manpro 6 - WordPress.com
advertisement

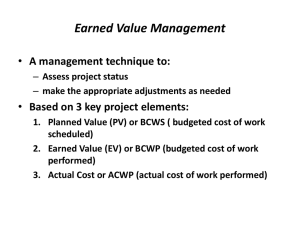
Materi Kuliah Manajemen Proyek INSTITUT MANAJEMEN TELKOM 1 PROJECT CONTROL 2 PROJECT CONTROL The process of keeping the project on target and as close to plan as feasibly posible is the subject control : 1.Planning concentrats on setting goals and direction, control guides the work toward those goals. 2.Planning allocate resources,control ensures effective on going utilization of those resources, 3.Planning antisipates the problems,control corrects the problems. 4.Planning motivates participants to achieve goals,control rewards achievement of goals. THE CONTROL PROCESS The process is achieved in three phases, setting performance standards, comparing this standards with actual performance, then taking necessary correction action. INFORMATION MONITORING 1.Data collecting 2.Information reporting 3 EVALUASI PROYEK Dalam kegiatan proyek ,Proyek Manajer harus melakukan : 1. Pengecekan kegiatan 2. Melakukan evaluasi 3. Melakukan koreksi sehingga pencapaian proyek (jadwal, biaya, prestasi fisik) dapat dijaga sesuai target. METODA EVALUASI PROYEK 1.Formative Evaluation Dilakukan selama perjalanan proyek 2.Summary Evaluation Dilakukan setelah proyek selesai INFORMASI UTAMA DALAM EVALUASI PROYEK 1.Graphics (Chart & Tabel) 2.Laporan (Lisan & Tulisan) 3.Observasi 4.Review Meeting 4 Controlling Cash 1. Control during the life of projecek : plan, publish, measure, compare, report, forecast, and correct. 2. Budget preparation : data collection, WBS, cost centre codes, 3. System budget : budget , commited cost, actual cost. Budgeted cost – Committed cost = Variance Negative Variance means that : 1. Poor control 2. Extra unbudgetted works was included 3. Some activity cost were underestimated 5 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS 1. Analisis Biaya dan Jadwal menggunakan Nilai Hasil a. Budgeted Cost of the work scheduled (BCWS) yaitu Jumlah anggaran yang disediakan untuk menyelesaikan kegiatan yang telah ditargetkan b. Actual Cost of the work Performed (ACWP) yaitu Jumlah biaya aktual dari pekerjaan yang telah dilaksanakan c. Budgeted Cost of the work Performed (BCWP) yaitu : Jumlah dana yang telah dikeluarkan untuk menyelesaikan kegiatan yang telah ditargetkan Variance Analysis AV = BCWS – ACWP (Accounting Variance) CV = BCWP – ACWP (Cost Variance) SV = BCWP – BCWS (Schedule Variance) TV = SD – BCSP (Time Variance) SD = Status date (ex. : week 20) BCSP = The date where BCWS = BCWP 6 Variance Variance menunjukkan besarnya penyimpangan yang terjadi pada suatu titik waktu/saat pelaporan. Variansi Biaya (Cost Variance) = BCWP – ACWP Variansi Jadwal (Shedule Variance) = BCWP – BCWS Varians Jadwal Varians Biaya Keterangan Positif Positif Pekerjaan lebih cepat dari jadwal & biaya < anggaran Nol Positif Pekerjaan tepat jadwal & biaya < anggaran Positif Nol Pekerjaan lebih cepat dari jadwal & biaya = anggaran Nol Nol Pekerjaan tepat jadwal & biaya = anggaran Negatif Negatif Pekerjaan lebih lambat dari jadwal & biaya > anggaran Nol Negatif Pekerjaan tepat jadwal & biaya > anggaran Negatif Nol Pekerjaan lebih lambat dari jadwal & biaya = anggaran Positif Negatif Pekerjaan lebih cepat dari jadwal & biaya > anggaran 7 Planned completion NOW Forecast Cost Over run BAC BCWS ACWP Cost variance BCWP Schedule Variance (cost) Forecast Project Time slip Schedule variance (time) 8 Realisasi 100 AKHIR AWAL 800 75 600 50 400 25 200 0 0 0 4 8 12 16 20 Kurva ‘ S ” 24 28 32 Varian Anggaran J F M A M J J A S O N D Varian 9 Variansi Biaya (Cost Variance) = BCWP – ACWP Variansi Jadwal (Shedule Variance) = BCWP – BCWS ACWP = Actual Cost of Work Performed BCWP = Budgeted Cost of Work Performed BCWS = Budgeted cost of Work Schedule Uraian Jan Feb Mar Apr Mei Jun Jul Agt BCWS 60 140 280 480 660 870 1020 1080 Pengeluaran ACWP 50 210 410 640 840 750 890 950 Nilai Hasil 40 100 210 380 530 660 900 880 Varinsi Biaya -10 -110 -200 -260 -310 -90 10 -70 Variansi Jadwal -20 -40 -70 -100 -130 -210 -120 -200 Anggaran BCWP 10 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS (Continued) 2.Technical Analysis Nilai aktual parameter teknis (yg didapat dari estimasi, pengukuran analitis, dan tes empiris) harus dibandingkan dengan parameter teknis yang diinginkan, untuk mengevaluasi dan mengukur perbedaan antara pencapaian dan keinginan (sasaran). 3.Performance Index Kinerja suatu proyek dapat diukur menggunakan Indeks Kinerja (performance index) : Indeks Kinerja Jadwal (Schedule Performance Index) SPI = BCWP/ACWP SPI < 1 berarti Waktu Pelaksanaan > Jadwal Indeks Kinerja Biaya (Cost Performance Index) CPI = BCWP/ACWP CPI < 1 berarti Pengeluaran > Anggaran. 11 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS (Lanjutan) Untuk mengetahui sampai sejauh mana pelaksanaan proyek telah dilaksanakan,dilakukan dengan menghitung CRITICAL RATIO (CR) Actual Progress Budgeted Cost CR = ---------------------x ------------------Scheduled Progress Actual Cost JIKA : CR = 1 Proyek kemungkinan selesai sesuai target CR ≠ 1 Proyek memerlukan penanganan untuk memonitor dan mengendalikan proyek Forecasting “To Complete” and “At Completion” FCTC (Forecasted Cost To Complete Project) BCAC - BCWP = ------------------BCAC = budgeted cost at completion CPI for the project FCAC (Forecasted Cost at Completion) = ACWP + FCTC 12 Status Date (SD) Forecasted ACWP FCAC BCAC FCTC BCWS ACWP Forecasted BCWP BCWP Initial target date 19 20 The Project Completion = 20 + (47-19)/SPI 47 Revised Completion date 50 13 SOAL LATIHAN 14 KEGIATAN KEGIATAN YANG MENDAHULUI DURASI (MINGGU) BIAYA LANGSUNG PER MINGGU ($K) PENYELE SAIAN KEGIATAN DLM (%) BIAYA YANG TELAH DIBELANJAKAN ($K) A - 10 10 100 100 B A 8 8 100 72 C A 6 18 100 96 D C 4 4 100 20 E C 2 18 100 40 F C 4 21 100 70 G B 4 20 50 50 H B 5 10 50 100 I B,C 5 12 10 12 J E 5 16 0 0 K F 4 0 0 0 L G 3 0 0 0 M J 3 0 0 0 N H,L 3 14 0 0 O D,K 3 16 50 60 P N 5 12 0 0 Q O 2 12 0 0 R I,P,Q 8 13 0 0 S M,R 6 11 0 0 620 15 Pertanyaan : 1. Buatkan rencana biaya dan jadwal proyek menggunakan gambar Network dan Bar Chartnya. dengan 2. Setelah proyek berjalan 30 minggu, apa komentar saudara yang meliputi (AV, SV dan CV) serta berapa FCAC (Forecasted Cost At Completion). 16 Materi kuliah 03052010 Manajemen Proyek INSTITUT MANAJEMEN TELKOM 17 Basic Project Control Steps • Define the project scope • Develop a project plan consistent with: – project scope – estimates (cost constraints) – schedule (constraints – resources available • Report progress and compare with budget and forecast • Control by taking corrective action 18 Five Phases of Project Management 19 Risk Management: • • • • Risk Identification Risk Quantification Risk Response Development Risk Response Control 20 Contingency - Plan for Change 21 Project Close-out 22 Project Closeout - Major Phases • • • • Obtain client acceptance Document the project Conduct the post implementation audit Issue the final report 23 Successful Project Management Plan the Work… Work the Plan 24 Successful Project Completion 25 Project Planning, Scheduling & Controlling 26 Materi kuliah 10052010 Manajemen Proyek INSTITUT MANAJEMEN TELKOM 27 FOUNDATION IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT • Start the project with a strong foundation. The templates and checklist (clear goals, effective communication, and management support) • The project proposal , • Project sponsor can use the charter template to formally authorize • the project and project manager. • The statement of work represents the formal agreement between • project stakeholders about the goals and constraints of the project. • The responsibility matrix clarifies the role and authority of each • project stakeholder. • Effective communication ,Use the communication planning matrix to identify who needs what information and how you’ll be sure to get it to them • As you initiate the project, use the definition checklist to guide the team 28 Project Proposal (Project name, Sponsor, Project Manager, Prepared by,Revision History) • • • • • • • • • • • • Project Goal ,Problem/Opportunity Definition ,Proposed Solution Project Selection and Ranking Criteria Project benefit category: ❑ Compliance/regulatory ❑ Efficiency/cost reduction ❑ Revenue increase Portfolio fit and interdependencies Project urgency Cost-Benefit Analysis Tangible Benefits (Benefit ,Value and probability,Assumptions driving value) Intangible Benefits (Benefit,Value and probability,Assumptions driving value) Cost Categories (Internal labor hours ,External costs,Equipment, hardware, or software,List other costs such as travel and training) Financial Return Business Requirements(Scope,Major project activities,Out of scope activities that are critical to the success of the project Major Obstacles ,Risks ,Schedule Overview Estimated Project Completion Date ,Major Milestones ,External Milestones Affecting the Project,Impact of Late Delivery 29 Project Management Context: • • • • • Project Phases and Life Cycle Stakeholders Leadership Skills General Management Skills Communications Skills 30 Project Phases and Life Cycle: • • • • Divide Project into Phases Better Management Control Review Deliverables and Performance Fast-tracking 31 Example of Project Phases: • • • • • Conceptual Design Detailed Design Coding and Testing Training and Documentation Deployment 32 Stakeholders: • Individuals and Organizations • Actively Involved in Project • Interests Affected by Project 33 Leadership Skills: • • • • • • • • Vision and Strategy Establishing Direction Aligning People Communicating Negotiating Motivating and Inspiring Influencing Organizations Overcoming Barriers to Change 34 General Management Skills: • • • • • • • • • Planning Finance and Accounting Personnel Administration Technology Organizational Development Delegation Team Building Conflict Management Solving Problems 35 Communications Skills: • • • • • • Writing Listening Speaking Presenting Media Relations Meeting Management 36 Scope Management: • • • • • Initiation Scope Planning Scope Definition Scope Verification Scope Change Control 37 Management activities • • • • • • Proposal writing Project planning and scheduling Project cost Project monitoring and review Personnel selection and evaluation Report writing and presentations 38 Human Resource Management • Organizational Planning • Staff Acquisition • Team Development 39 Communications Management: • • • • Communications Planning Information Distribution Performance Reporting Administrative Closure 40 Key Inputs, Tools & Techniques, and Outputs: • • • • • • • Communications Management Plan Project Records Performance Reports Change Requests Project Archives Formal Acceptance Lessons Learned 41 Key Inputs, Tools & Techniques, and Outputs: • • • • • Risk Management Plan Checklists Contingency Plans Reserves Contractual Terms 42 Risk Management: • • • • Risk Identification Risk Quantification Risk Response Development Risk Response Control 43 Management Processes: • • • • • Initiating Processes Planning Processes Executing Processes Controlling Processes Closing Processes 44