Using MySQLi Extension in PHP
advertisement
What is MySQLi?
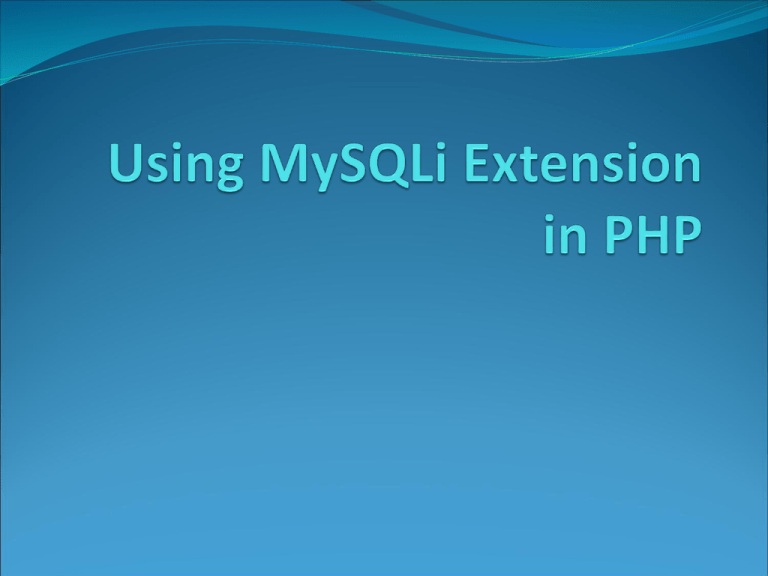
Since the mid-90s, Mysql extension has served as the
major bridge between PHP and MySQL.
Although it has performed its duty quite well,
situation has changed since the introduction of PHP 5
and MySQL 4.1
What is MySQLi?
To correct the issues of MySQL extension, a new
extenstion has been created for PHP5
It is called MySQLi
It supports all the latest features in MySQL server 4.1
or higher
The ‘i’ stands for any one of: improved, interface,
ingenious, incompatible or incomplete.
Major Features
Procedural Interface
An object-oriented interface
Support for the new MySQL binary protocol
that was introduced in MySQL 4.1.
Support for the full feature set of the MySQL C
client library
Why Make the Switch?
Maintainable
Similar Syntax
New Interface
Advanced Options
Speed
Security
Let’s see the code!
/* Connect to a MySQL Server */
$mysqli = new mysqli('hostname','username','password','database');
if ( mysqli_connect_errno() ) {
echo "Connection error. Errorcode: ".mysqli_connect_error();
exit;
}
/* Close the connection */
$mysqli->close();
How to Run a Query
if ($result = $mysqli->query('SELECT Name, Population FROM City
ORDER BY Population DESC LIMIT 5')) {
/* Fetch the results of the query */
while( $row = $result->fetch_assoc() ){
echo $row['Name'] ." (". $row['Population'] .")\n";
}
/* Destroy the result set and free the memory used for it */
$result->close();
}
else {
echo $mysqli->error;
}
Prepared Statements
One of the new features of MySQLi
Using this feature, it is possible to create queries that
are:
More secure
Have better performance
More convenient to write
Two types of Prepared Statements:
Bound Parameter
Bound Result
Bound Parameter Prepared
Statements
A Query template is created and sent to the MySQL
server
MySQL server validates it, stores it and returns a
special handle for future use
When a query needs to be executed, data to fill in the
template is sent to the server
A complete query is formed and then executed
Advantages
The body of the query is sent only once, later only data
to fill in are sent
Most of the work required to validate and parse the
query only needs to be done a single time, instead of
each time the query is executed.
The data for the query does not need to be passed
through a function like
mysql_real_escape_string()
to ensure that no SQL injection attacks occur. Instead,
the sent data is handled safely by server when it is
combined with the prepared statement.
Query Structure
The '?' placeholders can be used in most places
that could have literal data, e.g. a query could be
transformed from
SELECT Population FROM City WHERE Name = 'Dhaka';
to
SELECT Population FROM City WHERE Name = ?;
Let’s see a complete example of bound
parameter prepared statement
Using Bound Parameter Prepared
Statements
if( $stmt = $mysqli->prepare("INSERT INTO CountryLanguage
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)") ){
$stmt->bind_param('sssd', $code, $language,
$official, $percent);
$code = 'BAN';
$language = 'Bangla';
$official = 'F';
$percent = 77.8;
/* execute prepared statement */
$stmt->execute();
echo
$stmt->affected_rows. " Row inserted.\n";
/* close statement and connection */
$stmt->close();
}
The Format String
The following table shows the bound varaible types and
when to use them:
BIND Type
COLUMN Type
i
All INT types
d
DOUBLE and FLOAT
b
BLOBs
s
All other types
Bound Result Prepared Statements
Allow the value of variables in a PHP script to be tied
to the value of fields of data in a query result set.
Create a query
Prepare the query
Ask the MySQL server to execute the query
Bind PHP variables to columns in the query result
Request that a new row of data be loaded into the
bound variables.
Using Bound Result Prepared
Statements
if( $stmt = $mysqli->prepare("SELECT Code, Name FROM
Country ORDER BY Name LIMIT 5") ){
$stmt->execute();
/* bind variables to prepared statement */
$stmt->bind_result($col1, $col2);
/* fetch values */
while ($stmt->fetch()) {
echo $col1 ." ". $col2 ."\n";
}
/* close statement */
$stmt->close();
}
Using Bound Parameters and
Bound Results Together
It is possible to use bound parameters and bound
results together in a single prepared statement.
Lets see a more complete example that uses both of
these
Using Bound Parameters and
Bound Results Together
if ( $stmt = $mysqli->prepare("SELECT Code, Name FROM
Country WHERE Code LIKE ? LIMIT 5") ) {
$stmt->bind_param("s", $code);
$code = "B%";
$stmt->execute();
/* bind variables to prepared statement */
$stmt->bind_result($col1, $col2);
/* fetch values */
while ($stmt->fetch()) {
echo $col1 ." ". $col2 ."\n";
}
/* close statement */
$stmt->close();
}
More Reference
http://www.php.net/mysqli
THANK YOU