Caroline Goh
advertisement
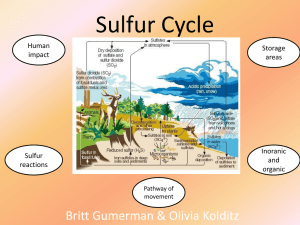
WHAT IS THE SULFUR CYCLE? ☺ The Sulfur Cycle is the transfer and transformation of sulfur compounds throughout the atmosphere, biosphere, pedosphere, and hydrosphere. ☺ Sulfur is an important nutrient for organisms as it makes up a significant part of certain amino acids, proteins and other biochemicals. ☺ Much of the sulfur in the present environment originated from deep sedimentary rocks and soil but due to human interference, it has been released onto the surface. PATHWAY OF MOVEMENT The sulfur cycle mainly consists of the movement of sulfur compounds from sedimentary rocks and soil to surface systems such as plants or coal factories, to the atmosphere, then back down to the ocean and soil through precipitation. ☺ Sulfur is mainly found in soil and sediment in the form of inorganic sulfur (S), sulfates (SO42–), reduced sulfur (H2S) and sulfides (S2−). ☺ Weathering and groundwater then bring the sulfur closer to the surface. ☺ The sulfur can be moved in two ways: ☺ Uptake by plants, providing them important nutrients ☺ Consumption by humans through coal & fossil fuel mining ☺ Factories burning and processing fossil fuels emit SO2 into the atmosphere, which is then converted into sulfate and sulfuric acid. ☺ Through acid precipitation, sulfur is redistributed to the biosphere and hydrosphere, settling into the soil and water, which will eventually continue onto the next steps of the cycle. ☺ Sulfur is also released through the digestion and excretion of living organisms. IMPACT OF HUMANS ☺ Human action has had a major effect on the sulfur cycle. As farming techniques and practices of humans has developed throughout the years, more sulfur in the soil has been released into the atmosphere as dust due to grazing and plowing of land, and river diversion. Sulfur has also been released by the decrease of plants covers that would restrict wind erosion in arid regions from human technology. ☺ Due to the drilling, burning and pumping of fossil fuels and coal in the pedosphere, large amounts of sulfur, originally meant to maintain in deep soil and sediments, have been released into the environment. There is an increase of oxidized sulfur (SO4) in the global cycle at the expense of the storage of reduced sulfur in the Earth’s crust. ☺ SO2 is released as an air pollutant through the production of fossil fuels and forms sulfuric acid (H2SO4) as a result of interacting with the water in the atmosphere. This reaction creates acid precipitation, which can damage both man-made and natural systems. ☺ Sulfur is also applied to land as fertilizer, as it is an essential biological element. CHEMICAL EQUATIONS H2S + 2CO2 + 2H2O → 2CH2O + 2H+ + SO42− (Sulfur Oxidation) Hydrogen Sulfide Formaldehyde Sulfate 2CH2O + SO42− → 2HCO3− + HS− + H+ (Sulfur Reduction) Formaldehyde + Sulfate -> Hydrogen Carbonate