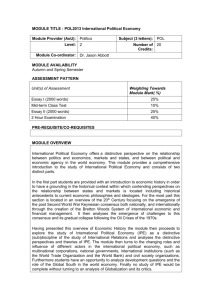
“International Political Economy” Lecture 1 What is International Political Economy? 1 Three features of this course theoretical This course locates IPE as a major subfield of international relations (IR) research Some contents of the course reflects my own research interests and outcomes empirical The hidden topic of this course is the rise of China 2 The position of IPE in IR Security Study International Relations (IR) International Political Economy • Security study is still dominant in Asia • In Europe, IPE is a more important subfield of IR than Security Study 3 The definition of IPE • IPE (International Political Economy): The politics of international economic relations • A subject to examine reciprocal and dynamic interactions between the pursuit of power and the pursuit of wealth • Interactions between the state and market 4 The concept of IPE International Politics State Economics Interaction Pursuit of Power Market Pursuit of Wealth Relations between the state and market In the world with the absence of the market, the state would allocate available resources to attain its political objectives In the world with the absence of the state, relative prices would allocate goods and services In the real world, the state and market exist with significant mutual impacts Interactions between the state and market State provides institutions and rules to sustain and develop the market The position of economic wealth has become crucial for state power state v.s. market Economic activity is defined by domestic/ global politics Market produces economic wealth that is one source of state power 7 The objectives of IPE To examine comprehensively and systematically interactions between politics and economics that hold different logics and mechanisms In details How do the state and its associated political processes affect the production and distribution of wealth? What influence do the functions and evolution of the market have on decision-making and interactions of political actors? The birth of IPE The main international issues in the 1950s and 1960s: Security affairs Significant changes in the 1970s The collapse of the Bretton Woods system in 1971 and the 1st Oil Shock in 1973 Intensive economic and trade frictions between US and Japan and Europe and Japan Growing interests in the North-South Problem (New International Economic Order in 1974) The birth of IPE (cont.) • The politicization of various economic issues • The existing theories and studies centered on security affairs could not explain and analyze international tensions regarding economic affairs • IPE that analyses interactions between international politics and economics emerged and developed as an important subfield of IR 10 The target of IPE Various economic issues among states The evolution of the international economic system and its relations with the states Economic policies and political processes regarding them within the state Cross-border economic relations among transnational actors (MNCs) Global issues (climate change issue) 11 Politics and economics Politics Economics Authoritative allocation of values (including resources) The allocation of resources through market mechanism Politics and economics originally have little relevance as disciplines, and mutually indifferent However, the state and market, the targets of each discipline, are interactive, and their relations are cyclical The logic and role of the state • The state is based on the concepts of territoriality and exclusivity, and its basic principle is sovereignty • The political actors within the state take advantage of economic activities and fruits from them to attain political objectives • The state implements fiscal, labor, and agricultural policies as well as economic regulations 13 The logic and role of the state (cont.) • The state controls the redistribution of incomes among the nation • The expansion and control of national wealth has become a crucial role for the state (the welfare state) • The provision of greater wealth for the people is indispensable for political leaders to get support from them 14 The logic and function of the market • The market is based on the concepts of functional integration and contractual relationships, and its basic principle is efficiency • The economic actors exchange goods and services based on market price • Imperative for the market is the absence of all forms of obstacle to the operation of the price mechanism 15 The logic and function of the market (cont.) The market economy incorporates temporal and geographical dynamism Temporal Producers continuously strive to improve efficiency and technology to win competition in the market Geographical Capitalists who are motivated to hunt for greater profits expand their operations beyond national borders Limitations to market efficiency • The market that relies on efficiency alone often tends to change other crucial values (community, family, human bond, social tradition) into market mechanisms • Market competition produces winners and losers, tending to unequal distribution of wealth within and between the nations 17 The universality of the market and the territoriality of the state • The market principle is universal and diffuses beyond national borders • The current international system does not form one government but comprises of some 200 sovereign states with individual governance systems • The states are protected by territorial boundaries that guarantee national autonomy and political unity 18