Heat Transfer, Greenhouse Effect, Ozone Layer Notes

Heat Transfer, Greenhouse Effect,
Ozone Layer Notes
How does the Earth get heated?
• Energy transfer from the sun
Energy
• The ability to do work or cause change
• Temperature
– The average amount of energy of motion of each molecule (the measure of how hot or cold something is)
• Gas
– Moving particles, the hotter they get the faster they move
The atmosphere moves energy
• Energy moves by heat transfer
• There are 3 types of heat transfer
– Conduction
– Convection
– Radiation
Conduction
• The transfer of heat energy from one substance to another through DIRECT contact
• The Earth ’ s surface heats the air (gas) molecules directing above it
• Molecules of air gain energy when they collide with the molecules in grains of hot sand.
Convection
• Transfer of energy from place to place by the motion of gas or liquid (fluids)
• Up and down movement of molecules not the side to side movement
Density and Convection
• The atmosphere gets less dense at higher altitudes
• Warm air is less dense than cold air
– Warm air has more energy, so molecules move faster than cold ones
– This makes them collide more, then they spread out
– More space between molecules = less dense
Radiation
• The transfer of the Sun ’ s energy to the Earth ’ s surface
• Solar radiation heats both the surface and the air
– Includes visible light
• Earth ’ s surface gives off a type of invisible radiation called Infrared radiation
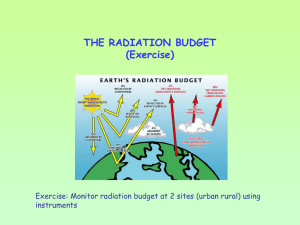
Earth’s absorption of Radiation
• 30% of incoming solar energy is reflected by clouds
• 70% is absorbed and becomes different forms of energy
– Absorbed by oceans, landforms, and living things
(photosynthesis and respiration)
• This absorbed energy heats the Earth’s surface
Transfer of Energy
Gases Absorb and Give Off Radiation
The Atmosphere affects light in 4 ways.
1. Absorbs Light
2. Reflects Light
3. Lets Light Pass Through
4. Emits (Gives Off) Light
On sunny days more visible light gets to the earths surface.
On cloudy days clouds reflect and absorb most of the sunlight
Forms of Radiation We Cant See
• Ultraviolet Radiation
– More energy than the light you can see
– Can cause sunburns and other damage
• Infrared Radiation
– Less energy than the light you can see
– Warms the materials that absorb it
Ozone Layer Protects Life
• Ozone - O
3
– Ozone in stratosphere is called the ozone layer
– Protects life on Earth
– Absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from sun
• Too much can cause sunburn, skin cancer, and can harm crops, plastic or paint
– Lets other types of radiation like visible light through
Greenhouse Effect
• Keeps Earth Warm
• Slow the movement of energy away from the Earth’s surface
• Greenhouse gases
– Includes carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and nitrous oxide
– Gases mix with gases in the air like nitrogen and oxygen. Not its own layer
– Found in the troposphere
– Absorbs and emits infrared radiation
Animation