Colonial Regions Part 2
advertisement

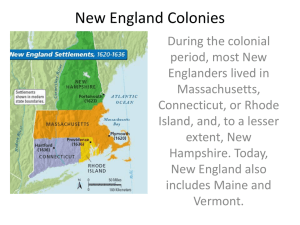
I. Distinct Cultural Regions Develop A. There Were Four Distinct Regions that Developed in the English Colonies of America. a) The New England Colonies b) The Middle Colonies c) The Southern Colonies d) The Backcountry II. Factors that influence the development of Geographic Regional Distinctions A. Climate – climate affects things like what people wear, what they eat, and the homes they live in. B. Social Norms – Humanly created rules of behavior, edict, rituals and taboos C. Religious Beliefs – Common religious beliefs or practices that shape the lives of the people. D. Values – Things that people hold in high regard or consider to be of great worth. E. Physical Geography –natural resources specific to a region that occur naturally that influence economic capabilities Regions of the 13 Colonies: Regional Differences between the Colonies New England Colonies A. The New England Colonies included a) Massachusetts Maine was a part of b) Rhode Island c) New Hampshire d) Connecticut B. New England Colonies were characterized by A. Climate – Long cold winters, rocky soil, population of mostly English settlers B. Social Norms – Heavily influenced by the Puritans and included things like mandatory church attendance, no dancing, and no playing of games C. Religious Beliefs – Centered around Puritanism which aimed to “purify” the practices of the Church of England D. Values – “The New England Way” which emphasized godliness, duty, hard work, and honesty VI. Natural Resources of the New England colonies A. Natural Resources a. Natural Harbors good for shipping and trade b. Abundant Forests with lots of Timber c. Atlantic Ocean offered good water for fishing and whaling d. Good land for grazing cattle VI. New England Colonies Natural Resources & Economic Development B. Economic Development whaling – provide oil from rendered lard Small Farms – families provided for themselves through subsistence farming Fishing – New England’s coast offers some of the worlds best fishing - Mackerel, Halibut, Cod, and clams Ship Building – Timber from pine trees and oak tree are ideal for building ships Trade – With good ports Triangular trade routs are developed between New England, Africa, and the West Indies (islands in the Caribbean) V. New England Colonies A. Subsistence Farming – growing enough food for your family and maybe a little extra used for trade. a) Long winters and short summers equaled a short growing season b) The soil was shallow and rocky which made farming difficult and less productive C. Triangular Trade – a trading route with three stops. a) 1 typical scenario of Triangular Trade • • • • A ship would leave New England with rum and iron The ship would go to Africa drop off the rum and iron and pick up slaves The ship would sail to the West Indies/ Caribbean and t here trade the slaves for sugar and molasses. The ship would take the sugar and molasses back to New England where they would use the molasses to make rum and the whole process would start again. Middle Passage Triangular Trade D. Middle Passage – This was the part of a Triangular Trade route where slaves were transported on ships from Africa to the Americas. a) Hundred of Africans died on this journey Middle Colonies I. The Colonies : A. B. C. D. New York Pennsylvania Delaware and New Jersey MIDDLE COLONIES II. Climate • • • • Longer Growing Season than New England Rich fertile soil allowed the growth of Cash Crops of grain Cold Winters Hot Humid Summers MIDDLE COLONIES C. Social Norms – Quaker Influence helped create an atmosphere of tolerance D. Religious Beliefs – Quakerism allowed other religious groups follow their own beliefs and practices E. Values - Believed in the equality of men and women, first group to stand up against slavery MIDDLE COLONIES IV. Natural Resources Excellent Harbors –With good ports for Trade Fast Flowing Rivers – trading and powering mills Mills were used to make flower from grains. Colonists ate 3 pounds of grain a day. Rich soil – excellent soil for farming Good fisheries Animals – Animals like beavers were trapped and killed for their pelts and furs (specifically beaver) Timber – for housing, ships, masts MIDDLE COLONIES Economy Breadbasket Colonies III. Cash Crops – Crops that are grown and intended to be sold for a profit. A. Types of cash crops included: fruits, vegetables , and above all grains B. Types of grains included: corn, wheat, and rye C. Immigrants Landless Europeans came to this Region to take advantage of its productive land SOUTHERN COLONIES A. The Southern Colonies Included: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Maryland Virginia North Carolina South Carolina Georgia SOUTHERN COLONIES II. Climate & Colonies A. Very hot and humid in the summers B. Warm Winters C. Enables Framers to grow crops year-round SOUTHERN COLONIES B. Social Norms – Societal rank based on the ownership of land and acceptance of slavery C. Religious Beliefs – varied from colony to colony, but Maryland is predominantly Catholic. D. Values - Politically conservative, strong allegiance to church, local government and white supremacy. SOUTHERN COLONIES ECONOMY A. Plantations –Large plantation were vital to the economy of the southern colonies –Plantation crops included: Cotton, Tobacco, Rice and Indigo, coffee, and sugar cane –Plantation crops required many laborers • • • • • • • Rake fields Break ground before planting Plant Flood crops (rice) Drain crops Hoe and weed crops Harvest crops – Plantation owners look for a cheep source of labor SOUTHERN COLONIES Growth of Slavery- Plantation owners turn to the following for cheap labor – Indentured Servants- poor Englishmen who agreed to become a servant/slave for five to seven year in exchange for passage to America » ( fulfilled time of service) – Native American were enslaved • They knew the land and could escape • They were not immune to European diseases and would die – Planters turn to enslave Africans SOUTHERN COLONIES B. Planter Class – Plantation owners i. – – – Elite families with the money or credit to buy land and slaves. More slaves = more production of rice, tobacco, indigo, cotton, or sugar cane which equaled more money Slave labor allowed the planter class to become very wealthy This class took over the government in the southern colonies SOUTHERN COLONIES Plantations Plantations were mostly self-sufficient Slaves were: Carpenters Barrel makers. Blacksmiths Tanners Curriers Shoemakers Spinners Weavers Knitters Distillers SOUTHERN COLONIES Slaves worked 15 hours a day They were Whipped, raped and beaten They lived in small one room cabins They were poorly clothed Working slowly They were under fed They made up 40% of the south’s population Damaging equipments They rebelled by: Acting stupid Backcountry - Climate varied depending on latitude - Mainly settled by the Scots-Irish immigrants • Northern & Middle • Southern Colonies – Colonies – Shorter Warm climate, good growing season, cold soil for farming, winters, fertile soil English Settlers and good for farming, enslaved Africans population with a mixture of immigrants from all over Europe