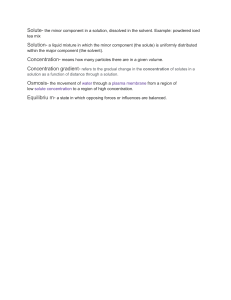
Name: ___________________________ Solutions Notes What is a solution? A solution is a homogenous mixture (uniform composition throughout). Solutions can be a solid, liquid, or a gas. Parts of a Solution: 1. Solute : substance being dissolved into another substance 2. Solvent : the dissolving medium Creation of Solutions - “Like Dissolves Like” This is the general rule to determine whether a solution will form. “Like” refers to the solvent and solute being either polar or nonpolar. Polarity of a molecule is a result of how the electrons are shared and arranged. Polar molecules have electrons shared in a way that causes one end of a molecule to be slightly positive while the other end is slightly negative. Water is a polar molecule. The two hydrogen atoms have a slightly positive charge, while the oxygen atom has a slightly negative charge. Water is referred to as the “Universal Solvent”. Other Properties of Water: Cohesion - the tendency of water molecules to lightly bond with other water molecules. Surface Tension - the tension that is created when water molecules are more attracted to other water molecules than to the air above. Adhesion - the tendency of molecules to stick to surfaces. When Substances Combine: 1. 2. 3. 4. Soluble - a substance that dissolves in a solvent Insoluble - a substance that does not dissolve in a solvent Immiscible - two liquids that cannot be mixed, they separate after mixing (water & oil) Miscible - two liquids that are able to be mixed together Solubility - maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent. Solubility Terminology: Saturated - solution that contains the maximum amount (g) of dissolved solute Unsaturated - solution contains LESS than the maximum amount (g) of dissolved solute. Supersaturated - solution contains MORE than the maximum amount of dissolved solute. Concentration - the amount (g) of solute dissolved in a specific amount of solvent Concentrated - large amount of solute for the amount of solution. [small amount of solvent] Dilute - small amount of solute for the amount of solution. [large amount of solvent] Solution Formation Which do you think will dissolve faster: a cube of sugar or some granulated sugar? Why? Some granulated sugar – it is broken into smaller pieces so it will dissolve quicker What factors affect the amount of solute that can be dissolved in a solution? stirring, temperature, & surface area (particle size) **Remember that like dissolves like = polar dissolves polar** Stirring Effects When you stir sugar & water together you are getting the sugar ( solute) to dissolve faster in the water (solvent). Each tiny grain of sugar contains millions of sugar molecules. The water hits each grain and causes it to break apart. When it breaks apart the pieces are so small that you can’t see them. By stirring you are causing fresh, unused water molecules to go and stick to the sugar molecules. The more you stir, the more the sugar grains are exposed to fresh solvent & it gets dissolved. Temperature As you raise the temperature of a sugar & water mixture the water molecules will move around faster. The faster the water molecules move, the harder they will hit the sugar molecules which will cause them to break apart and dissolve. The higher the temperature, the faster the water (solvent) will move, which will allow for more sugar (solute) to be dissolved. Particle Size When you are trying to dissolve something in water you are actually getting billions of water molecules to crash into the solute (thing that is dissolving) at high speeds. It would be easier to dissolve something that is crushed than something that is cubed. The water molecules would have less to break apart with granulated sugar versus cubed sugar. If something can dissolve in something else it is soluble in the solvent. Electrolytes & Nonelectrolytes When a compound is dissolved in water it might be able to conduct electrical current through it. This type of compound is called an electrolyte. All ionic compounds are electrolytes, so all ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in H2O. NaCl, KCl, MgO, & etc… are all ionic compounds so they will conduct electricity. Compounds that do not conduct electricity in water are called non-electrolytes. Many covalent, molecular compounds (2 or more non-metals) are non-electrolytes and do not conduct electricity. Tell whether the following compounds are electrolytes or not: NaCl CH4 AlCl3 electrolyte CaCl2 electrolyte non-electrolyte CO non-electrolyte electrolyte ClF non-electrolyte LiF electrolyte H2O non-electrolyte