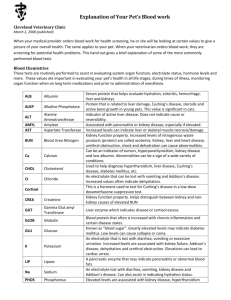
CBC Interpretation CBC tells us 3 things: Oxygen delivery (RBC), infection (WBC), & hemostasis/clotting (PLT) Oxygen delivery: RBC, Hgb (carries O2), Hct • Multiply by 3: (RBC 3 Hgb 9 Hct 28) • RBC increased in: hemoconcentration, COPD • RBC decreased in: hemodilution, chemo, dietary deficiency, hemolytic anemia, leukemia • MCV (mean corpuscular volume): average volute in the red blood cell. >100 = macrocytic; cells need Vit B12 and folate to divide, if they do not divide they become large, <80 = microcytic: if cells lack iron and protein they lack volume • MCH (mean corpuscular hemoglobin): average protein/hemoglobin inside the cell • MCHC (mean corpuscular hematocrit): average hematocrit inside the cell • RDW (red cell distribution width): size and shape of the cell, used in conjunction with anemia Infection: WBC “Never Let Monkey’s Eat Bananas”, Neutrophils, Lymphocytes • Neutrophils: Bacterial • Lymphocytes: Viral • Monocytes: Chronic inflammatory process (eosinophils & basophils) • Eosinophils: Parasites, Allergies, Asthma • Basophils: Parasites, Allergies, Immune response • Segs: mature Neutrophils • Bands: immature Neutrophils Clotting: Platelets • PLT: platelets show body’s clotting ability, go hand in hand with LFTS (liver function tests), clotting factors are made by the liver. Clot is made of Finbrin Mesh & Platelet; Fibrinogen is converted by Thrombin into Fibrin. Fibrinogen is synthesized in the liver, platelet synthesis is regulated by thrombopoietin, a hormone that is produced by the liver and kidneys (ex. ETOH) LFTS (Liver Function Tests) ALT: (Alanine Aminotransferase) an enzyme found in the liver and increases with liver damage • Used to monitor liver disease such as ETOH abuse, cirrhosis, and liver tumors. Medications can also cause an increase in ALT (Tylenol OD) • Dependent on vitamin B6 and will be decreased in low B6 & cirrhosis • Pt will be jaundice, fatigue, N/V, dark urine, pale stools, itching, ascites (the accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, causing abdominal swelling), and mental changes (decreased LOC) AST: (Aspartate Aminotransferase) another enzyme found primarily in the liver, but is also found in the heart, muscle, pancreas, kidney & brain AST & ALT are often measured together. Dependent on B6 • Increased for the same reasons as above, however this can also be elevated d/t damage of other organs, which is why they are evaluated together • Levels may also be elevated in bile duct blockage (gallbladder stones) and muscle injury such as heart attacks, injections, and strenuous exercise. Lipase: an enzyme secreted by the pancreas to break down triglycerides (fat) • Most commonly elevated in acute pancreatitis. Also elevated in duct obstruction, malignancy, cholecystitis, SBO, DKA & liver disease • Excreted by the kidney and can be found in Pts /c renal failure • Onset 24-48 hours after symptoms and continuous for 5-7 days, making in more useful in acute pancreatitis rather than chronic Amylase: another enzyme excreted by the pancreas to break down CHO • Most commonly elevated on acute and chronic pancreatitis, but also in ulcers, obstructions, gallbladder attacks and cancer • Onset is 12 hours and normalizes in 48-72 hours, is cleared through the kidneys Albumin is blood plasma protein synthesized by the liver. It’s the main protein in human blood, and transports hormones such as thyroid, estrogen, and cortisol. It tells us if our Pt has liver or kidney disease or if the body is not absorbing enough proteins (malnutrition) • Increased in liver disease, ascites, burns, malabsorption syndrome and malnutrition Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) Evaluates glucose levels, electrolytes, acid/base balance, kidney function. Glucose: Normal 70-110 direct measurement of glucose in blood, Elevated in DM or corticosteroids Decreased in poor PO intake Sodium (NA+) Normal 135-145: Hypernatremia: dehydration, too much sodium in IVF. S/Sx: confusion, muscle weakness, seizures; Hyponatremia: water intoxication, decreased dietary intake, S/Sx: weakness, confusion Potassium (K+) Normal 3.5-5: Hyperkalemia: renal failure, rhabdomyolysis, acidosis (K shifts from cell into serum) S/Sx: cramping. Hypokalemia: dehydration, vomiting, diarrhea, endocrine Magnesium (Mg) Normal 1.5-2.5: need normal Mg to maintain normal K, muscles depend on Mg to function, increases absorption of Ca, replacing Mg may fix Ca. Hypermagnesia: kidney failure. S/Sx: decreased HR. Hypomagnesia: ETOH abuse, diuretics, V/D. S/Sx: seizures, cramping Calcium (Ca+) Normal 8.5-10.5: Hypercalcemia: cancer (Ca moves from bone into serum). S/Sx: weakness, thirsty. Hypocalcemia: decreased Vit D (these go hand in hand), renal failure. S/Sx: cramping. Calcium binds to albumin; if albumin is low, so is Ca+. Common cause is malnutrition. Chloride (Cl-) Normal 95-105: Follows Na+. Hyperchloremia: dehydration, metabolic acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, too much NS. S/Sx: lethargy, weakness. Hypochloremia: overhydrated, CHF, V/D, burns. S/Sx: shallow breathing, decreased BP, tetany Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Normal: 8-20: measures RENAL Function and LIVER function. Urea is formed in liver and is end product of metabolism. Elevated in shock, sepsis, dehydration, CHF, MI (decreased blood flow), GI Bleeding, any time your body doesn’t have enough blood. Decreased in liver failure, malnutrition, overhydration Creatinine Normal 0.6-1.3: used to diagnose RENAL function, excreted by kidneys. Elevated in renal disease & rhabdomyolysis Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) Normal >60: equation of how much blood passes through the kidney each 1 minute. Changes with factors such as age, race, and sex. Used to decide if Pt needs dialysis: <60 for 3 months = chronic kidney disease, <15=kidney failure Urinalysis Reference Range/Normal Values • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Color --- Yellow (light/pale to deep amber) Clarity/Turbidity – Clear to cloudy pH – 4.5-8 Specific Gravity – 1.005-1.025 Glucose – < 130 mg/d Ketones – negative Nitrites – negative Leukocyte esterase – Negative Bilirubin – Negative Urobilirubin – Small amount (0.5-1 mg/dL) Blood – < 3 RBCs Protein – <150 mg/d RBCs – < 2 RBCs/hpf WBCs – <2-5 WBCs/hpf Squamous epithelial cells – < 15-20 squamous epithelial cells/hpf Casts – 0-5 hyaline casts/lpf Crystals – Occasionally Bacteria – None Yeast – None Review patient chart. Temperature ___________ (Oral, Temporal, Axillary, Tympanic, Rectal) (98.6) Pulse – rate _____, strength (strong, weak), rhythm (regular, irregular) (60-100 bpm) Perform hand hygiene. Resp – rate _____, rhythm (regular, irregular), depth (shallow, deep, normal), effort (labored, unlabored) (12-20 resp/min) Identify patient, introduce yourself, Blood pressure (LA, RA) _______________ (120/80) MAP ___________ explain procedure. Possible Pressure Points • Elbows • Sacrum Oxygen (rate & route) _________________________________ • Heels/Ankles Pain? Provoked ___________ Quality ____________ Radiate/Where ________ • Scapula Scale (0-10) ________ Time/when did it start ____________ Pulse oximeter ______________ (>90) Provide privacy. Neurological Assess hair & nails as you go Symptoms __________________ LOC ___________ Orientation? ___________ Affect/behavior ____________ Speech ____________ Facial symmetry ________ Ability to move extremities _________________ Gait _________________ JVD Pupils (equal, round, reactive to light PERRL) bilat _________ mm Neurovascular/Neuromuscular Strength ______________ Numbness/Tingling? ______________ Plantar/& dorsiflexion _________________ Nail beds (color, cap refill x10 fingers) __________ x10 toes__________ Edema General/Local Location, amount, pitting/nonpitting _____________________ Pulses (quality, presence) radial _____________ pedal _____________ Pallor (pink, warm & dry (W/D), intact) _______________________ Integrity ______________________________________________________ Turgor (elastic, tenting) Radial Pulse Mucous membranes ______________ Sub Q Sub Q Glasgow Coma Scale Eye opening ____ Best motor _____ Best verbal _____ Respiratory Symptoms _________ Breathing probs _________ regularity _________ Chest symmetry ________ Oxygen type __________ Cough ? __________ Sub Q Sputum (color, amount, consistency) ________________________ X Breath Sounds/What heard, where __________________________________ Cardiovascular Symptoms ____________________ Apical (count 60 secs)____________ JVD __________ Heart rhythm _________________ Sub Q LOC: Squeeze Push Pull Check for swelling Pedal Pulse Gastrointestinal Symptoms __________________ Eating difficulties ________________ Nutrition risk _____________________ Appetite ______________________ 1. Abdomen (flat, rounded, scaphoid) (soft, firm, distended) 2. BS x 4 quadrants (hypoactive, hyperactive) 3. Abdomen tenderness/Pain _______ Belching/flatus __________ Last BM ? ________Stool color, description _____________ Genitourinary Symptoms ____________________ Bladder distention _________________ Urinary elimination (voiding difficulties, catheter) _____________________ Any Pain/burning with urination? For Females, any discharge? Voiding difficulties (burning, dribbling, nocturia, etc.) __________________ Purposeful Rounding /QH Activity order ________________ Position _________ Antiembolism devices ___________ ROM __________ Assistive devices ______________________________ Activity assist _____________ Family Present _______ Bed Safety Information Brakes, alarms, side rails, low position, call light HOB degrees ______________ Turn assist _________ Urine description (amount, clarity, color, odor) _____________________ Report <30 ml/hr Peripheral IV Site assess ____________________________ Incision/Wound Dressing ________________ Patency ____________ Description ___________________________ Size ______________ Potty ______________ Pain ______________ Surrounding tissue ___________________ Drainage ________________ Care _________________ Dressing ____________________ Pressure ulcer description ________________________________________ Nutrition Diet type __________________ feeding assist _____________ NOTES: