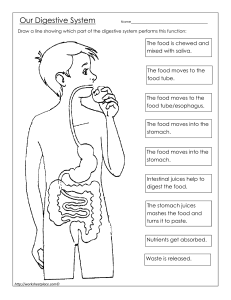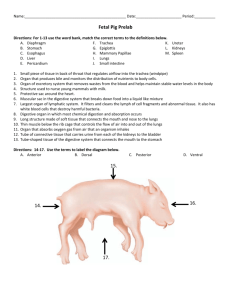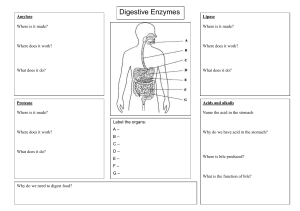
Body Organs By:Maamae Akua Fobi A. Organs are the body's recognizable structures (for example, the heart, lungs, liver, eyes, and stomach) that perform specific functions. The Brain The brain is a complex organ that controls thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger and every process that regulates our body. Together, the brain and spinal cord that extends from it make up the central nervous system, or CNS. A picture of the brain The Lungs The lungs are the major organs of the respiratory system, and are divided into sections, or lobes. The right lung has three lobes and is slightly larger than the left lung, which has two lobes. The lungs are separated by the mediastinum. This area contains the heart, trachea, esophagus, and many lymph nodes. A picture of the lungs The Heart The heart is a muscular organ about the size of a fist, located just behind and slightly left of the breastbone. The heart pumps blood through the network of arteries and veins called the cardiovascular system. A icture of the heart The Stomach The stomach is a J-shaped organ that digests food. It produces enzymes (substances that create chemical reactions) and acids (digestive juices). This mix of enzymes and digestive juices breaks down food so it can pass to your small intestine. Your stomach is part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. A picture of the Stomach The intestines The intestine is a muscular tube which extends from the lower end of your stomach to your anus, the lower opening of the digestive tract. It is also called the bowel or bowels. A picture of the intestines This is the end of my presentation