Chapter 15
advertisement

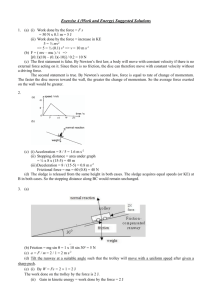
Chapter 15 Energy Assignments 15.1 Math Skills 1-3 p 448; AQs 1-9 p452 15.2 Math Skills 1-3 p 458; AQs 1-6 & 9-10 15.2 Learning Targets for Energy Conversion and Conservation Describe a situation in which energy is transformed from one form to another Explain how energy is conserved Give an example in which gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy are changed from one to the other Solve equations that equate initial energy to final energy Describe the relationship between energy and mass MP 1. A 10 kg rock is dropped & hits the ground at 60 m/s. Calculate PE before it was dropped. Ignore friction! PE beginning = KE end PE beg. = KE end = ½ m*v2 PE beg.= KE end = 0.5*10 kg*(60 m/s)2 PE beg. = 18,000 J MP 2. Diver w/mass = 70.0 kg stands atop 3.0 m high platform. Calculate PE on platform and KE as he enters water (ignore friction) PE beginning = KE end = mgh KE end = 70.0*9.9 m/s/s*3.0 m KE end = 2100 J (? speed entering water) KE = ½ m*v2 2100 J = 0.5*70.0 kg*v2 2100 = 35*v2 (divide both sides by 35) 60 = v2 (take the square root of both sides) V = 7.7 m/s MP 3. A pendulum w/ 1.0 kg weight is set in motion from 0.04 m above lowest point of path. What is KE at the lowest point? Ignore friction. PE beginning (KE=0) = KE low point (PE=0) = mgh mgh = 1.0 kg*9.8 m/s/s*0.04m PE beginning = mgh = 0.4 J PE beginning = KE end = 0.4 J 1. Describe how energy can be converted from one form to another in a wind-up toy Elastic PE stored in the wound up spring is converted to KE as the spring unwinds and the toy moves. 2. State the law of energy conservation. Energy cannot be created or destroyed (only transformed) 3. What energy change is taking place as an object falls in free fall? PE is being converted into KE as it falls. 4. Explain Eintstein’s conclusion about the relationship between energy and mass. Energy and mass are equivalent, and can be converted into one another 5. What type of energy change results when friction slows down an object? Friction causes the conversion of kinetic energy into thermal energy 6. Describe the energy of a playground swing at its highest position. The swing has maximum PE and no KE at its highest point. 9. A 0.15 kg ball is thrown into the air and rises to a height of 20.0 m. How much KE did the ball initially have? KE beginning = PE end KE beg. = PE end = mgh KE beg.= PE end = 0.15 kg*9.8 m/s/s*20 m KE beg. = 29 J 10. A 125 g steel ball with a KE of 0.25 J rolls along a horizontal track. How high up an inclined track will the ball roll if friction can be ignored? KE beginning = PE end KE beg. = PE end = mgh (solve for h) KE / mg = h h = 0.25 J / 125 kg*9.8 m/s/s h = 0.20 m