I Like Cake
The History of Federalism in
America
Defining federalism
Citizens elect officials to each level of govt
Each level of government taxes citizens
Each level has a primary responsibility for
certain areas of public policy
Unitary System
Power is in hands of national government
Subnational units are administrative, not
political
– School text in France and US
How many govts are there?
1 federal government
50 state governments
3,000 counties
19,000 municipalities
Townships 17,000
14,000 School districts
31,555 Special districts (i.e. Port Authority)
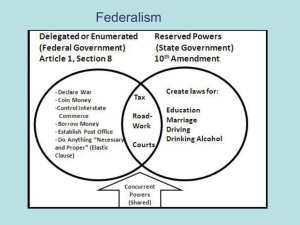
Constitutional Basis of Federalism
National Government
– Article 1- “No state shall”
coin money, engage in
treaty, lay duties, engage in
war
– Article 1, Section Congress
shall do what is "necessary
and proper" and “general
welfare”
– Article 6-Supremacy
Clause "supreme law of
the land“
States
– guarantee to every state in
this union a republican
form of government
– “The powers not delegated
to (fed govt) are reserved
to the states respectively,
or to the people.”
Constitution & Federalism
Fed #51 “ a double security against majority
tyranny”
Divide the power of government within the levels
of government (sep of powers) but also across
governments (between state and national
governments)
Different governments will control each other
against the oppression of governments
States Rights vs. Nationalists
Nullification
– Then and Now
Dual Federalism
1789-1937, Layer cake
model
two distinct layers of
government
Separate powers and
spheres of influence
– Feds, internal
improvements, tariffs, etc
– States- commerce,
banking, insurance,
slavery, health, education,
criminal, etc
Hammer v. Dagenhart (1918)
Great Depression and Demise of
Dual Federalism
Federal Emergency Relief Act of 1933
Cooperative Federalism
Eisenhower Era
– Interstate Highways
– Urban Renewal
– Airport Construction
Great Society programs
– Medicaid and Medicare
– Education Aid
– Model Cities
Today
– Clinton crime, education policy (100k new police)
– Bush – Leave No Child Behind
– Obama- stimulus package, health care
Categorical grants
Federal grant of $ to state
interstate highways, poverty, crime,
education, pollution
Categorical grants specified use of money
– Alabama Syndrome
Marble Cake Federalism
Intermingling of federal,
state, and local authority
Example of education
– Feds- Leave no child
behind, Special education,
Labor laws
– States- labor laws,
curriculum, testing
– Local- hire the teachers,
finance
Food Stamp Program
National Goal- improve nutrition in low
income households
Feds provide $, pay 62% of administrative
costs
States- determine eligibility standards
Supplemental Nutrition
Assistance Program
Feds revise eligibility criteria
–
–
–
–
–
–
Up to 130% of poverty line (2,389 family of 4)
Able bodied adults can receive for 3 months
Disabled vet, child of vet
State EBT/Debit Card
No discrimination race, gender, sex orientation
Most legal immigrants eligible
Rick Perry- happy or sad?
New Federalism
1968-present
– Reduce the power of the national government
– Less $$, fewer strings (?)
Block Grants
provided unrestricted grants to states and
localities
Entitlement, not competition
Energy Efficiency and Conservation
Block Grant Program (2009)
”$2.7 billion will be awarded through
formula grants. In addition, approximately
$454 million will be allocated through
competitive grants” (energy.gov)
Grants can be used for
Development of an energy efficiency and conservation strategy
Building energy audits and retrofits, including weatherization
Financial incentive programs for energy efficiency
Transportation programs to conserve energy and support renewable
fuel infrastructure
Building code development, implementation, and inspections
Installation of distributed energy technologies
source reduction, recycling, and recycled content programs
Reduction and capture of greenhouse gas emissions generated by
landfills or similar waste-related sources
Installation of energy efficient traffic signals and street lighting
Installation of renewable energy technologies on government buildings
Any other appropriate activity that meets the purposes of the program
and is approved by DOE
Rick Perry- happy or sad?
Reagan’s New Federalism
More block grants, less money
Federal aid to state and local govts fell by
39%.
Buffalo 1977- 31% of their revenues from
Washington, by 1992 they got only 6%.
Reagan’s New Federalism
Choose your own?
– You can make any
kind of cake you want
– You have fewer
ingredients
– Have to pay for it
yourself
Rick Perry- happy or sad?
Popular Support
In which of the following people in
government do you have the most trust and
confidence?
– Federal government 19%
– State government 22%
– Local government 37%
Coercive or Regulatory
Federalism, 1980 Democratic Unfunded Mandates
–
–
–
–
Asbestos Hazard Emergence Act of 1986
Safe Drinking Water Act 1986
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990
National Voter Registration Act of 1993
GOP Unfunded Mandates
– No Internet taxation
– No Child Left Behind
– Help America Vote Act
HAVA
Update their voting machines (no punch
card)
each polling location have at least one
voting system accessible to individuals
with disabilities
develop a single, uniform, official,
centralized, interactive computerized
statewide voter registration list
Cake Analogy?
Baking Analogy- You
can have any cake
you want as long as it
has chocolate
State Mandates Under Obamacare
Adjust eligibility in Medicaid to new
federal rules (16 million+)
Establish high risk insurance pools for
people with preexisting conditions (by Jan
1, 2014); create insurance exchanges
Require insurance companies to allow
dependents up to 26 stay on parent’s
insurance
Rick Perry- happy or sad?
Who Pays
Who Decides
Example
Categorical Grants 70%/Feds/ 30%
states
National
government sets
goals, states
limited discretion
Food Stamps
Block Grants
60% Feds/O%
states (less money
State government
Energy Efficiency
Unfunded
Mandates
0% Feds/100%
States
National
government
HAVA, ADA
Popular Support
Which level of government does the best
job of dealing with the problems it faces
– Federal government 14%
– State government 21%
– Local government 41%
Constitution & Federalism Redux
Fed #51 “ a double security against majority
tyranny”
Divide the power of government within the levels
of government (sep of powers) but also across
governments (between state and national
governments)
Different governments will control each other
against the oppression of governments
General Trends
Primary constraints are political, not
constitutional
Federal role is reduced, 16% of state and
local governments budgets
Intense state experimentation
Bipartisan belief in devolution
Devolution Theory
“enhance the responsiveness and efficiency
of the federal system based on the theory
that state and local governments can do a
better job of providing services for
citizens"
How Much Devolution is there?
"if we exclude Social Security, Medicare,
net interest on the federal debt, and defense
from the total expenditures of federal,
state, and local governments in the United
States, 80 percent of what remains is
administered by state and local
governments" (1999, 3).
Constitution
Article 1, Section 8
– Congress shall do what is “necessary and
proper” to promote “interstate commerce”
10th Amendment
– powers not delegated to federal government
are "reserved to the states or the people”
Supreme Court’s changing interpretation of
the commerce clause
Revisiting the Commerce Clause
21 drinking Age and highway funding
US v. Lopez
– Gun Free School Zones Act of 1990
– Does it relate to commerce
Why Federalism Matters
Determines who pays (welfare $148 v.
$360)
Determines how much uniformity of policy
there will be (death penalty)
Determines who makes the decisions
(textbooks)
Determines accountability
Basic Tradeoff
a more centralized system is likely to be
more uniform, equitable, and accountable
decentralized system is likely to be more
democratic and flexible
Who should make decision on…
Marriage
Death penalty
Environmental standards
Education
Gun Control
Welfare reform
Benefits of Federal System
Diversity of Needs
Enhances popular sovereignty
Proximity to Citizens
Local control
Innovation and Experimental Lab
Disadvantages of Federalism
exacerbates economic inequalities.
justice varies from state to state
allows local minorities to block the will of
national majorities (civil rights)
Spillover effects and competition