Overview of the Brain
advertisement
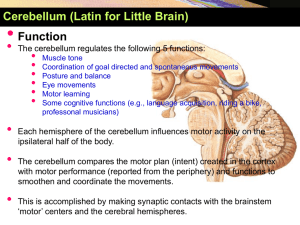
Institute on Neuroscience ION/Teach Build-A-Brain! This Is Your Brain Directional Terms Middle English words for front, back, top and bottom Nonhuman animals are oriented differently So are their brains The Cerebrum Frontal Lobe • • • • • • reasoning planning parts of speech movement emotions problem-solving Parietal Lobe perception related to: • touch • pressure • temperature • pain Temporal Lobe Occipital Lobe • Hearing or audition • memory • Vision or sight Lobes are only organized like this in the brains of mammals Brain Stem & Spinal Cord •Diencephalon -Hypothalamus – the 4 F’s -Thalamus—sensory relay station •Midbrain -Tectum -Processing visual and auditory stimuli -Lower vertebrates: vision -Tegmentum -basal ganglia: motor activity •Hindbrain -Pons - ”bridge” (plus nuclei) -Medulla oblongata -Cerebellum The Cerebellum • Functions: coordination of balance, locomotion and movement • Note: All vertebrates have a cerebellum which varies in size depending on the class of animals Brain Complexity & Surface Area •Convolutions = folds •Increase surface area •Reflect more complexity (in cerebrum and/or cerebellum only) How does this brain compare to other vertebrate brain models? Vertebrate Brain Diversity • Brain diversity across vertebrate classes • Size of forebrain related to "intelligence" of species • behavioral complexity? • Compare across species to consider structure-function relations • e.g. olf bulb or cerebellum Vertebrate Brains and Brain Diversity Brain Diversity & Adaptations Understanding an animal’s behavior or how it interacts with its environment can help you make predictions about what its brain might look like Knowing about an animal’s brain can help you make predictions about its behavior or sensory systems Relative brain size is more important than overall brain size Who has the best brain? That depends on what you need it for. Evolutionary increase in relative brain size. • Humans and several other animals have much larger brains than expected, based on body mass. Hypothesized • Ratio was named the “encephalization quotient”, by H. J. reasons: Jerison. climate change eating fruit! improved vasculature neoteny How are dog and cat brains different? • Which do you think has a proportionally larger olfactory bulb? • How about cerebral cortex? Which has more wrinkles (convolutions)? • How about the cerebellum? Which is bigger? Which has more convolutions? Dog vs. Cat Brains and Behavior of Aquatic Mammals: A Comparison of Dolphins, Sea Lions and Manatees Comparison Porpoise Sea Lion Manatee Class Mammal Mammal Mammal Primary way to find food (forage) echolocation visual tactile Diet shrimp, fish fish sea grasses Vocalizations complex -- mother-pup I.D. Territorial no yes no Dominance hierarchy yes yes no Tricks Acrobatic/balance Acrobatic/balance -- Olfaction Lobes and nerves absent Pup I.D. probably Cerebral cortex Guess! Guess! Guess! Sea Lion Bottle-nose Dolphin Marine Mammal: Florida Manatee Compare Marine Mammal Brains Consider These Brains Forebrain/Cor tex Midbrain (Visual) Cerebellum (Coordination ) What do these brains tell you about the behavior of these animals? Forebrain/Cor tex Midbrain (Visual) Cerebellum (Coordination ) • Now Build Your Own Brain! It can be a brain from a real or imaginary creature • Supplies: Play-Doh (at least four different colors), your imagination, and hands! • What does the relative size of different brain regions say about the environment of the animal?