chapter 8

CHAPTER 8
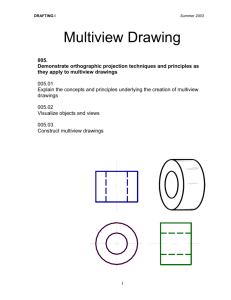
Multiviews
Learning Objectives
• Select appropriate views for presentation
• Prepare single- and multiview drawings
• Create detail views
• Draw view enlargements
Learning Objectives
• Establish runouts
• Explain the difference between firstand third-angle projection
• Create multiview drawings using firstand third-angle projection
• Prepare formal multiview drawings from an engineer’s sketch and actual industry layouts
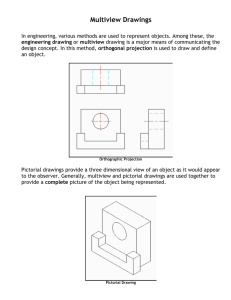
Orthographic Projection
• System for drawing and dimensioning complex three-dimensional items
• Changes physical objects and threedimensional ideas into two-dimensional drawings
• Uses descriptive geometry
Orthographic Projection
• Lines of sight perpendicular to plane of projection
• Surface of the object parallel to the plane of projection:
• Surface appears true size and shape
• Surface of the object not parallel to the plane of projection:
• Surface appears foreshortened, or shorter than true length
• True geometry view
Orthographic Projection
Multiviews
• Multiview projection
• Multiview drawing
• The result of multiview projection
• Represents the shape description of the object
Multiview Standards
• ASME
• ASME Y14.3, Multi and Sectional View
Drawings
• ISO
• Alternate view definition systems
The Glass Box Visualization Method
• Sides of the glass box are planes of projection
• Six total sides, or views:
• FRONT
• TOP
• RIGHT-SIDE
• LEFT-SIDE
• BOTTOM
• REAR
The Glass Box Visualization Method
• Sides unfold at hinge lines, also known as:
• Fold lines
• Reference lines
The Glass Box Visualization Method
• Arranges views in third-angle projection
• Projection techniques:
• 45 ° mitre line
• Arcs
• Transfer
Third-Angle Projection
• Primary multiview projection method
• Common in the United States
• Identified by the third-angle projection symbol
• Angle of projection block near the title block
First-Angle Projection
• Common in countries other than the United
States
• Identified by the first-angle projection symbol
• Angle of projection block near the title block
Third-Angle versus First-Angle
Projection
View Selection
• Six views possible:
• FRONT
• TOP
• RIGHT-SIDE
• LEFT-SIDE
• BOTTOM
• REAR
View Selection
• Seldom necessary to use all six views
• Only draw the number of views necessary to completely described the object
• Front view usually most important
• Establishes other views
• Always one dimension common between adjacent views
Selecting the Front View
• Represent the most natural position of use
• Provide the best shape description or most characteristic contours
• Have the longest dimension
• Have the fewest hidden features
• Be the most stable and natural position
Selecting the Front View
Selecting Two or Three Views
• Most contours
• Longest side
• Least hidden features
• Best balance or position
Two-View Drawings
One-View Drawings
• Thickness identified in a note or title block
• All shape and dimensional information in one view
• If in doubt, drawn the adjacent view
Partial Views
• Symmetrical objects drawn in limited space
• Simplify complex views
• Break lines show that a portion of the view is omitted
Detail View
• Increases the scale of part of a view
• Use when detail cannot be clearly dimensioned due to:
• Drawing scale
• Complexity
Removed Views
• Out of normal arrangement with other views
• Avoid when possible, but may be necessary when:
• Limited space
• Enlarge the view
• Can appear on a different sheet from where the view is taken if necessary
Viewing Plane Lines for Removed
Views
Arrow Method for Removed Views
Views with Related Parts
Rotated Views
• Rotated from normal alignment with other views
• Avoid when possible, but may be necessary when:
• Limited space
• Enlarge the view
• Keep all views on one sheet
• Angle and direction of rotation under the view title
• ROTATED 90 ° CW
• ROTATED 90 ° CCW
Projecting Chamfers
• Slanted edge or a line
Projecting Circles
• Line of sight perpendicular to a circular feature
• Feature appears round
• Circle projected onto an inclined surface
• View is elliptical in shape
Projecting Arcs
Projecting Rounded Corners
• Represented as a contour only
• Fillets
• Rounds
• Break corners
Projecting Rounded Curves and
Cylindrical Shapes
• Phantom lines sometimes used to accent rounded feature
Runouts
Line Precedence
• Object lines take precedence over hidden lines and centerlines
• Hidden lines take precedence over centerlines
• Cutting-plane lines take precedence over centerlines
Line Precedence