equipment: All stages of qualification applicable (DQ, IQ, OQ and PQ) In some cases: Not all stages of qualification may be required – e.g. electrical supply systems 3.1 – 3.4 Validation | Slide 7 of 27 August 2006 Validation General (continued) Systems: Qualified before equipment Equipment: Qualified before routine use Systems and equipment: Periodic requalification, as well as requalification after change Certain stages done by the supplier or a third party Maintain the relevant documentation, e.g. – standard operating procedures (SOPs), specifications and acceptance criteria, certificates and manuals 3.5 – 3.9 Validation | Slide 8 of 27 August 2006 Validation General (continued) Qualification should be done in accordance with predetermined and approved qualification protocols The results of the qualification should be recorded and reflected in qualification reports The extent of the qualification should be based on the criticality of a system or equipment, e.g. – Blenders, autoclaves or computerized systems 3.10 – 3.11 Validation | Slide 9 of 27 August 2006 Validation Blender Discuss the approach of qualification of a newly installed blender Validation | Slide 10 of 27 August 2006 Validation Stages of qualification Design qualification Installation qualification Operational qualification Performance qualification 3.11 Validation | Slide 11 of 27 August 2006 Validation Stages of qualification Design qualification Installation qualification Operational qualification Performance qualification Change control 3.11. Validation | Slide 12 of 27 August 2006 Validation Design qualification User requirements should be considered when deciding on the specific design of a system or equipment A suitable supplier should be selected for the appropriate system or equipment (approved vendor) 4.1 – 4.2 Validation | Slide 13 of 27 August 2006 Validation Installation qualification Correct installation as per plan and protocol Normally advised to prepare requirements for calibration, maintenance and cleaning at this stage Identification and verification of all system elements, parts, services, controls, gauges and other components Calibrate the measuring, control and indicating devices – against appropriate, traceable national or international standards 5.1 – 5.4 Validation | Slide 14 of 27 August 2006 Validation Installation qualification (2) Documented records for the installation – installation qualification report Indicate satisfactory installation Include details, e.g. – The supplier and manufacturer – System or equipment name, model and serial number – Date of installation – Spare parts, relevant procedures and certificates 5.5 Validation | Slide 15 of 27 August 2006 Validation The handout shows a typical format for "An installation qualification protocol / report" It reflects the minimum information that should be included This is an example – and should be used as such Specific formats need to be designed for a specific system or piece of equipment 5.5 Validation | Slide 16 of 27 August 2006 Validation Operational qualification Systems and equipment should operate correctly – operation verified as in the qualification protocol Studies on critical variable to include conditions encompassing upper and lower operating limits and circumstances (i.e. “worst case conditions”) To include verification of operation of all system elements, parts, services, controls, gauges and other components 6.1 – 6.3 Validation | Slide 17 of 27 August 2006 Validation Operational qualification (2) Documented records (Operational qualification report) Finalize and approve SOP (operation) Training of operators provided – training records Systems and equipment released for routine use after completion of operational qualification, provided that: – All calibration, cleaning, maintenance, training and related tests and results were found to be acceptable 6.4 – 6.7 Validation | Slide 18 of 27 August 2006 Validation The handout shows a typical format for: "An operational qualification protocol / report" It reflects the minimum information that should be included This is an example – and should be used as such Specific formats need to be designed for a specific system or piece of equipment 6.7 Validation | Slide 19 of 27 August 2006 Validation Performance qualification Systems and equipment should consistently perform in accordance with design specifications – verified in accordance with a performance qualification protocol Documented records – performance qualification report Show satisfactory performance over a period of time Manufacturers to justify the selected period 7.1 – 7.2 Validation | Slide 20 of 27 August 2006 Validation The handout shows a typical format for: "A performance qualification protocol / report" It reflects the minimum information that should be included This is an example – and should be used as such Specific formats need to be designed for a specific system or piece of equipment 7.2 Validation | Slide 21 of 27 August 2006 Validation Defined schedule Periodic Requalification After change 8.1 – 8.3 Validation | Slide 22 of 27 August 2006 Validation Defined schedule Frequency based on Factors Results of calibration maintenance, verification Periodic Requalification After change Extent based on Risk assessment Part of Change control procedure 8.1 – 8.3 Validation | Slide 23 of 27 August 2006 Validation What about "old manufacturers" who have not performed DQ, or IQ for existing, in-use systems and/or equipment? Validation | Slide 24 of 27 August 2006 Validation Qualification of “in-use” systems and equipment Data to support and verify the suitable operation and performance of systems and equipment Should include operating parameters and limits for critical variables, calibration, maintenance and preventive maintenance, standard operating procedures (SOPs) and records 9.1 – 9.2 Validation | Slide 25 of 27 August 2006 Validation Validation | Slide 26 of 27 August 2006 Validation Group session Validation | Slide 27 of 27 August 2006