2. Methos of separation of mixtures
advertisement

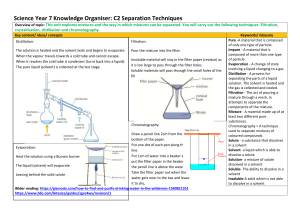
There are different substances within a mixture can be separated as they are not chemically bonded, therefore, retain their individual properties. Different techniques can be used, depending on the their physical properties. Techniques include: magnetisation, filtration, centrifugation, evaporation, simple distillation, fractional distillation, separating funnel, chromatography DECANTATION The careful pouring off of a liquid from a mixture containing both liquid and solid. Colander, strainer, FILTRATION coffee filter Is used to separate a solid suspended in a liquid or gas. Based on size Substances separated into a filtrate and a residue ◦ Filtrate = liquid that passes through the filter paper ◦ Residue = solid that remains on the filter paper EX: ◦ Sand and water ◦ Water from rivers is filtered to remove solid particles. CENTRIFUGATION Is the process based on the densities of the particles in that mixture. Used to separate insoluble solid or suspension from a liquid It is used to accelerate sedimentation Blood – Mixture of red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma.. EVAPORATION To separate a solid disolved in a liquid. Heating the solution until the solvent evaporates living behind the solid residue. For separating a mixture (solution) of a soluble solid and a solvent. miscibility: the capacity of a liquid to dissolve into another. DISTILLATION For separating a mixture of miscible liquids. (liquid from a solution). Based in the difference of the Boiling points of each liquid. Ex. ◦ water from a salt solution ELECTROLYSIS The CHEMICAL separation of the hydrogen atoms from oxygen atom in a water molecule. CHEMICAL SEPARATION – PURE SUBSTANCE