Chapter Five Slideshow
advertisement

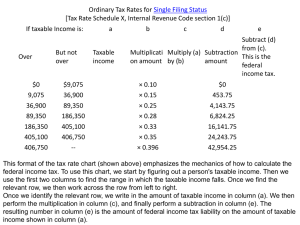
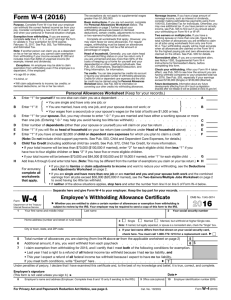
KEEPING YOUR JOB Chapter 5 Notes Money Management Understanding and Preparing Work Forms When you begin your first paying job, you will need to be aware of a number of forms. Most of these forms ask for information that employers are required by law to keep. Some are completed before you can start work (Social Security Card and work permit, if you are under 16), while others are completed when you begin working (W-4) and by the employer after you have worked during the year (W-2). You should be familiar with these forms! FORM W-4 When you report to work you will be asked to fill out a FORM W-4, Employee’s Withholding Allowance Certificate. The information you put on this form will determine the amount of money your employer will deduct from your check for income taxes. On this form you declare your total number of allowances – persons claimed that reduce the amount of tax withheld from your paycheck. The more allowances you claim, the less tax you will have withheld. You may automatically claim yourself; other allowances can be made for spouse and children. HOW MANY ALLOWANCES DO I CLAIM Most students either claim EXEMPT or 0 under allowances. Some choose to claim 1 if they are paying their own way. Exempt Status – means that you DO NOT have to have ANY federal income tax withheld from your check. Who can claim exempt? You cannot claim exemption from federal withholding taxes for 2007: If you are exempt from federal withholding taxes, you must certify on the W-4 form that you meet both of the following conditions: If your income exceeds $900 and includes more than $300 of unearned income (interest and dividends), and another person can claim you as a dependent on their return. Last year you had a right to a refund of ALL federal income withholding because you had no liability, and this year you expect a refund of ALL federal income withheld because you expect to have no tax liability Exemptions expire each year so new W-4’s have to be filed. Social Security Because all workers in the U.S. must pay a social security tax from wages earned, all have a social security number. Your social security number is your permanent work identification number. While you are working, your employers withhold social security taxes from your pay and contribute matching amounts. When you become eligible, benefits are paid to you. Children born in the U.S. must have number before they are one if their parents would like to claim them as a dependent on their tax return. If your card is lost or damaged, you can order a replacement card. The Social Security Administration sends statements out each year updating you on your total contributions into the system. Your Social Security Statement is a concise, easy-to-read personal record of the earnings on which you have paid Social Security taxes during your working years and a summary of the estimated benefits you and your family may receive as a result of those earnings. Click on this link for a calculator that will help you estimate your retirement benefit! http://www.ssa.gov/OACT/quickcalc/ How does Social Security Work? Social Security Defined – A social insurance program that covers most of the Nation's work force. It is often the basic retirement plan to which other benefits are added. It provides retirement, disability, survivor, and Medicare benefits. The money you pay into the system gets immediately paid back out to the people who are currently getting Social Security checks In 1935, when Social Security started, there were many more people paying into the system than those receiving benefits. The ratio of workers to retirees meant that workers did not have to pay much into the system in 1935 to support the retirees In the future, the retirement of millions of baby boomers will hurt the ratio -there will be so many retired people that the working people will not be able to support them. Social Security is a BIG part of a lot of people’s retirement plans so how much trouble is the program really in? Will it be there for you when you retire? That is up for a ton of debate. Pay attention and you’ll see news stories on it each and every week! Social Security in the news! For example, let’s check out the type of news clips you can expect to see in the news… http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/6840592/ http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/7725312/ Example of Political Debate about Social Security: http://youtu.be/g-HlSXQoyl8 ASSIGNMENT: Go online and find a current article from a reputable news source (For example: Newsweek, CNN, MSNBC) that does at least one of the following: Explains the basics about social security Talks about Social Security reform Discusses whether or not Social Security is really in trouble Discusses the current political debate about social security Print the article, read it underlining or highlighting the key points. Open up Microsoft Word. Also, open up the “Social Security Article Review” Assignment in the Chapter 5 folder. Write a two to three paragraph response summarizing the article and giving me your opinions on the topic discussed. FORM W-2 Form W-2 lists income you earned during the year and all the amounts withheld by the employer on your behalf. These amounts include federal, state, and local income taxes, & the social security tax. An example W-2 Form can be seen at the following links: http://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/fw2.pdf http://www.classroomtools.com/tax_w2.htm Your employer MUST provide you with a copy of your W-2 no later than January 31st of the year following the one in which you were employed – even if you only worked part of the year! If they don’t send you one... Contact them! Once employees receive their W-2’s, they can compare how much they paid in federal income tax to how much they were supposed to pay in federal income tax. It is then easy to determine if the employee owes more or if they have a refund due to them! Employees have until April 15th each year to file their tax returns to either pay up or request their refund! Tax Fraud Before you file your return, you have to make sure you declare ALL OF YOUR INCOME! One of the most common forms of tax fraud is the underreporting of tips! Tax Fraud – Fraud is a deception deliberately practiced in order to secure unfair or unlawful gain. As it relates to taxes, it's simply "cheating" by intentionally paying less tax than is legally due. Here are some examples: Deliberately underreporting or omitting income, Overstating the amount of deductions Keeping two sets of books Making false entries in books and records Claiming personal expenses as business expenses Claiming false deductions Employee Responsibilities to Employers Competent Work Thrift Punctuality Pleasant Attitude Loyalty and Respect Dependability Initiative Interest Self-Evaluation Responsibilities to Other Employees and Customers Other Employees Teamwork Thoughtfulness Loyalty To Customers Helpfulness Courtesy Employer’s Responsibilities Adequate Supervision Fair Personnel Policies Safe Working Conditions Open Channels of Communication Recognition of achievement Compliance with employment laws EMPLOYMENT LAWS In the last fifty years, many laws have been passed to provide protections to American workers. Department of Labor is in charge of the biggies: Minimum Wage, regular working hours, equal opportunities, no discrimination, safe working conditions etc.... Some laws you should be aware of: Social Security Act (Federal Insurance Contributions Act of 1935) Enacted as a social insurance program to provide aide to the elderly and disabled. Medicare was added to this act in 1965. It provided hospital and medical insurance protections for elderly retired persons and other qualified persons. EMPLOYMENT LAWS Unemployment Compensation – important part of the Social Security Act provides that every state must have an unemployment insurance program that provides benefits to workers who lose their job through no fault of their own. After a waiting period, laid-off workers may collect a portion of their regular pay for a certain length of time. Fair Labor Standards Act – popularly known as the Wage and Hour act... Set the minimum wage (initially at 25 cents/hour ). A minimum wage is the legally established lower limit on wage employers must pay. The federal minimum wage currently at $7.25. Another provision of the act states that hourly workers cannot be employed for more than 40 hours in a week without paying them overtime. Employers must pay the employees 1 ½ times their regular rate for any such hours. Minimum wage law has some exceptions... Jobs with tips is an example. US Department of Labor Overtime Laws: http://www.dol.gov/dol/topic/wages/overtimepay.htm Worker’s Compensation – the name for laws that give financial security to workers and their families for injury, illness, loss of income, or death that occurs as a result of the job or working conditions. “Liability without fault” – employers are liable even if it wasn’t their fault.