Chapter 07 - UCO College of Business
advertisement
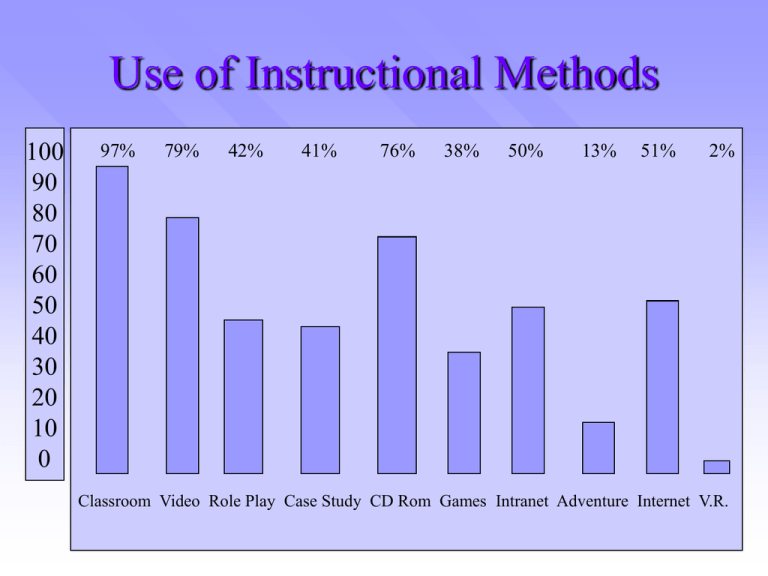
Use of Instructional Methods 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 97% 79% 42% 41% 76% 38% 50% 13% 51% 2% Classroom Video Role Play Case Study CD Rom Games Intranet Adventure Internet V.R. Training Methods Three categories of training methods: 1. Presentation methods 2. Hands-on methods 3. Group building methods Presentation Methods Presentation methods include lectures and audiovisual techniques Variations of the Lecture Method Method Description Standard lecture Trainer talks while trainees listen and absorb information. Two or more trainers present different topics or alternative views of the same topic. Speaker visits the session for a certain time period. Primary instruction is conducted by guest speaker. Two or more speakers present info. & ask questions. Groups of trainees present topics to the class. Team teaching Guest speakers Panels Student presentations Audiovisual Techniques Audiovisual Techniques includes overheads, slides, and video – Example: » Ethics » Training » Video Hands-On Method Hands-on methods refer to training methods that require the trainee to be actively involved in learning. These methods include: 1. On-the-job training 2. Simulations 3. Case studies 4. Business games 5. Role plays 6. Behavior modeling On-the-Job Training Companies spend between $90 and $180 billion annually on informal on-the-job training. OJT refers to new or inexperienced employees learning through observing peers or managers performing the job and trying to imitate their behavior. OJT can be useful for: – – – – Newly hired employees Upgrading experienced employees’ skills Cross-training Orienting transferred employees Principles of On-the-Job Training Preparing for Instruction 1. 2. 3. Break down the job into important steps Prepare materials Decide how much time you will devote to OJT Actual Instruction 1. 2. 3. Tell the trainee the objective of the task Show the trainee how to do it Explain key points or behaviors 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Show the trainee how to do it again Have the trainee do one or more single parts of the task and praise him for correct reproduction Have the trainee do the entire task and praise him for correct reproduction If mistakes are made, have the trainee practice Praise the trainee for his success in learning the task Self-Directed Learning Self-directed learning involves having employees take responsibility for all aspects of learning – when it is conducted and who will be involved. For example, at Corning Glass, new engineering graduates participate in an OJT program called SMART (self-managed, awareness, responsibility, and technical competence) Advantages and Disadvantages of Self-Directed Learning Advantages – Trainees learn at their own pace – Fewer trainers – Reduces costs associated with travel & meeting rooms Disadvantages – Trainees must be willing and comfortable learning on their own – From the company perspective, results in higher development costs – Development time is longer Self-Directed Learning Steps necessary to develop effective selfdirected learning: 1. Conducting a job analysis 2. Writing trainee-centered learning objectives directly related to the tasks 3. Developing the content for the learning package 4. Breaking the content into smaller pieces (“chunks”) 5. Developing an evaluation package Apprenticeship Apprenticeship is a work-study training method with both on-the-job and classroom training. To qualify as a registered apprenticeship program under state or federal guidelines, at least 144 hours of classroom instruction and 2,000 hours or one year, of on-the-job experience are required. Simulations Simulation is a training method that represents a real-life situation, with trainees’ decisions resulting in outcomes that mirror what would happen if they were on the job. Examples: – Flight simulation – AA Flight 965 crash Case Studies Case study is a description about how employees or an organization dealt with a difficult situation. Trainees are required to analyze and critique the actions taken, indicating the appropriate actions and suggesting what might have been done differently. Example: – Case study in T & D class for TNA at org. level Process for Case Development 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify a story. Gather information. Prepare a story outline. Decide on administrative issues. Prepare case materials. Business Games Business games require trainees to gather information, analyze it, and make decisions. Business games are primarily used for management skill development. Games stimulate learning because participants are actively involved and they mimic the competitive nature of business. Example: – HR games Role Plays Role Plays involve having trainees act out characters assigned to them. Information regarding the situation (e.g., work or interpersonal problem) is provided to the trainees. Example: – MBTI Role Play Behavior Modeling Behavior modeling involves presenting trainees with a model who demonstrates key behaviors to replicate and provides trainees with the opportunity to practice the key behaviors. Examples – Wait person – Training video Observing behaviors behaviors Vicarious reinforcement Activities in a Behavior Modeling Training Program Introduction (45 min) – Present key behaviors using video. – Give rationale for skill module. – Trainees discuss experiences in using skill. Skill Preparation and Development (2 hr. & 35 min.) – View model. – Participate in role plays and practice. – Receive oral and video feedback on performance of key behaviors. Application Planning – Set improvement goals. – Identify situations to use key behaviors. – Identify OTJ applications of the key behaviors. (1 hr.) Examples of Key Behaviors in Problem Analysis Get all relevant information by – Rephrasing the question or problem – Listing the key problem issues – Considering other possible sources of info Identify possible causes If necessary, obtain additional info Evaluate the info. To ensure that all essential criteria are met Restate the problem considering new info Determine what criteria indicate that the problem or issue is resolved Group Building Methods Group building methods refer to training methods designed to improve team or group effectiveness. Training is directed at improving the trainees’ skills as well as team effectiveness. Group building methods involve trainees sharing ideas and experiences, building group identity, understanding the dynamics of interpersonal relationships, and getting to know their own strengths and weaknesses and those of their coworkers. Examples: – Class’s Monday morning pre-exercises Adventure Learning Adventure learning focuses on the development of teamwork and leadership skills using structured outdoor activities. Adventure learning is also known as wilderness training and outdoor training. Examples: – OU ropes courses Team Training Team training involves coordinating the performance of individuals who work together to achieve a common goal. Three components of team performance are: – Knowledge – Attitudes – Behavior Components of Team Performance Team Performance Behavior Knowledge Attitude Main Elements of the Structure of Team Training Methods: Information-Based Demonstration-Based Video Practice-Based Guided Practice Role Play Tools: Team Task Analysis Performance Measurement Task Simulation & Exercise Feedback Principles Strategies: Cross-Training Coordination Training Team Leader Training Team Training Objectives Content Knowledge Skills Attitudes Action Learning Action Learning involves giving teams or work groups an actual problem, having them work on solving it an committing to an action plan, and then holding them accountable for carrying out the plan.





















