Precedent Powerpoint one
advertisement

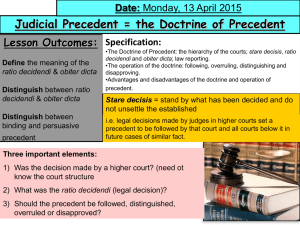
Doctrine (rules) of Precedent Overview, Binding and Persuasive predent PRECEDENT – a definition Precedent is a major source of law – …precedent is all the decisions I have made in the past that other judges now follow. Precedent is also known as CASE LAW PRECEDENT – and Stare Decisis It means – let the previous decision stand. It’s important because Points of law decided in previous similar cases must be followed. Earlier decisions influence later cases that are similar. Higher courts assume priority over lower courts. Higher courts therefore BIND lower courts. The system is predictable, fair and consistent. Binding precedent is the most important part of Stare decisis - it provides consistency in law A Level Law - Hierarchy of courts Civil Courts Binds all Courts but only On European law Binds itself And lower courts European Court of Justice Supreme Court Only court that can Overrule it’s own decisions Binds itself And lower courts Court of Appeal Civil Division Binds itself And lower courts Divisional courts Binds itself And lower courts High Court Doesn’t bind any court Magistrates Court County Court A Level Law - Hierarchy of courts Criminal Courts Binds itself And lower courts Binds itself And lower courts Binds itself And lower courts Supreme Court Only court that can Overrule it’s own decisions Court of Appeal Criminal Division Queens Bench Divisional court Doesn’t bind any court Crown Court Doesn’t bind any court Magistrates Court Stare Decisis – where’s it all written down? For stare decisis to work – judges need access to details of past cases. Earliest cases – 13th century. 1865 – Council of Law Reporting established. Most widely used modern record – All England Law Reports. LEXIS – electronic law reporting system. Huge increase in electronic systems and data-bases on-line through the internet. Web portal to cases and blogs on law - See Matrix Churchill blog. Case notes of A level law. LRC E law student. PRECEDENT and the ratio decidendi It means the reason for deciding If the obiter dicta explains how I got to my decision . . . the ratio decidendi is the heart of the actual decision itself The ratio decidendi is what later judges must follow - the essence of Stare decisis The ratio decidendi is the KEY to the decision that has been made. The ratio decidendi BINDS later judges hearing similar cases. This especially the case in lower courts and the same court. PRECEDENT and Obiter Dicta It means other things said. As I make my judgement, I may give supporting arguments and points that explain how I arrived at my decision in order to make my judgement clearer. how the decision might affect future situations Obiter dicta may include… my thought processes why I arrived at this decision, and not another… PRECEDENT – THE KEY TERMS PROBLEMS •Cases often end with more than one speech. Upto 9 in the Supreme Court. STARE DECISIS •No sub-headings in judgments to help separate ratio decidendi from obiter dicta. ‘Other things said’ – judges in future cases do not have to follow it. OBITER DICTA Precedent – all the decisions made in the past that other judges now follow Stand by what has been decided – do not unsettle the established. The reason for the decision. Judges in the same or lower courts must follow where facts are similar. RATIO DECIDENDI