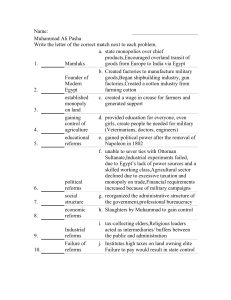
23.Reforms, Revolutions, and War
advertisement

KICK OFF NOVEMBER 25, 2013 Afghan prisoners in Guantanamo Bay who refuse 9 consecutive meals are considered to be on hunger strike. Medical officials resort to force feeding the prisoners, by inserting a tube up their nose and into their stomachs. Force-feeding, as practiced at Guantanamo Bay, is torture. What do you think prison guards should do? Should they continue to force feed prisoners, let them starve to death, or something different? What are the effects of such choices? Turn in your vocabulary words and packet from last week! STARVING FOR THE VOTE Women in the late 1800s went on hunger strikes after being imprisoned for wanting to vote. Parliament passed an act that allowed women who were sick from hunger to leave prison to recover. Once they were well, the police would take them back to prison. CHAPTER 23 REFORMS, REVOLUTIONS, AND WAR REFORMS IN GREAT BRITAIN Section 23.1 FOLDABLE • Stack two pieces of paper on top of one another, so that one is an inch above the other (about the tip of your thumb). • Fold the bottom downward, so that you can see 4 tabs. • On the top tab, write “Reforms in the British Empire.” • On the second tab, write “Social” (pg. 686 - 689) • On the third tab, write “Political” (pg. 686-690) • On the last tab, write “Voting” (pg. 686-689) •Social Reforms (pg. 686 - 689) •Political Reforms (pg. 686-690) •Voting Reforms (pg. 686-689) •Partner-read the section and list the reforms under the appropriate tab. SOCIAL REFORMS •Sadler report leads to the Factory Act of 1833, which limits the working hours of women and children and requires schooling for children •many people support the goals of the Chartists and suffragists, although government is slow to respond •Abolition of slavery POLITICAL REFORMS •Reform Act of 1832 gave industrial towns representation •Victorian Era makes Britain more democratic •Act of Union in 1801 creates the United Kingdom, Ireland grows to resent British rule, seeks selfgovernment after the Potato Famine •Canada, Australia, and New Zealand become selfgoverning colonies VOTING REFORMS •Reform acts in 1832 and 1867 increase the number of men who could vote in Britain •By the end of the 1800s, many reforms sought by the People’s Charter are granted •Some suffrage granted to women in 1918 •Women get same voting rights as men in 1928 KICK OFF DECEMBER 2, 2013 What was the best part of your Thanksgiving break? What was the worst part? QUICK QUIZ! Take out a piece of paper. You may share it with a friend. Have your notebook on your desk. QUICK QUIZ! 1. What were the three categories of reforms in Great Britain during the Victorian Era? •2. Name one effect of the Reform Act of 1832. •3. What did the Act of Union in 1801 create? •4. What year did women get the same voting rights as men in Great Britain? QUICK QUIZ! 1. What were the three categories of reforms in Great Britain during the Victorian Era? A: Social, Political, and Voting •2. Name one effect of the Reform Act of 1832. •A: •3. What did the Act of Union in 1801 create? •4. What year did women get the same voting rights as men in Great Britain? INVENTIONS PRESENTATIONS! REVOLUTION IN FRANCE (AGAIN?!) Section 23.2 THE REVOLUTION OF 1830 After Napoleon, Louis XVIII restored as king After Louis’ death, brother Charles X took over, tried to rule absolutely Citizens revolted in 1830, Charles abdicated Louis Philippe chosen as king in a constitutional monarchy Popular with middle class at first, but didn’t last BIRTH OF A REPUBLIC Economic struggles led to new revolution in 1848 Louis Philippe abdicated, French formed a republic w/ Louis Napoleon as president Second Republic gave way to Second Empire as Louis Napoleon refused to give up power Elected Emperor Napoleon III the following year Captured during Franco-Prussian War, deposed as emperor, France proclaimed Third Republic THE DREYFUS AFFAIR Jewish army captain, Alfred Dreyfus, falsely accused and convicted of selling secrets to Germany Humiliated in public ceremony Evidence cleared Dreyfus in 1906 after Emile Zola’s “J’accuse” Divided French society, showed anti-Semitism Led to intense Jewish nationalism and Zionist movement PARTNER ACTIVITY Copy the timeline from page 692 into your notebook. Include at least 3 symbols or visuals. Then, answer the “Interpreting Time Lines” question.