SMS - FltPlan.com
advertisement

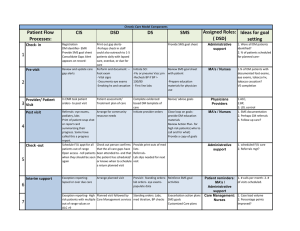
SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Condition where risks are managed to acceptable levels Allocation of resources Organized set of principles, programs, processes and procedures A Safety Management System (SMS) is: “A systematic approach to managing safety, including the necessary organizational structures, accountabilities, policies and procedures.” ICAO Doc. 9859, Sec. 1.4.2 ▪ It is believed that the Federal Aviation Administration will soon mandate that operators of jet aircraft and/or aircraft over 12,500 lbs. develop and deploy SMS programs. ▪ SMS will enable the operation to become a proactive versus simply reactive enterprise by actively seeking safety information that uncovers latent conditions and active failures. ▪ At all levels of the organization, it is simply good business. Management commitment and responsibility Safety accountability of managers Appointment of key safety personnel SMS Implementation Plan Coordination of the Emergency Response System Documentation Hazard Identification Processes Safety performance monitoring and measurement Risk assessment and mitigation processes The management of change Training and education Safety Communication Just Culture Internal Safety Investigations Continuous improvement of the safety system Reporting Culture - Willing front line participation is imperative because you are in direct contact with threats Informed Culture - Effective require the collection, analysis and dissemination of information from incidents and nearmisses, as well as proactive checks Flexible Culture - Possessing the capability of adapting effectively to changing demands (operational or safety) Learning Culture – Willingness and competence to draw the right conclusions from safety information and implement major reforms where the need is indicated Just Culture - A just culture is defined as an atmosphere of trust in which people are encouraged and even rewarded for providing essential safety information, but in which they are also clear about where the line must be drawn between acceptable and unacceptable behavior. A Just Culture is critical for reporting, reporting is critical for learning, and learning is critical for improving safety. Threat - External events or errors, objects or conditions with the potential to cause harm Consequence - Foreseeable outcome of a threat described in operational terms Risk - The safety assessment of the consequence of a threat, expressed in terms of probability and severity, often in alphanumeric convention The Safety Management System is a social construct that welcomes, encourages and shares responsibility for continuous safety improvement with everyone in the company.