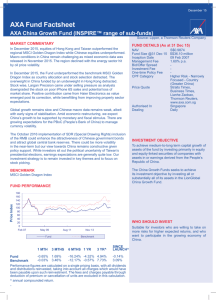
AXA at a glance Synopsis of the 2009 Corporate
advertisement
Impact of the crisis on the insurance industry Violeta Ciurel President&CEO AXA Life Insurance Romania The International Insurance Mediation Conference Istanbul, March 28, 2011 1 AXA Group Global Ambition To become THE PREFERRED COMPANY in the industry for our clients, employees, suppliers, shareholders 4 Key figures 31 Dec 2009 5 90.1 billion euros in consolidated revenues 3.9 billion euros in operating earnings 3.5 billion euros in adjusted earnings income 1,014 billion euros in assets under management The AXA Group is present in 57 countries 96 million individuals and businesses have placed their trust in AXA 18,000 AXA volunteers gave time to the community 216,000 employees and exclusive sales associates around the world, dedicated to delivering AXA customers the solutions and services they need and expect, including: 104,000 employees, 24,000 salaried sales force, 88,000 tied agents. 400,000 individual shareholders AXA Life Insurance in Romania Entrance on the Romanian market in 2010 by acquiring a small company Our ambition is to achieve to build, together, AXA’s business in Romania and become a preferred, profitable and trustworthy company. In Romania, AXA currently operates in the life insurance sector (offering financial plans for children, individual and family protection) and on the health insurance sector (offering corporate life and health plans) By bringing innovative products, well trained agents and improved customer experience AXA wants to redefine a market of promises into a market of proofs. 6 Financial crisis - Background Crisis started in US in 2008 in the banking sector due to: Mortgage home loans in US Long term mispricing the real risk, over-leverage, reducing credit quality Credit rating agencies Lack of appropriate regulation and supervision Lack of liquidity in the market Systemic risk caused by large/global banks Consequences: Decrease of economic growth Government intervention: direct support, credit guarantees, insurance, 7 nationalization Fall of the stock markets, assets value, real estate value Reducing the interest rates Reducing the value of pension funds and life insurance UL investment Indirect exposure at the financial institutions which went into bankruptcy But for insurance…. Insurance industry is not at the origin of the crisis, but witnessed and was impacted! Insurance were in a strong position when crisis started and were well capitalised Insurance industry had a stabilizing impact on the financial industry overall due to: Long term investment policy Prudent investment policy Insurance cannot not generate systemic risk Overall losses much lower than in the banking sector (21%) Effects on insurance: 8 Direct and indirect Different for life insurance, pensions and general insurance Short term and long term Direct effects Decrease of the population income; reducing the purchasing power Increase of the surrenders and lapses Reducing sales Competition with substitute products Reputational risk Decrease consumer confidence Increasing the hedging price Lower interest for investing in financial sector, mainly for the individual investors Increase demand for RI Positive effects: 9 Companies focused more on clients – communication and quality of services Focus on increasing the efficiency of the internal processes Focus on core-business, divesting or decreasing the non core-business More demand for the protection products and guarantee products New approach on supervision Indirect effects - Short term Changing the solvency position of certain insurance companies Biggest impact on D&O liability insurance and credit and 10 guarantee insurance Decrease of the asset value – stock, real estate, “mark to market” valuation etc Exposure to “toxic assets” Reducing the interest rate - pressure on the liabilities Insurance premium volume Profitability of the companies Solvency margin, extra capital needed mainly for the companies offering guaranteed products Weaker insurance B/S from equity and corporate bonds losses Assets-liabilities management Increased risk management costs Industry losses USD 261 bill vs. USD1230 bill losses in banking sector (Bloomberg 2010); total capital raised at industry level – about 160 billion USD Write downs, credit losses and capital raised (including guarantees) of the major insurance companies during 2007 - January 2010 (billion USD) Insurance company 11 Losses Capital raised Shortfall 1 American Insurance Group (AIG) 98,2 98,1 -0,1 2 ING Groep NV 18,6 24,1 5,5 3 Ambac Financial Group Inc 12,0 1,4 -10,6 4 Aegon NV 10,7 4,0 -6,7 5 Hartford Financial SVCS GRP 9,7 6,4 -3,3 6 Fortis 9,3 22,7 13,4 7 Swiss Re 8,5 2,9 -5,6 8 Metlife Inc 7,2 4,0 -3,2 9 Allianz SE 7,0 2,0 -5,0 10 Allstate Corp 6,6 0,0 -6,6 11 Prudential Financial Inc 6,6 5,9 -0,7 12 MBIA Inc 5,7 1,0 -4,7 13 Aflac Inc 5,2 0,0 -5,2 14 Genworth Financial Inc-CL A 4,8 0,6 -4,2 15 XL Capital 4,0 2,6 -1,4 16 CNA Financial Group 3,1 1,2 -1,9 17 Zurich Financial 3,1 0,0 -3,1 18 Altele 40,7 14,8 -25,9 - Total US companies 188,9 127,4 -61,5 - Total European companies 69,0 59,9 -9,1 TOTAL 261,0 191,7 -69,9 Source: Bloomberg; OECD, The Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Sector and Policy Responses, April 2010, pg. 8. Medium and Long term effects Life Insurance 12 Decrease of the appetite for UL Lower interest rates and higher hedging costs on volatile markets Solvency capital increase Decrease of the profitability Consumer capacity affected differently (more in emerging markets) “De-risking” / “re-risking” General Insurance Premium increase for certain lines (D&O, credit & guarantees, professional liability) due to claims ratio Change of the UW policy Exclusions Change of the RI prices Key learning points for insurers Time to go for new strategies for insurers Protect the company financial position Protect the existing portfolio Intensify the client communication Maintaining the operational control mechanisms to prevent financial crime and fraud that can increase during the crisis time Setting up adequate reserves for the longevity risk Adequate measurements of integrated risk management – Solvency II Corporate governance Leading the business for the future! 13 Key learning points for the regulators 14 Discouraging taking short term risks by the management of the companies Reviewing the role of the rating agencies – regulation? Relate the remuneration system for the co management with the risk, short term and mainly medium and long term objectives Discourage risk taking with no consequences Better regulation for the financial guarantee insurance Accounting convergence, IFRS Solvency II – consistent risk based capital adequacy across Europe Macro prudential monitoring and improved supervision Supervision / Group supervision – based on risk exposure Greater policyholder security Transparency of the financial products Free competition and market Change of behavior in the market THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION! 15