Understanding by Design
advertisement
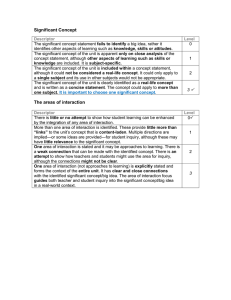
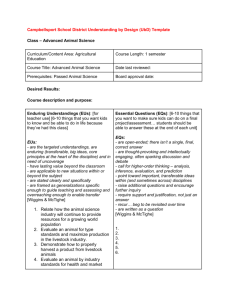
Understanding by Design Backward Design McTighe & Wiggins GOALS To understand the “big idea” of planning through Backward Design by McTighe & Wiggins To explore the 3 steps of Backward Design To apply the 3 steps to a unit of study in your program To co-plan a unit for implementation WHERE ARE WE? How do we make sense of it all? PUTTING THE PIECES TOGETHER SMART Goals The SEF System Assessments Literacy Numeracy Technology Assessment For Leaning ETC… Our Experience with Planning Activity-Focused Teaching Coverage-Focused Teaching “Teach, test, and hope for the best!” What are the explicit big ideas that are guiding our teaching? What is the plan for ensuring learning? WE ARE ALL DESIGNERS! Starting with the end in mind! Where in our current reality do we already plan using Backward Design? 3 Steps: 1) Identify Desired Results 2) Determine Assessment Evidence 3) Plan Learning Experiences The Heart of the Matter “How do we make it more likely – by our design – that more students really understand what they are asked to learn?” To Understand Means …. To make connections To use, transfer and apply To really get it To explain, interpret, apply, see other perspectives, demonstrate empathy, think about one’s thinking To focus on big ideas STEP 1 – PLANNING FOR THE DESIRED RESULTS What do we expect our students to understand, know and do? (DuFour) The 3 parts of step 1 include: Enduring Understandings Essential Questions Knowledge/Skills LOGICALLY….. If the desired result is for students to understand that … and consider the questions … Then, you need evidence of the students’ ability to (K/S) … Then, the tasks to be assessed need to include … Then, the learning activities need to help students to … ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS Students will understand that … Involves the Big Ideas that give meaning and importance to facts Can transfer to other topics and fields of study (connections) Is usually not obvious and easily misunderstood ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS Students will understand that … Justifies the use of a skill Is a specific insight that is inferred from a topic of study Big Idea – goes beyond discrete facts or skills to focus on larger concepts, principles or processes. TIPS Use the response stem – Students will understand that … Consider the questions in the arrow See ONTARIO Revised Science Curriculum as excellent examples of Big Ideas EXAMPLE – GR. 3 SCIENCE Strand: Understanding Life Systems Topic: Growth & Changes in Plants Big Idea: Plants are important to the planet Enduring Understanding: Our choices and actions can help and/or harm the environment ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Have no simple “right” answer; they are meant to be argued Are designed to provoke and sustain student inquiry, while focusing learning and final performances Often address the conceptual foundation of a discipline ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Raise other important questions Naturally and appropriately recur Stimulate vital, ongoing, rethinking of big ideas, assumptions and prior lessons No more than 2-3 questions should be created ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Example – Gr. 3 Science How do plants survive in harsh or changing environments? How does conflict between humans and nature affect plants? KNOWLEDGE & SKILLS K – Students will know ….. S – Students will be able to ….. What key knowledge and skills will students acquire as a result of this unit? What should students be able to do as result of such knowledge and skill? Cluster ON Curr. expectations LOGICALLY….. If the desired result is for students to understand that … and consider the questions … Then, you need evidence of the students’ ability to (K/S) … Then, the tasks to be assessed need to include … Then, the learning activities need to help students to … STEP 2 - ASSESSMENT Culminating Task – through what authentic performance task will students demonstrate the desired understandings? Consider: explain, interpret, apply, see from different points of view, empathize with, reflect on CULMINATING TASK EXAMPLE – GR. 3 SCIENCE In pairs, you will assume a role and present an oral report on how your point of view affects plants. Roles: Home Builder, Nursery Owner, Biologist, Police, Naturalist (Ptbo. Green-Up), Doctor, City Council CULMINATING TASK EXAMPLE – GR. 3 SCIENCE Develop levels 3-4 criteria for the culminating task STEP 2 - ASSESSMENT Other Evidence: Write, Say and Do (Damien Cooper’s Work) Know your Students: Plan for necessary accommodations and modifications LOGICALLY….. If the desired result is for students to understand that … and consider the questions … Then, you need evidence of the students’ ability to (K/S) … Then, the tasks to be assessed need to include … Then, the learning activities need to help students to … STEP 3 – LEARNING EXPERIENCES What do the students need to know and be able to do in preparation for the culminating task: Determine starting point – KWL Develop Teaching-Learning Cycle – What/How will I teach? How will I differentiate? How will I build in metacognition? OTHER The unit is about 3-6 weeks in length as it is specific and precise. Report card comments for a subject and language are done in advance of the unit. You can now focus on the teaching-learning as the planning is done! ENJOY!