Han Dynasty
advertisement
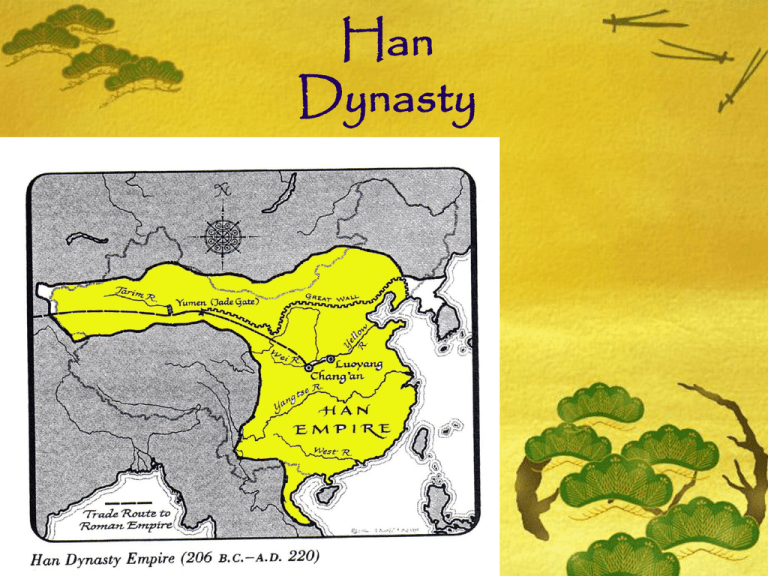
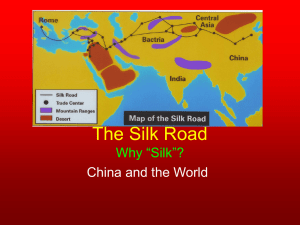
Han Dynasty j Quick Review What continent is China located on? Name the two major rivers. What isolated China from the rest of the world? What was the social order of the Shang? Name 3 of the Shang’s advances. Describe oracle bones. What philosophy believed in going with the flow of nature, yin and yang, and the 3 jewels? What philosophy believed in the law (fa), legitimacy (shi), and arts of the ruler (shu), and had harsh punishments? What philosophy believed in the return to ethics by fathers and leaders acting as good role models? What were the Terra Cotta Soldiers? Who was Shi Huangdi? What occurred under standardization? What were the benefits of the Great Wall? What were the costs of the Great Wall? n This was not the Golden Age of China, but life was very good for many of the people because of the demand for Chinese silk and the creation of the major trade route, the Silk Road. East meets West The silk road connected the East to the West for the first time in history. This allowed people to trade items, learn about different customs and cultures and be exposed to new ideas. Traded items on the Silk Road Silk cloth, grain, porcelain, rhubarb, herbal medicines, herds of horses, camels, dates, raisins, jade, horses, metal works, glass, musical instruments, glassware, carpets, spices, dyed cloth, gold, ivory, spices, cotton cloth, pearls, precious stones, bolts of silk The Silk Road People who traveled the Silk Road were constantly exposed to new ideas, sights, sounds and tastes. Traveling along the Silk Road, meant encountering unexpected surprises, discoveries and new knowledge. Buddhism in China As trade flourished, different people came together, and their contact led to cultural exchange and diffusion. It was during this period in the 1st century A.D. that traders and Buddhist missionaries first brought Buddhism to China. Han Tombs Han writing tells us very little about their daily life. Han tombs, however, tell us quite a lot. The Hans buried clay models of their homes and belongings, in their tombs. Models included details like little clay furniture and little bronze oil lamps. Arts & Science New literature & music So much was lost during the book burnings of the Qin. The Han people tried very hard to replace the literature that was lost during Qin times, especially the works of Confucius. They created new works of literature and music. Art Beautiful murals were painted on the walls of palaces. Scroll painting began. Craftsmen made jade jewelry and carvings, gold ornaments and belt hooks, delicate paintings with wire thin brush strokes. Iron and Pottery Iron was used for making plows and other cast iron objects. Glazed pottery was brightly painted with lively hunting scenes mountains, trees, clouds, dragons, tigers, and bears. Medicine Their medicine was advanced. They invented acupuncture. Science Their science was also advanced. During Han times, these ancient people invented paper. They also invented an instrument that told them when an earthquake was happening called the seismograph. Public Schools One of the Han emperors agreed with Confucius that education was the key to good government. He started a system of public schools, for boys only, taught by Confucian teachers. Jobs Jobs were given to educated people and nobles. People were paid for their work. City Life Only about 10% of the population lived in the cities. Cities were neatly laid out with main streets and alleyways. Each city was surrounded by a strong wall, made of earth and stone. As cities are today, the ancient Han cities were centers of government, education, and trade. Entertainment Most marketplaces, throughout the city, had free entertainment. Musicians played bells, drums and string instruments, and jugglers and acrobats performed and danced. The Poor The poor lived in houses packed together. They had very little food, and little to no sanitation. Many of the young males joined street gangs. Gangs wore distinctive clothes and armor, that identified their gang. Teen gangs roamed the cities, terrorizing people. The Rich The rich rushed to imitate the imperial palace. They built elaborate homes, decorated with drapery, and cashmere carpets. They furnished family tombs with stone lions. On the lions, and on other sculpture, they added inscriptions mentioning how much each item had cost! Merchants & Craftsmen As in Shang times, merchants were hardly recognized as men. Once the canals were built, some merchants and craftsmen became rich. Life in the Country Country folk were farmers. They lived in one or two story mud houses with tiled or thatched roofs. They had curtains on the windows. Barns and other buildings surrounded the house. Several families lived in one house to allow them to work their fields together. They still did not own their farms, but farms were larger in size, because families had learned to team up. This solved a major problem. Together, they were able to produce more food, some years, than they needed, which allowed them to trade food for other items.