Slide 1 - Mrs. Wells
advertisement
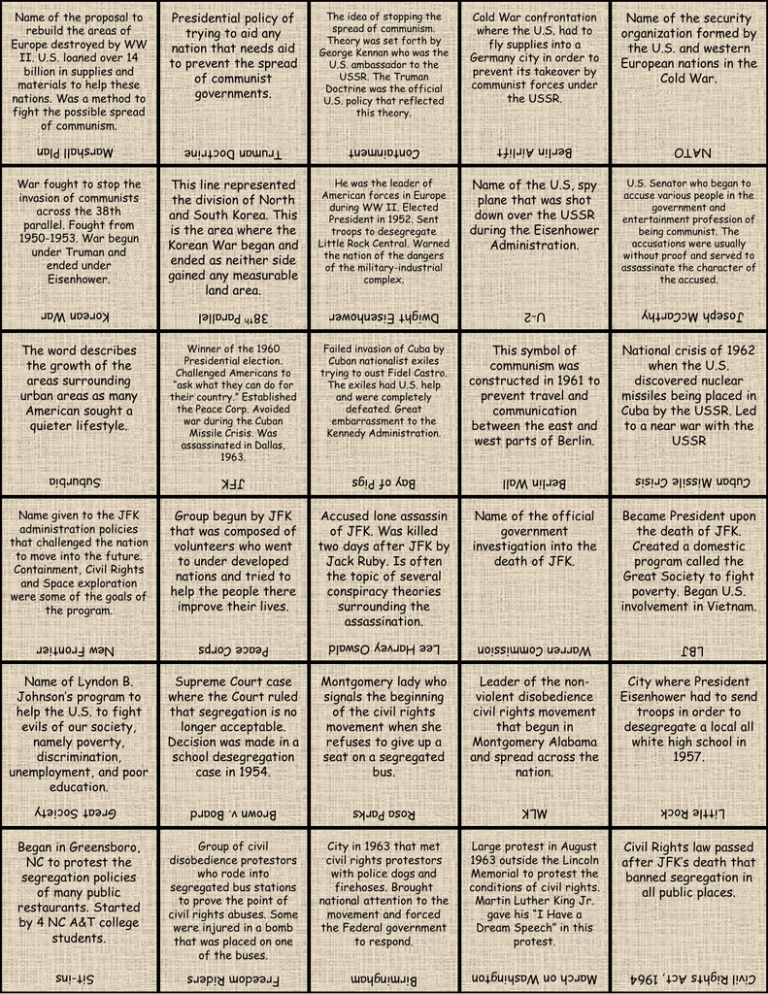
He was the leader of American forces in Europe during WW II. Elected President in 1952. Sent troops to desegregate Little Rock Central. Warned the nation of the dangers of the military-industrial complex. Name of the U.S, spy plane that was shot down over the USSR during the Eisenhower Administration. 38th Parallel Dwight Eisenhower U-2 Winner of the 1960 Presidential election. Challenged Americans to “ask what they can do for their country.” Established the Peace Corp. Avoided war during the Cuban Missile Crisis. Was assassinated in Dallas, 1963. Failed invasion of Cuba by Cuban nationalist exiles trying to oust Fidel Castro. The exiles had U.S. help and were completely defeated. Great embarrassment to the Kennedy Administration. This symbol of communism was constructed in 1961 to prevent travel and communication between the east and west parts of Berlin. JFK Bay of Pigs Berlin Wall Group begun by JFK that was composed of volunteers who went to under developed nations and tried to help the people there improve their lives. Accused lone assassin of JFK. Was killed two days after JFK by Jack Ruby. Is often the topic of several conspiracy theories surrounding the assassination. Name of the official government investigation into the death of JFK. U.S. Senator who began to accuse various people in the government and entertainment profession of being communist. The accusations were usually without proof and served to assassinate the character of the accused. National crisis of 1962 when the U.S. discovered nuclear missiles being placed in Cuba by the USSR. Led to a near war with the USSR Cuban Missile Crisis This line represented the division of North and South Korea. This is the area where the Korean War began and ended as neither side gained any measurable land area. Name of the security organization formed by the U.S. and western European nations in the Cold War. Joseph McCarthy Truman Doctrine Marshall Plan Korean War Suburbia Name given to the JFK administration policies that challenged the nation to move into the future. Containment, Civil Rights and Space exploration were some of the goals of the program. Cold War confrontation where the U.S. had to fly supplies into a Germany city in order to prevent its takeover by communist forces under the USSR. Containment The word describes the growth of the areas surrounding urban areas as many American sought a quieter lifestyle. The idea of stopping the spread of communism. Theory was set forth by George Kennan who was the U.S. ambassador to the USSR. The Truman Doctrine was the official U.S. policy that reflected this theory. Berlin Airlift War fought to stop the invasion of communists across the 38th parallel. Fought from 1950-1953. War begun under Truman and ended under Eisenhower. Presidential policy of trying to aid any nation that needs aid to prevent the spread of communist governments. NATO Name of the proposal to rebuild the areas of Europe destroyed by WW II. U.S. loaned over 14 billion in supplies and materials to help these nations. Was a method to fight the possible spread of communism. Became President upon the death of JFK. Created a domestic program called the Great Society to fight poverty. Began U.S. involvement in Vietnam. New Frontier Peace Corps Lee Harvey Oswald Warren Commission LBJ Name of Lyndon B. Johnson’s program to help the U.S. to fight evils of our society, namely poverty, discrimination, unemployment, and poor education. Supreme Court case where the Court ruled that segregation is no longer acceptable. Decision was made in a school desegregation case in 1954. Montgomery lady who signals the beginning of the civil rights movement when she refuses to give up a seat on a segregated bus. Leader of the nonviolent disobedience civil rights movement that begun in Montgomery Alabama and spread across the nation. City where President Eisenhower had to send troops in order to desegregate a local all white high school in 1957. Little Rock Brown v. Board Rosa Parks MLK Group of civil disobedience protestors who rode into segregated bus stations to prove the point of civil rights abuses. Some were injured in a bomb that was placed on one of the buses. City in 1963 that met civil rights protestors with police dogs and firehoses. Brought national attention to the movement and forced the Federal government to respond. Large protest in August 1963 outside the Lincoln Memorial to protest the conditions of civil rights. Martin Luther King Jr. gave his “I Have a Dream Speech” in this protest. Civil Rights law passed after JFK’s death that banned segregation in all public places. March on Washington Civil Rights Act, 1964 Birmingham Freedom Riders Great Society Began in Greensboro, NC to protest the segregation policies of many public restaurants. Started by 4 NC A&T college students. Sit-ins