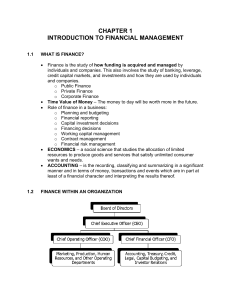
The kinds of Business can be classified under the following headings: 1. Production • refers to the process of using various inputs to create an output that has value and contributes to the utility of individuals Agriculture • is the business sector encompassing farming and farming-related commercial activities. Construction • the backbone of the country • similar to production Mining & Petroleum • mining industry is involved in the extraction of precious minerals and other geological materials. • the majority of the world relies on petroleum for many goods and services; also has major influence on world politics and the global economy Manufacturing • process of converting raw materials or parts into finished goods through the use of tools, human labor, machinery, and chemical processing 2. Transportation -there is of course a demand in transportation -land , rail, air, sea 3. Communication • technology is very much in this countries • service provider needs internet 4. Public Utilities 5. Wholesale and Retail Trade 6. Finance 7. Insurance 8. Real Estate 9. Government 10. Service Misc. Service Industries Classification a. Personal Services • Education • Laundries and carpet • Cleaning • Tax preparation • Health club Shoe repair Beauty shops Child care Travel agencies Photographic studios b. Business services • Data processing • Interior design • Accounting • Collection agencies • Advertising • Commercial photography • Market research • Commercial art • Maintenance • • • • • • c. • • • • • • • • • • • • d. • • • • • • e. • • • • • • • • f. • • • g. • • • • • h. • • • • i. j. • • • k. • Consulting Recreational and amusement services Movies Carnival Bowling alleys Golf course Amusement parks Racetracks Tennis courts Pool halls Musical groups Ice skating rinks Video rentals Botanical gardens Lodging and housing services Hotels Sporting and recreation camps Motels Trailer parks Rooming houses Camp site for transients Automotive repair services and garages Auto rental Exhaust system shops Truck rental Car washes Parking lots Transmission repair Paint shops Tire retreading Educational services Libraries Correspondence schools Data processing school Health services Physicians Nursery care Dental labs Dentist Medical labs Motion picture industry Production Theaters Distribution Drive-ins Legal services Social services Child care Job training Family services Misc. repair services Radio/television Reupholstery Welding Watch and septic tank cleaning Sharpening l. Financial services • Banking • Insurance • Real estate agencies • Investment firms m. Misc. services • Architectural • Surveying • Engineering • Utilities • Telecommunications • • • • 3 Kinds of Business 1. Trade/Commerce • send goods to another country that is manufactured here. • the any movement of goods • retailing, bringing goods to the company 2. Industry • translation of input into output 3. Service • give satisfaction to customer • increase demand in service today, industrial revolution service now become highly specialized Forms of Business Organization • Proprietorship • Partnership • Corporation • Limited life • Often set up through LLCs/LLPs Corporation • Advantages • Unlimited life Advantages • Easy transfer of ownership • Ea • Limited liability • Subject to few regulations • Ease of raising capital • No corporate income taxes • Disadvantages Disadvantages • Double taxation • Difficult to raise capital • Cost of setup and report filing • Unlimited liability Proprietorships and Partnerships se of formation Balancing Shareholder Value and Society Interests • The primary financial goal of management is shareholder wealth maximization, which translates to maximizing stock price. • Value of any asset is present value of cash flow stream to owners. • Most significant decisions are evaluated in terms of their financial consequences. • Stock prices change over time as conditions change and as investors obtain new information about a company’s prospects. • Managers recognize that being socially responsible is not inconsistent with maximizing shareholder value. Stock Prices and Intrinsic Value • In equilibrium, a stock’s price should equal its “true” or intrinsic value. • Intrinsic value is a long-run concept. • To the extent that investor perceptions are incorrect, a stock’s price in the short run may deviate from its intrinsic value. • Ideally, managers should avoid actions that reduce intrinsic value, even if those decisions increase the stock price in the short run. Some Important Business Trends • Corporate scandals have reinforced the importance of business ethics, and have spurred additional regulations and corporate oversight. • Increased globalization of business. • The effects of ever-improving information technology have had a profound effect on all aspects of business finance. • Stockholders now have more control of corporate governance. Conflicts Between Managers and Stockholders • Managers are naturally inclined to act in their own best interests (which are not always the same as the interest of stockholders). • But the following factors affect managerial behavior: • Managerial compensation packages • Direct intervention by shareholders • The threat of firing • The threat of takeover Conflicts Between Stockholders and Bondholders • Stockholders are more likely to prefer riskier projects, because they receive more of the upside if the project succeeds. By contrast, bondholders receive fixed payments and are more interested in limiting risk. • Bondholders are particularly concerned about the use of additional debt. • Bondholders attempt to protect themselves by including covenants in bond agreements that limit the use of additional debt and constrain managers’ actions.