Congestive Heart Failure Dr Jancko
advertisement

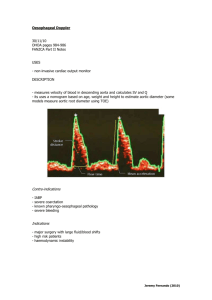
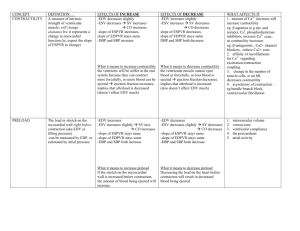
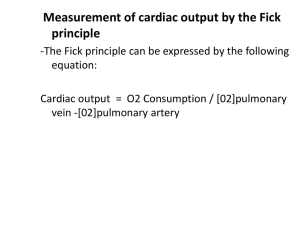
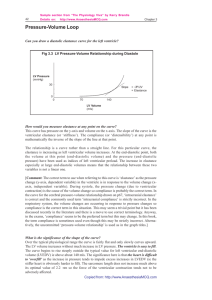
OVERVIEW OF TREATMENT OF CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE OVERVIEW Background and Historical Perspective Determinants of Cardiac Output and Hemodynamic Intervention Newer Therapeutics EVOLUTION IN CONCEPTS Cardio-renal (pre 1970) : Digoxin, diuretics Hemodynamic 1970’s and 1980’s: + Inotropics, VD Neurohormonal 1990’s: RAS, SNS DETERMINANTS OF CARDIAC PERFORMANCE HEART RATE CONTRACTILITY PRELOAD VASODILATOR THERAPY AFTERLOAD RATE PRELOAD LV CONTRACTILITY AFTERLOAD CO = SV x HR EF = CO HEART RATE COMPENSATORY RESPONSE ATROPHINE ISUPREL PACER CONTRACTILITY Inherent property of the myocardium Allows the heart to increase its extent and force of shortening independent of the Starling mechanism Not directly measurable CONTRACTILITY DIGITALIS DOBUTAMINE DOPAMINE ISUPREL EPINEPHRINE CALCIUM GLUCAGON AMIRANOME (Miliron) STARLING’S LAW THE MORE A MYOCARDIAL FIBER IS STRETCHED DURING DIASTOLE, THE MORE IT WILL SHORTEN IN SYSTOLE IT WILL ALSO SHORTEN WITH GREATER FORCE PRELOAD The length to which a cell is stretched prior. To the next contraction The volume or pressure generated in the ventricles at end-diastole Degree to which a cell is stretched in diastole (preload) force during systole AFTERLOAD IMPEDANCE OF BLOOD FROM THE VENTRICLE Determined by: The volume and mass of blood ejected from the ventricle The compliance and total cross-sectional area of the vascular space into which the blood is ejected. AFTERLOAD – RESISTANCE PROXIMAL IMPEDENCE SYSTEMIC VASCULAR RESISTANCE SVR= (MAP-RAP) (80) CO MAP= MEAN ARTERIAL PRESSURE RAP= RIGHT ATRIAL PRESSURE CO= CARDIAC OUTPUT BASIC HEMODYNAMIC PARARMETERS Preload = Afterload = PCWP SVR LVEDP = LA = PVP = PCWP = PAP 1 3 2 4 1 2 3 4 VASODILATOR DRUGS AGENT ARTERIAL VENOUS (Afterload) (Preload) Nitropusside +++ +++ Nitrates ++ +++ Hydralazine ++++ + Prazosin ++ ++ Nesiritide (Natrecor) ++ +++ Clinical Profile of Nesiritide Vasodilation (venous > arterial) Rapidly improves symptoms of congestion Does not increase heart rate (decreases myocardial oxygen demand) Is not proarrhythimic Neurohormonal suppression (decreases aldosterone, endothelin-1) Mild diuresis/natriuresis Clinical Profile Nesiritide (cont.) No evidence of tachyphylaxis Symptomatic hyptension as low as 4% in the VMAC study Dosing convenience (bolus plus standarddose IV infusion PATIENT PRESENTATION P.E. CXR EKF BP OUTPUT R.A. P.A. PCW BNP SOB CHF ST 110/70 20cc/hr 15 45/30 30 ++ SOB CHF ST 210/120 40cc/hr 15 45/30 30 ++ SOB CHF ST 80/50 20cc/hr 15 45/30 30 ++ SOB CLEAR ST 80/50 20cc/hr 15 45/30 6 + LETHARGIC CLEAR ST 80/50 0 2 25/4 3 N SOB HAZY ST 110/70 20cc/hr 15 45/20 12 + UNCONCIOUS CHF VT 60/40 0 15 45/30 30 + ALERT CLEAR MSR 240/140 20cc/hr 8 30/18 18 + ALERT CLEAR MSR 80/50 20cc/hr 20 50/20 12 ++ LETHARGIC CLEAR ST 80/50 20cc/hr 8 30/8 8 N EVOLUTION IN CONCEPTS Cardio-renal (pre 1970): Digoxin, diuretics Hemodynamic 1970’s and 1980’s: + Inotropics, VD Neurohormonal 1990’s: RAS, SNS CLINICAL APPROACH Control Volume (Rx Symptoms) Hemodynamic Stability Slow Progression Diuretic Inotropic Vasodilators Neurohormonal NEUROHORMONAL FACTORS IN HEART FAILURE PROGRESSION Circulating (RAS, SNS) Abnormality in regional blood flow, renal sodium retention Endothelin (ET-1, ET-2, ET-3) Vasoconstrictors Natriuretic Peptide, (ANP) Vasodilators, suppresses RAS Cytokines (TNF , Interleukin) Depresses contractility, anorexia and cachexia Neurohormonal Intervention in Heart Failure Heart Failure Reninangiotensin system ACE inhibition Sympathetic nervous system Beta Blockade ACE INHIBITORs (ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYMES INHIBITORS) GENERIC BRAND NAME BENAZEPRIL LOTENSIN CAPTOPRIL CAPOTEN ENALAPRIL VASOTEC FOSINOPRIL MONOPRIL LISINOPRIL ZESTRIL, PRINIVIL MOESIPRIL UNIVASC PERINDOPRIL ACEON QUINAPRIL ACCUPRIL RAMIPRIL ALTACE TRANDOLAPRIL MAVIK ARBs (ANGIOTENSION RECEPTOR BLOCKERS) GENERIC BRAND NAME CADESARTAN ATACAND EPROSARTAN TEVETEN IRBESARTAN AVAPRO LOSARTAN COZAAR OLMESARTAN BENICAR TELMISARTAN MICARDIS VALSARTAN DIOVAN BETA BLOCKERs GENERIC BRAND NAME ACEBUTOLOL SECTRAL ATENOLOL TENORMIN BETAXOLOL KERLONE BISPROLOL ZEBETA CARTEOLOL CARTROL ESMOLOL BREVIBLOC METOPROLOL LOPRESSOR, TOPROL NADOLOL CARGARD PENUTOLOL LEVATOL PINDOLOL VISKEN PROPRANOLOL INDERAL SOTALOL BETAPACE TIMOLOL BLOCADREN ALPHA AND BETA BLOCKERs GENERI9C BRAND CARVEDILOL COREG LABETALOL NORMADINE, TRANDATE Changes LVEF (EF units) Effect of Carvedilol on Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Placebo 6.25mg bid 12.5mg bid 25mg bid Carvedilol Patients receiving diuretics, ACE inhibitors, digoxin; follow-up 6 months; placebo (n=84), carvedilol (n=261). Mulitcenter Oral Carvedilol Heart Failure Assessment Adapted from Bristow et al. Circulation. 1996;94:2807-2816. P<.05 vs placebo. DRY WET WARM COLD CLINICAL ASSESSMENT Warm vs. Cold (Perfusion)- Pulse Pressure Dry vs. Wet (Congestion)- Jugular Venus Pressure Rapid Assessment of Hemodynamic Status Congestion at Rest NO Low Perfusion At Rest NO YES A Warm & Dry (Low Profile) L Cold & Dry YES B Warm & Wet (Complex) C Cold & Wet Possible Evidence of Low Perfusion: Narrow pulse pressure Sleepy/obtunded Low Serum sodium Cool extremities Hypotension with ACE inhibitor Renal Dysfunction (one cause) Signs/symptoms of Congestion: Orthopnea/ PND JV Distension Hepatomegaly Edema Rates (rare in chronic heart failure) Elevated est. PA systolic Valsalva square wave Profiles and Therapies of Advanced Heart Failure Congestion at Rest NO NO Low Perfusion YES At Rest Inotropic Drugs Dobuamine Milrinone Calcium Sensitizers YES Warm & Dry PCW and CI Normal Warm & Wet PCW elevated CI normal Cold and Dry PCW low/normal CI decreased Cold & Wet PCW elevated CI decreased NI SVR High SVR Vasodilators Nitroprusside Nitroglycerine Nesiritied WARM UP THEN DRY OUT DRY WARM WET 1. 2. COLD 1. 2. Vasodilators Positive Inotropics 1. 2. 3. Diuretics Vasodilators Positive Inotropics Vasodilators Diuretics NEWER THERAPEUTICS I. Biventricular Pacing I. EECP I. Measurement of BNP levels