Computation Fluency
advertisement

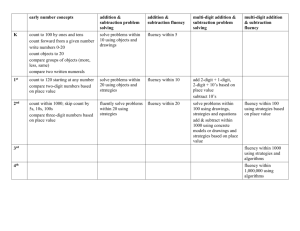
Computation Fluency A spectrum of learning over grades The Goal The goal of computational fluency is to become proficient at solving everyday problems. What it takes To become proficient at solving everyday problems, students must recognize the operation that is required to solve the problem – they must understand the concepts of operations and place value. They must also develop fact fluency. Five Components of Mathematical Proficiency Conceptual Understanding Comprehension of mathematical concepts, operations, and relations. Procedural Fluency Skill in carrying out procedures flexibly, accurately, efficiently, and appropriately. Strategic Competence Ability to formulate, represent, and solve mathematical problems. Adaptive Reasoning Capacity for logical thought, reflection, explanation, and justification. Productive Disposition Habitual inclination to see mathematics as sensible, useful, and worthwhile, coupled with a belief in diligence and one’s own efficacy. Students go through stages in their computational fluency Recognize situations that call for adding, subtracting, multiplying or dividing (for situations involving fractions and decimals too). Use simple counting strategies to solve these problems. Develop more efficient strategies based on number sense (compensating, estimating, etc.) Pick up some combinations fluently before others – using a mix of recalled facts with strategies. Learn about place value. Adding and subtracting Use place value strategies (counting the tens, counting the ones) Learn the multi-digit algorithms (based on place value and sophisticated strategies) The Concrete-Representational-Abstract sequence works well here (ObjectsPictures-Symbols) See CGI Problem Sets, CRA for Multi-digit Subtraction. Multiplying and dividing Learn about area and array models for multiplying. Generalize area models from 1 digit to 2 digit factors. Connect area models to the distributive property. Learn the multi-digit algorithms (based on the distributive property). See Multi-digit Multiplication Learning Progression, examples & resources, and Multi-digit Division with examples. If not by the end of 4th grade: Teach strategies explicitly and provide at least 10 minutes per day of additional support if needed: Math Facts packet, ORIGOMath, PALS Math Practice fluency in middle school and high school within all content areas. See IISD Developing Fluency Packets, Origo and PALS Math overviews, and math across the curriculum ideas.