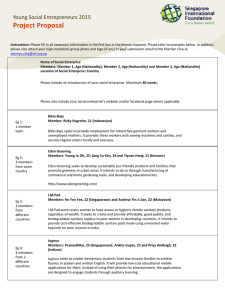
Process Water System Design Phase

Reminder:
Resistivity (ohms) is the reciprocal to conductivity (micro-Siemens )
1
BEWARE of Biofilm Buildup
SOURCE: http://www.fda.gov/ICECI/Inspections/InspectionGuides/ucm074905.htm
164
Process Water System
Design Phase
• Assemble cross-functional team
• Determine quality of feed water
• Determine required specifications
• Write protocols
Pre-validation
• Calibration of instruments
• Validation of test methods
3
Purified Water System Design Considerations
• 316LSS material of construction
• Sanitary electro-polishing and passivation
• Sanitary clamp fittings or orbital welds
• Lines sloped to drain 1/8 in/ft
• Recirculation loop 3-5ft/sec
• Sanitary pumps, Submicron filters (0.2
μm) on tanks and vents
• Use-point fittings or GMP valves
• Sanitary diaphragm-type and stem valves only. No ball, gate, plug, butterfly, globe or disc valves.
• Drains must have air-break to prevent back-siphoning
• Minimize dead-legs to 6D
• Control biofilm buildup
(recirculation, 85oC, ozonation)
• No added substances
SOURCE: Manfredi, Joe, “Myths, Rumors, Fantasies about Water
System Design”, Pharmaceutical Technology CGMP Compliance 2006, pp 28-38
4
Water for Pharmaceutical Use
Typical deionizer schematic
from water softener
HCl NaOH
6
5
4
3
2
1
Eluates to neutralization plant
6
3
2
5
4
1
Water must be
UV light kept circulatin g
Cationic column Anionic column filter 5 µm
Hygienic pump
Return to deioniczer
Cartridge filter 1 µm
Ozone generator
Outlets or storage.
Drain line
Air break to sewer
Installation Qualification
• Assure that the system is installed per design criteria
• Test water before and after each piece of equipment in-line. Not just at point-of-use!
• Use that data to write your SOPs
(backflushing, regeneration, etc.)
• For example . . .
6
Qualification of Mixed Bed Deionizers
Regeneration
Anion
Cation
In-Use
Dilute Base
Monitor feed water and effluent
• Conductivity
• PSID (scaling)
• Run length gallonage
• Amount of regenerate
• Rinse water gallonage
• Silica
(channeling)
• Bacterial load
• Other (eg. Air quality)
Cation
&
Anion
Mixed
Bed
Air Dilute Acid To Waste Purified Process Water
Mixed bed regeneration requires backwashing for separate treatment with acid and base. They are mixed with air before start-up.
7
Operation Qualification
• Is the system operating correctly?
– Pumps at right pressure?
– Water flow correct?
• Continue to test feed water, sample ports and points-of-use
• Monitor system changes to validate the SOPs
8
Water Validation and the
Corporate Audit
• Allow extra time to audit the water system
• Trained persons are needed to maintain the water system
• Must check for specifications and acceptance criteria for each sampling point
9
Water for Process Use
• Designed, constructed and validated to prevent microbial proliferation and assure quality
• SOPs for maintenance, cleaning & sanitization on frequent basis
• Monitor & test to assure conformance to chemical, physical and microbiological specifications
• Sanitary sampling ports after each component
• Check at point-of-use daily
• Record & document test results
• Alert & action limits
• Corrective action plan
10
Performance Qualification
• Test all sample ports for 30 consecutive days
(spring, summer, fall and winter)
• Validation complete after one full year
• Trend analysis may help avoid having to revalidate
• Develop change control procedures
• Establish acceptance criteria for each piece of equipment
• Establish alert and action limits
• Develop corrective action plans
• Confirm the action had the desired affect
11