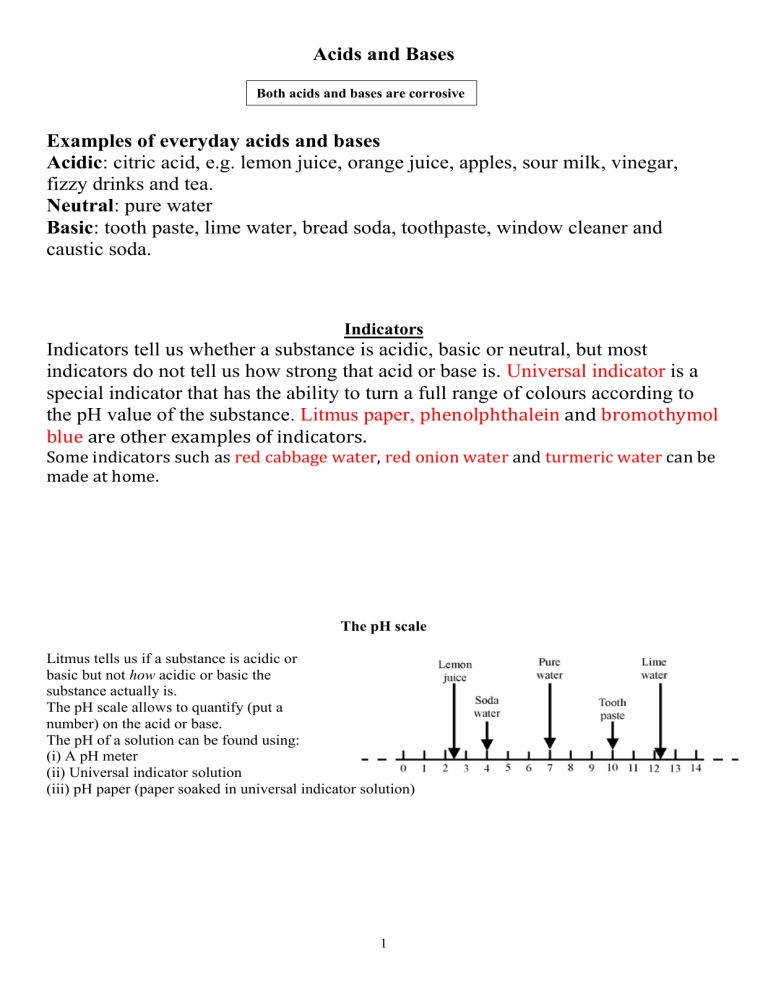
Acids and Bases Both acids and bases are corrosive Examples of everyday acids and bases Acidic: citric acid, e.g. lemon juice, orange juice, apples, sour milk, vinegar, fizzy drinks and tea. Neutral: pure water Basic: tooth paste, lime water, bread soda, toothpaste, window cleaner and caustic soda. Indicators Indicators tell us whether a substance is acidic, basic or neutral, but most indicators do not tell us how strong that acid or base is. Universal indicator is a special indicator that has the ability to turn a full range of colours according to the pH value of the substance. Litmus paper, phenolphthalein and bromothymol blue are other examples of indicators. Some indicators such as red cabbage water, red onion water and turmeric water can be made at home. The pH scale Litmus tells us if a substance is acidic or basic but not how acidic or basic the substance actually is. The pH scale allows to quantify (put a number) on the acid or base. The pH of a solution can be found using: (i) A pH meter (ii) Universal indicator solution (iii) pH paper (paper soaked in universal indicator solution) 1 The pH scale tells us how acidic or basic a solution is pH greater than 7: the substance is alkaline pH less than 7: the substance is acidic pH 7: the substance is neutral Universal Indicator pH Scale 2 Common strong acids and bases Acids hydrochloric acid sulfuric acid Nitric Acid Bases sodium hydroxide calcium hydroxide calcium carbonate HCl H2SO4 HNO3 NaOH Ca(OH)2 CaCO3 Alkalis are bases that are dissolved in water Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) is an example of an alkaline substance. Neutralisation The properties of an acid are counteracted or neutralised by a base; this type of reaction is called a neutralisation reaction. When an acid reacts with a base the hydrogen in the acid is replaced by a metal and a salt is formed General formula to represent neutralisation reaction: Acid + → Base Salt Example 1 hydrochloric acid HCL + + sodium hydroxide NaOH → sodium chloride → NaCl Example 2 hydrochloric acid 2HCl + + calcium carbonate CaCO3 → calcium chloride → CaCl2 3 + + + Water Water + H2O CO2 + Water + CO2 + H2O A. Reaction of Metal Oxides with Acids Salt + Water Metal Oxide + Acid For example, Copper Oxide + Sulfuric Acid Copper Sulfate + Water B Reaction of Metal Carbonates with Acids acid + metal carbonate → salt + carbon dioxide + water A. Reaction of Metal hydroxide with Acids Metal hydroxide + Acid Salt + Water For example, The word equation for this reaction is: hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide → sodium chloride + water The chemical equation is: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O 4