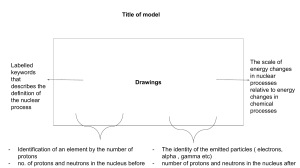
CHAPTER ONE NOTES Matter = anything that takes up space Chemistry = the science of the structure, properties, and transformation of matter Physical change examples: grinding peanuts into peanut butter; making a paper airplane; ice melting; copper bar into wire Chemical change examples: cooking; burning wood SIGNIFICANT NUMBERS: Nonzero #s = significant Zeros at the beginning of a number = NOT significant Zeros between nonzero digits = significant Zeros at the end of a number that has a decimal = significant COVERSIONS: Conversion factor = ration of 2 different units, used as a multiplier to change metric units EX. Convert 351 grams to pounds EX. Convert 1.844 gallons to millileters Temperature Conversions: DENSITY = mass/volume g/mL; g/L (gas); g/cm³ Specific gravity = numerically the same as density (related to density of water aka 1.00g/mL) Energy = capacity to do work kinetic- anything that moves (mechanical, light, heat energy are main examples; plane, car, human walking) has this energy. When motion stops, object has zero kinetic energy depends mostly on object speed potential – energy stored that arises from its capacity to move or cause motion according to its position depends mostly on object position. law of conservation of energy- energy can’t be created or destroyed HEAT- measure in calories (needed to raise temperature) Specific Heat- the amount of heat necessary to raise the temperature of 1.0 g of something by 1 degrees C CHAPTER TWO NOTES Mixture Types: homogeneous (Kool-Aid; air we breath; copper alloy) cant see diff. substances heterogeneous (raison bran; blood) at least 2 components can be observed Elements: consists of identical atoms 118 total (98 naturally occurring; rest chemically created) Compounds: pure substance that is made up of two or more elements in a fixed ratio by mass Mass number: sum of the # of protons and neutrons in nucleus Atomic number: The# of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Isotopes: Atoms with the same # protons ; different # of neutrons. ELECTRON CONFIGURATION: ORBITS AND SHELLS