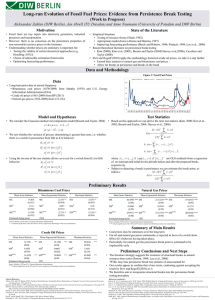
Persist
advertisement

Persistence in Science by All Students David Asai asaid@hhmi.org http://4.bp.blogspot.com/_PuZoLkvmBbc/SdUaLNywcBI/AAAAA AAADMM/zUMDJeuLi0M/s320/The+Little+Red+Hen.png 4 P’s 1) 2) 3) 4) Perspective Persistence Privilege Potential 1) Perspective Diversity benefits science. Diversity…. 1. …..is a property of a group. Science depends on groups. 2. …..adds: (i) perspective, (ii) interpretation, (iii) tools. Scientific breakthrough often results from a different approach, a different interpretation, and/or a different set of tools. 3. ….trumps homogeneity and ability when: (i) hard problem, (ii) multiple ways to look at the problem; (iii) large set of problem-solvers - Scott Page, The Difference, 2007, Princeton University Press Persons, in millions Opportunity: increasingly diverse talent pool 250.00 non-Hispanic White all minorities 200.00 “Majority Minority”: 150.00 • All U.S. by 2042 100.00 • 18 yrs and younger by 2018 50.00 0.00 2010 2050 Challenge: we fail to take advantage of the diverse talent pool U.S. talent pool 28.5% URM Scientific workforce 9.1% URM NSF data for 2006, from Expanding Underrepresented Minority Participation, National Academies, 2011. 50% dx/dt: achieving parity? 40% 30% U.S. population 2100 20% 10% Science Ph.D.s 1970 1990 2010 2030 2050 2070 2090 2110 2) Persistence Fraction who are Underrepresented Minorities (%) Undergraduate years are critical 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 US population undergrads science science baccalaureates PhDs NSF WEBCASPAR (2000-05) Percentage of 2004 STEM aspirants who completed STEM degrees 45 40 5-year completion 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 white Asian American Latino Black Native American Data from Higher Education Research Institute, UCLA G. Huang et al., 2000. Entry and persistence of women and minorities in college science and engineering education. U.S. Dept. Education, National Center for Education Statistics 1. Predictors of success in college 2. 5-year outcomes of students entering STEM programs: – – – – Complete STEM baccalaureate in 5 years Persist in STEM discipline Switch to a non-STEM discipline Drop out of school Persistence of undergrad STEM aspirants 50 45 40 35 30 Whites + Asians 25 URMs 20 15 10 5 0 Complete Persist Switch Drop out G. Huang et al., 2000, Entry and persistence of women and minorities in college science and engineering education, US. Dept. Education, National Center for Education Statistics 3) Privilege http://www.warhw.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/11/PrivilegeMeans2.bmp Faculty privilege Biology 231 is the third course in our four-semester core curriculum for Biology majors. In addition, many pre-professional students from other majors, like XXXX, also take BIOL 231. Our Our course course is is aa rigorous rigorous attempt attempt to to link molecular structure with biological function. We first focus on the macromolecules of the cell, including proteins, membranes, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates; in each case the message is that structure leads to function. We then discuss in quantitative detail the energetics of cell biology, including membrane potentials, the use of ATP in coupled reactions, the metabolism of glucose and oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP, and photosynthesis. Then we put some of these pieces together, discussing in detail selected aspects of cell biology, including signal transduction, cotranslational insertion of membrane/secreted proteins, intracellular trafficking of membrane bounded organelles, and cell motility. All All exams exams are are answered answered with with short short essays essays or or calculations (no calculators permitted!). The emphasis is on precise problem solving. For many, BIOL 231 proves to be the “weed-out” course. “Majority rules” http://d1jrw5jterzxwu.cloudfront.net/sites/default/files/styles/article_header_image/public/article_media/changethemascotsign.jpg http://www.nikkeiview.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/PEKIN-CHINKS.jpg …is deciding what’s best for others. “mismatch hypothesis” “…as a result of the mismatching, many blacks and Hispanics who likely would have excelled at less elite schools are placed in a position where underperformance is all but inevitable because they are less academically prepared than the white and Asian students with whom they must compete.” Justice Clarence Thomas, 2013 concurring opinion, Fisher v. U Texas Testing the “mismatch hypothesis” M. Kurlaender and E. Grodsky. 2013. “Mismatch and the paternalistic justification for selective college admissions.” Sociology and Education. • University of California – Elite: Berkeley, San Diego, UCLA (30% acceptance) – Not-quite-elite: Davis, Irvine, Riverside, Santa Barbara, Santa Cruz (59% acceptance) • 2004, “Guaranteed Transfer Option” (GTO) (2,300 students) • Several hundred chose to attend elite campus Findings…. • GPAs of GTO students statistically same as elite students. • GTO students no more or less likely to drop out of elite schools. • GTO students less likely to drop out than peers who chose non-elite schools. • Mismatch effects no greater for minorities than for whites and Asians. What can we do? http://4.bp.blogspot.com/_PuZoLkvmBbc/SdUaLNywcBI/AAAAA AAADMM/zUMDJeuLi0M/s320/The+Little+Red+Hen.png 1. Learn to talk about difference. http://img2-2.timeinc.net/ew/i/2012/10/17/debate.jpg What’s important in mentoring? 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% Mentors 40% Mentees 30% 20% 10% 0% Gender Race Talk about diversity Byars-Winston, Benbow, leverett, Pfund, Branchaw, Owen, 2013. 2. Learn from other programs • • • • Meyerhoff Scholars (UMBC) Science Posse (Brandeis) BSP (UC Berkeley) BUSP (UC Davis) (1) (2) (3) (4) Research experiences Mentoring Community-building High expectations 3. Change the metaphor High school – 4 yrs Undergrad for B.S. – 4 yrs Graduate school for Ph.D. – 4 yrs Post-doc 1 – 1 yr Post-doc 2 – 2 yrs Tenure-track faculty position http://www.sadeem.ae/Pipeline_at_Kuparuk.jpg Watershed • Inputs from many different sources, different environments, different pathways. • Boundaries between stages are not always exact. • Outcome is huge (the ocean) and there are many different places for the water to eventually go. 4) Potential Course-based Research Experiences Undergraduate student research 1. Apprentice-based research experience • Late • Expensive • Relies on selection 2. Course-based research experience (CRE) • Early • Scalable and less expensive • Emphasizes development of potential SEA-PHAGES project • Created by Tuajuanda Jordan and her team at HHMI in 2007 • Adapt PHIRE course developed by Graham Hatfull (U Pittsburgh) • Deliver the course nationally (2008-present) – In AY 2012-13: • > 2,000 students (mostly first-year UGs) • 75 schools (31 states, PR, DC) Two semesters: Mycobacterium smegmatis GenBank Scientific accomplishments: • • • • > 3,000 new phages > 48,000 genes (865 novel genes) 9 new clusters 82% of mycobacteriophage GenBank sequences contributed by SEA-PHAGES students • 16 publications (10 with undergrad co-authors) • New insights from the aggregated data Learning (from Jordan et al., 2013) Grades in lecture course Retention 100 0.4 95 0.35 0.3 90 0.25 85 0.2 0.15 80 0.1 75 0.05 0 A B C D F 70 Three S’s to a successful CRE 1. Science – (i) genuine scientific problem; (ii) lead scientist 2. Skills – (i) technical simplicity; (ii) minimal prerequisites 3. Structure – (i) flexible scheduling; (ii) parallel activities; (iii) clear milestones Hatfull et al., 2006. PLoS Genetics 2: e92 4th important element: $$ SEA-PHAGES: approx. $200 per student for supplies, EM, DNA sequencing (excludes salaries) Informal survey of 15 research universities: average $47 (<$10 - $150) per student in intro Bio lab (excludes salaries) Average $150 ($85 - $210) per student in advanced lab courses $47. Flip the equation. Introductory courses = opportunity to make a difference 1) 2) 3) 4) Perspective Persistence Privilege Potential “A great scientist (Mirror, mirror, on looks like me” http://theuglytruth.files.wordpress.com/2009/09/snow-white-mirror.jpg White.jpg http://disney-clipart.com/snow-white/jpg/Snow-White/Snow- the wall…) Geoffrey Beene