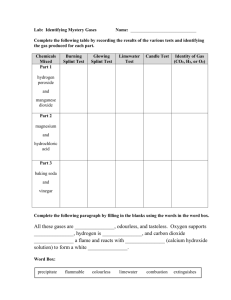
LAB: IDENTIFYING MYSTERY GASES Air is made up of a mixture of many gases, including nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and hydrogen. Most of these gases are colourless, odourless, and transparent, making them difficult to distinguish from one another. So how can we tell them apart? Different gases exhibit different chemical properties, such as reactivity with other chemical substances. These chemical properties are like fingerprints and allow for a gas' identity to be discovered. Pre-Lab : Make sure to read the lab procedure on page 270-271 before answering the Pre-Lab questions. /15 Answer all questions in the space provided below. 1. In your own words, what is the reason or purpose behind this lab? 2 marks To answer the next three questions, please go to the class website (sciencemrluth.weebly.com) under the SNC1D/Chemistry tab and watch the video ‘Gas Tests’: 2. How did the presenter identify oxygen gas? 1 mark 3. How did the presenter identify hydrogen gas? 1 mark 4. How did the presenter identify carbon dioxide gas? 1 mark Complete the following: Oxygen Test The splint should be… burning glowing (circle one) 3 marks If oxygen is present, the splint will: ____________________________________ What chemical property of oxygen allows you to identify it? ____________________________________ Hydrogen Test The splint should be… burning glowing (circle one) 3 marks If hydrogen is present, what will happen? ____________________________________ What chemical property of hydrogen are you testing for? ____________________________________ Carbon Dioxide The splint should be… burning glowing (circle one) 4 marks If you put a burning splint into carbon dioxide, what will happen? ___________________________________ The chemical test for carbon dioxide uses a liquid called ___________________________________________ A positive test for carbon dioxide, means the limewater will look ____________________________________ PURPOSE: How can you test for oxygen, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen gas produced in chemical reactions? MATERIALS: Goggles 4 test tubes test-tube rack hydrogen peroxide solution manganese dioxide powder toothpick 3 wooden splints Hydrochloric acid solution Magnesium ribbon Test-tube stopper candle sodium bicarbonate powder SAFETY PRECAUTIONS: Hydrochloric acid is corrosive. Any spills on the skin, in the eyes, on clothing should be washed immediately with cold water. Report any spills to your teacher. Hydrogen peroxide is a strong irritant. Do not get in eyes. Manganese dioxide is also toxic. Report any spills to your teacher. PROCEDURE: REFER TO ‘SCIENCE 9 PERSPECTIVES TEXTBOOK’ ON PAGE 270-271 Waste Disposal: Dispose of all mixtures into the waste containers provided at the end of the lab benches. Clean up your workstation, put away all materials and wash your hands. DISCUSSION QUESTIONS: Answer the following questions using complete sentences, if necessary. 1. In a chart format, two physical properties and two chemical properties for each gas produced in this lab. 2. Why did you record your observations before proceeding with each chemical reaction? 3. Which gas seemed to be the most hazardous in this activity? Why? Observations Table 1: (descriptive title) _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ STARTING SUBSTANCES (REACTANTS) PART NAME Potassium Iodide powder 1 Manganese Dioxide powder Hydrogen Peroxide Hydrochloric acid 2 Sodium hydrogen carbonate powder (Baking soda) limewater Hydrochloric Acid 3 Mossy zinc OR Magnesium metal PROPERTIES (AT LEAST 3) OBSERVATIONS AFTER MIXING (AT LEAST 2) WHAT HAPPENS WHEN THE STARTING MATERIALS ARE ADDED TOGETHER? RESULTS OF BURNING SPLINT TEST RESULT OF GLOWING SPLINT TEST RESULT OF LIMEWATER TEST NOTES 1. Using the chart below, state two physical properties and two chemical properties for each gas produced in this lab. Gas Physical Properties 2. What problems, if any, did you encounter in carrying out each of these tests? 3. Which gas seemed to be the most hazardous in this activity? Why? 4. What improvements, if any, would you make to the procedure in future tests? Chemical Properties