Chapter 24 The Age of Reform- 1791-1911
advertisement

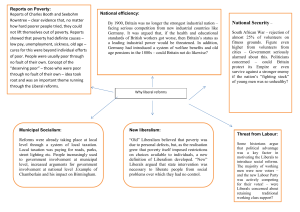
Chapter 24 The Age of Reform- 1791-1911 Sections Covered Section 1- Liberal Reforms in Great Britain Section 3- Revolution and Reform in France Section 4- Latin Americans Win Independence Chapter 24 Section One Liberal Reforms in Great Britain and Its Empire I. Reforms of the 1800s A. Voting Restrictions 1. Only property owners could vote. 1 out of 16 men 2. People voted in the open- bribery and intimidation 3. District boundaries no longer represented how the population was distributed 4. No non-Anglican Protestants could hold political office B. Reform Bill of 1832 1. Took seats away from less populated areas and gave them to the industrial cities 2. People with less property the right to vote a. Still needed property to vote. 1 in 5 men could not vote 3. Whig Party won strong support I. Reforms of 1800s continued A. Social and economic change 1. Factory Act of 1833- reformed the horrible working conditions of women and children 2. Slavery abolished in all colonies in 1833 3. Eliminated the Corn Laws- tax on imported grain a. Drove up the cost of bread B. The Chartist movement- 1830s-1840s 1. William Lovett founded London Workingmen’s Association 2. Wanted universal male suffrage and secret ballot 3. Redrawn districts and salaries for members of Parliament a. So poor people could become lawmakers 4. Reforms proposed in People’s Charter 5. Most goals were made into law II. Disraeli and Gladstone A. Both supported Reform Bill of 1867 1. Doubled the number of eligible voters B. Benjamin Disraeli- prime minister- Conservative Party 1. Great in foreign affairs 2. Britain gained control of Suez Canal 3. Queen Victoria became Empress of India C. William Gladstone- prime minister- Liberal Party 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Concerned with domestic and financial affairs Education Act of 1870- elementary school system- free in 1891 1872, began to use secret ballot in all elections Relaxed voting restrictions nearly all men able to participate Problems with Ireland- wanted Home Rule- Potato Famine III. Reforms of the Early 1900s A. Labour Party formed 1900 1. Believed too little being done to help working 2. Workers allowed to organize into unions B. Fabians 1. Aimed to improve society through socialist ideas C. Liberal Party Reforms 1. 2. 3. Social welfare laws- old-age pension, health insurance, and unemployment insurance, employment offices Parliament Act of 1911- took away House of Lords power Law that gave House of Commons salary D. Suffragettes- led by Emmeline Pankhurst 1. Women who campaigned for their right to vote IV. Changes in the British Empire A. Canada 1. Lord Durham given broad powers to reform a. Grant self government b. United into one state 2. British North America Act of 1867 a. Divided Canada into four provinces 3. Expands its borders IV. Changes in the British Empire continued B. Australia 1. Used as a penal colony 2. Settlers soon after 3. Aborigines – original habitants pushed into interior- many die from new diseases 4. Britain claimed the entire continent in 1829 IV. Changes in the British Empire continued A. New Zealand 1. 1840 took control of islands 2. 1852 granted a constitution and became selfgoverning 3. First to grant women the right to vote Assignment • Homework – Work on “The Growth of Democracy in Great Britain” worksheet