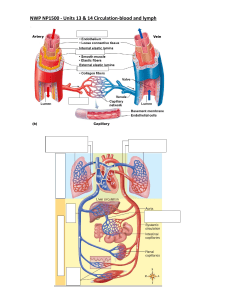
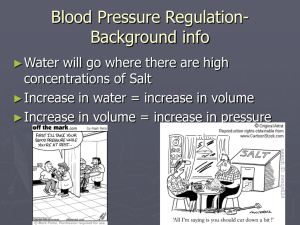
Q1. The body fluids of an osmoconformer would be __________ with its __________ environment. A) hyperosmotic; freshwater B) isotonic; freshwater C) hyperosmotic; saltwater D) iso-osmotic; saltwater E) hypoosmotic; saltwater Answer: D Q2. A freshwater fish was accidentally placed in salt water. After several minutes in this saline water, it died. What is the most logical explanation for its death? A) Loss of water by osmosis in cells in vital organs resulting in cell death and eventually organ failure. B) Salt diffused into all the fishʹ s cells causing them to swell and, in some cases, lyse. C) The kidneys were not able to keep up with the water removal necessary in this hyperosmotic environment creating an irrevocable loss of homeostasis. D)The gills became encrusted with salt, resulting in inadequate gas exchange and a resulting asphyxiation. E) Brain cells lysed as a result of increased osmotic pressure in this hyperosmotic environment; death by loss of autonomic function. Answer: A Q3. What is the main nitrogenous waste excreted by birds? A) ammonia B) nitrate C) urea D) uric acid Answer: D Q4. Materials are returned to the blood from the filtrate by which of the following processes? A) filtration B) ultrafiltration C) selective reabsorption D) secretion E) active transport Answer: C Q5. Which group possess excretory structures known as protonephridia? A) flatworms B) earthworms C) insects D) vertebrates Answer: A Q6. Which group possess excretory organs known as Malpighian tubules? A) earthworms B) flatworms C) insects D) jellyfish Answer: C Q7. What is unique about transport epithelial cells in the ascending loop of Henle in humans? A) They are the largest epithelial cells in the body. B) They are not in contact with interstitial fluid. C) Their aquaporin-less membranes are impermeable to water. D) 50% of their cell mass is comprised of smooth endoplasmic reticulum. E) They are not affected by high levels of nitrogenous wastes. Answer: C Q8. How does ADH function at the cellular level? A) ADH stimulates the reabsorption of glucose through channel proteins. B) It causes membranes to include more phospholipids that have unsaturated fatty acids. C) It causes an increase in the number of aquaporin molecules of collecting duct cells. D) It decreases the speed at which filtrate flow through the nephron leading to increased reabsorption of water. Answer: C Q9. How do ADH and RAAS work together in maintaining osmoregulatory homeostasis? A) ADH monitors osmolarity of the blood and RAAS regulates blood volume. B) ADH monitors appropriate osmolarity by reabsorption of water, and RAAS maintains osmolarity by stimulating Na+ reabsorption. C) ADH an RAAS work antagonistically; ADH stimulates water reabsorption during dehydration and RAAS removal of water when it is in excess in body fluids. D) Both stimulate the adrenal gland to secrete aldosterone which increases both blood volume and pressure. E) Only when they are together in the receptor sites of proximal tubule cells, will reabsorption of essential nutrients back into the blood take place. Answer: B Q10. Natural selection should favor the highest proportion of juxtamedullary nephrons in which of the following species? A) a river otter B) a mouse species living in a tropical rain forest C)a mouse species living in a temperate broadleaf forest D) a mouse species living in the desert E) a beaver Answer: D Q11. Cells in the Bowman's capsule that wrap around capillaries of the glomerulus are called: A) fenestrae B) podocytes C) pedicels D) macula densa Answer: B Q12. A woman with High Blood Pressure is given diuretics. The intent was to have: A) her urine output decrease A) her urine output increase B) her stop urinating for the next 24 hours C) her blood volume increase D) her K+ levels increase Answer: A