League Of Nations EXAMPLES
advertisement
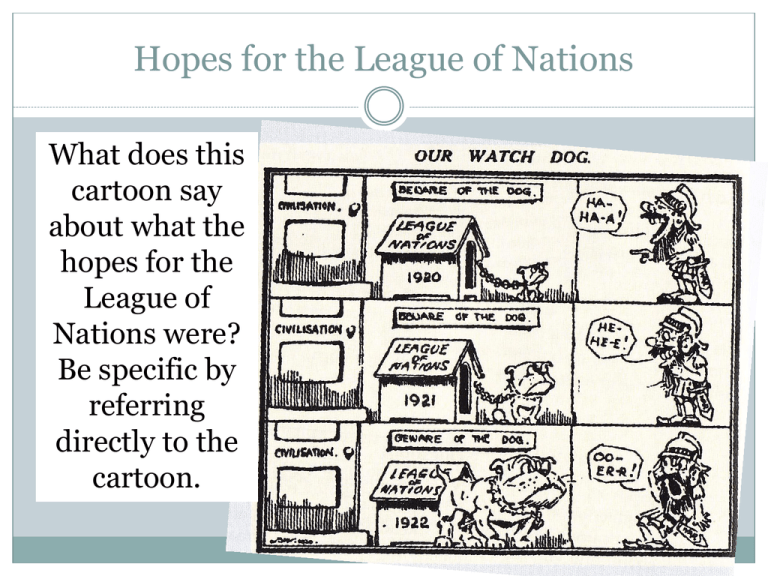
Hopes for the League of Nations What does this cartoon say about what the hopes for the League of Nations were? Be specific by referring directly to the cartoon. Can YOU Resolve International Disputes? REAL EXAMPLES FROM THE LEAGUE OF NATIONS CASE ONE The Aaland Islands (1921) The Aaland Islands (1921) Islands located between Sweden and Finland Finland possessed the islands but most people wanted to be governed by Sweden Neither could come up with a decision that pleased both sides so they asked the League of Nations to intervene The Aaland Islands (1921) Do you: a) Give the Island to Sweden since most people wanted to join that country b) Do nothing and let Finland and Sweden settle the issue on their own c) Let Finland keep the islands, but ensure that no weapons are ever placed there The Aaland Islands (1921) Answer: c) Let Finland keep the islands, but ensure that no weapons are ever placed there Both sides accepted the decision and this remains enforce to the present day CASE TWO Teschen (1919) Teschen (1919) Teschen was a small town between Poland and Czechoslovakia. Its main importance was that it had valuable coal mines there which both the Poles and the Czechs wanted to make their newly formed economies strong. January 1919: Polish and Czech troops fight in the streets of Teschen. Many died. Teschen (1919) Do you: a) Split the town so both the Czechs and the Poles have access to the coal b) Place the town under the protection of the League of Nations to administer the coal as it seems fit c) Support the Poles by sending them reinforcements; after all, Teschen was part of Poland Teschen (1919) Answer: a) Split the town so both the Czechs and the Poles have access to the coal The League decided that the bulk of the town should go to Poland while Czechoslovakia should have one of Teschen’s suburbs. This suburb contained the most valuable coal mines and the Poles refused to accept this decision. Though no more wholesale violence took place, the two countries continued to argue over the issue for the next twenty years. CASE THREE Upper Silesia (1921) Upper Silesia (1921) The treaty that ended WWI gave the people of the region the right to a referendum in order to determine whether they wished to be part of Poland or Germany In the vote 700,000 voted to join Germany and 500,000 opted for Poland The close results sparked violent protests The League was asked to settle the dispute Upper Silesia (1921) Do you: a) Respect the results and hand over the territory to Germany b) Split the province in two parts, handing one to Germany and another to Poland c) Decide to administer the region as a protectorate of the League of Nations for 2 years until another vote is held Upper Silesia (1921) Answer: b) Split the province in two parts, handing one to Germany and another to Poland Both groups within the province and both countries involved accepted the ruling CASE FOUR Memel, Lithuania (1923) Memel (1923) Memel was an area and port in Lithuania that was to be administered by the League of Nations after WWI Most people living there were Lithuanians and resented the fact that a French general was in charge of their territory Lithuanians invaded the port and the League had to step in Memel (1923) Do you: a) Send in forces to squash the rebels and reinforce the League’s control over the region b) Return the area of Memel to Lithuania, but keep the port as an International Zone c) Cede the port and all of the Memel region to Lithuania to satisfy the desire of the population Memel (1923) Answer: b) Return the area of Memel to Lithuania, but keep the port as an International Zone Lithuania accepted the decision, however how could the response of the League be viewed as a failure? CASE FIVE Greece & Bulgaria (1925) Greece & Bulgaria (1925) Bulgaria and Greece shared a border In 1925, sentries patrolling this border fired on one another and a Greek soldier was killed. The Greek army invaded Bulgaria as a result. Greece & Bulgaria (1925) Do you: a) Tell Greece to leave and promise Bulgaria that Greece will be punished by the League for the invasion b) Send in forces to help Bulgaria defeat the Greeks c) Support Greece by reprimanding Bulgaria and demanding that Bulgaria issue a public apology for the shooting Greece & Bulgaria (1925) Answer: a) Tell Greece to leave and promise Bulgaria that Greece will be punished by the League for the invasion The Bulgarians asked the League for help and the League ordered both armies to stop fighting and that the Greeks should pull out of Bulgaria. The League then sent experts to the area and decided that Greece was to blame and fined her £45,000. Both nations accepted the decision. CASE SIX Invasion of the Ruhr (1923) Invasion of the Ruhr (1923) Germany failed to make a payment on war damages owed to Allies because they simply did not have the money. France and Belgium didn’t believe Germany and claimed it needed to be taught a lesson. They invaded the Ruhr area, Germany’s most important industrial region. Invasion of the Ruhr (1923) Do you: a) Diplomatically negotiate a new payment schedule between Germany and Belgium and France b) Send troops to Germany to forcefully remove Belgium and France c) Support Belgium and France because they are important League members Invasion of the Ruhr (1923) Answer: c) Support Belgium and France because they are important League members Within Europe, France was seen as a senior League member – like Britain . Here were two League members clearly breaking League rules. For the League to enforce its rules, it needed the support of its major backers in Europe, particularly Britain and France. Few countries criticised what France and Belgium did. How do you think these actions were viewed internationally? CASE SEVEN Corfu (1923) Corfu (1923) 5 Italian surveyors, working for the League of Nations to map the unclear border between Albania and Greece, were killed on the Greek side of the border. Mussolini, the Italian dictator, demanded compensation from Greece. When Greece refused, Mussolini bombarded and occupied Greek island of Corfu. Corfu (1923) Do you: a) Support Italy by forcing Greece to pay the compensation demanded b) Place economic sanctions on Italy to persuade it to leave Greece alone c) Invite both sides to a conference in Switzerland to negotiate a peaceful solution Invasion of the Ruhr (1923) Answer: a) Support Italy by forcing Greece to pay the compensation demanded Even though the League wanted to condemn Mussolini’s aggressive actions, France and Britain did not want to upset the new Italian dictator. Therefore, they put pressure on Greeks to accept Mussolini’s demands. Mussolini only withdrew his forces once the Greeks had apologised and paid. CASE EIGHT Manchurian Crisis (1931-1933) Manchurian Crisis (1931-1933) Japan invaded Manchuria, which was part of China, to expand its living space and to get more resources. Japan already claimed special interests in the area because Japan ran the South Manchuria Railway and controlled some cities along its route. Japan blew up a section of the Railway and accused China of being responsible for the sabotage. China denied. Japan invaded. Manchurian Crisis (1931-1933) Do you: a) Condemn Japan’s actions and order the withdrawal of troops b) Send a coalition force to forcefully remove Japan from China c) Impose economic sanctions to persuade Japan to hand over Manchuria Manchurian Crisis (1931-1933) Answer: a) Condemn Japan’s actions and order the withdrawal of troops Japan kept Manchuria and left the League of Nations in 1933. League members did not want to impose economic sanctions because the Great Depression had already damaged the world economy too much. Britain and France did not want to use military action because they feared Japanese reprisals against their colonies in the Far East. CASE NINE Abyssinian Crisis (1935-1936) Abyssinian Crisis (1935-1936) Abyssinia was the only independent black African state. Italy wanted Abyssinia because it already had land along Abyssinia’s borders and because it wanted to show the world its newfound strength and power. Italy invaded. Abyssinian Crisis (1935-1936) Do you: a) Give certain areas of Abyssinia in return for Italy’s withdrawal of troops b) Impose economic sanctions by cutting off trade with Italy. c) Offer to act as an arbitrator between Italy and Abyssinia to come to a peaceful resolution Abyssinian Crisis (1935-1936) Answer: All of the above The League of Nations attempted all these solutions. However, non-League nations continued to trade with Italy. The economic sanctions did not include oil, coal or iron. The Abyssinian public refused to accept a concession of land to the Italians. The Italians refused to negotiate, knowing that they had military strength and that Britain and France were very reluctant to go to war again. Italy-Ethiopia War (1935) Evaluating the Effectiveness of the League of Nations Country Membership Had 42 founding members, but throughout its existence many members joined and left the League of Nations Member Joined Left Japan 1919 March 1933 Germany 1926 October 1933 Italy 1919 December 1937 USSR 1934 December 1939 France 1919 June 1940 Britain 1919 April 1946 Britain and France considered most powerful both wanted to avoid war at all costs. Which important country was NEVER part of the League of Nations? Discussion Question How do you think the effectiveness of the League of Nations was hampered by the absence of the United States? League of Nations Summary After considering the examples given, what do you think was a serious weakness of the League of Nations? 2. What do the following cartoons tell us about the successes and/or failures of the League of Nations? 1. Cartoon 1 Japan China Cartoon 2 Cartoon 3 Hitler & the League of Nations Hitler’s Aims Reverse the Treaty of Versailles 2. Unite all German speaking peoples 1. Greater Germany including all Germans into one homeland Germans in Austria, Czechoslovakia, Poland, etc... 3. Lebensraum (“living space”) Greater Germany would include +85 million people would need more land to provide enough food and raw materials 4. German rearmament Hitler’s Land Gains Hitler’s Successes Reoccupation of the Saar region Saar under occupation of the League of Nations for 15 years after WWI Vote held in 1935 90% of population voted to be reunited with Germany Reoccupation of the Rhineland 1936: Hitler marches troops into Rhineland; takes control back from the French who had received Rhineland under the Treaty of Versailles Met with no resistance – French unwilling to fight Later 98% of population voted for German reoccupation Hitler’s Successes Anschluss with Austria 96% of Austrians spoke German; Hitler was born in Austria; strong Nazi party in Austria March 1938: German troops march into Austria; Austria made a province of Germany Nazis later claimed that 99% of Austrians voted for Anschluss Sudetenland Hitler’s Successes Mainly a German –speaking area given to Czechoslovakia upon its creation post-WW1 Pro-Nazi Sudeten leader strongly supported Hitler told this leader to demand separation from Czechoslovakia Czechoslovakia refused needed fortifications to prevent German invasion thought they would be supported by the League of Nations British Prime Minister (Chamberlain) did not want a war over Sudetenland met with Hitler, Mussolini and French Prime Minister in Munich and they agreed that Hitler would have the Sudetenland if he promised to stop expanding Chamberlain met privately with Hitler and they promised never to go war with each other again Poland Demanded the return of Danzig and Polish Corridor. Signed a treaty with Italy to help each other should there be a war. Signed a pact with Russia prevent war on 2 fronts Russia would not object to a German invasion of Poland Russia and Germany would divide Poland between them Germany invaded Poland British and French issued an ultimatum that Germany must leave or risk war Germany did not reply Britain declares war on Germany What do these cartoons tell us about the successes and/or failures of the League of Nations?







