a) add, subtract, multiply, divide, and simplify rational algebraic
advertisement
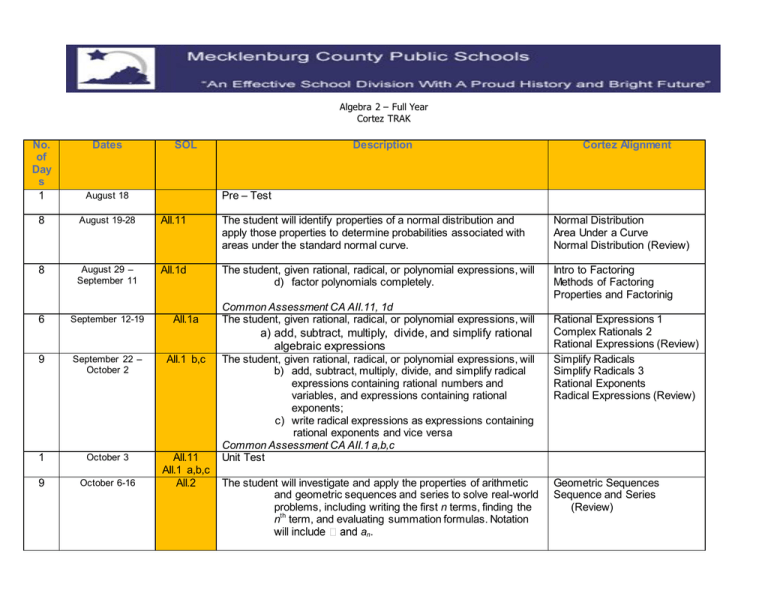
Algebra 2 – Full Year Cortez TRAK No. of Day s 1 Dates SOL Description Cortez Alignment August 18 8 August 19-28 AII.11 The student will identify properties of a normal distribution and apply those properties to determine probabilities associated with areas under the standard normal curve. Normal Distribution Area Under a Curve Normal Distribution (Review) 8 August 29 – September 11 AII.1d The student, given rational, radical, or polynomial expressions, will d) factor polynomials completely. Intro to Factoring Methods of Factoring Properties and Factorinig 6 September 12-19 Pre – Test AII.1a Common Assessment CA AII.11, 1d The student, given rational, radical, or polynomial expressions, will a) add, subtract, multiply, divide, and simplify rational algebraic expressions 9 September 22 – October 2 AII.1 b,c 1 October 3 9 October 6-16 AII.11 AII.1 a,b,c AII.2 The student, given rational, radical, or polynomial expressions, will b) add, subtract, multiply, divide, and simplify radical expressions containing rational numbers and variables, and expressions containing rational exponents; c) write radical expressions as expressions containing rational exponents and vice versa Common Assessment CA AII.1 a,b,c Unit Test The student will investigate and apply the properties of arithmetic and geometric sequences and series to solve real-world problems, including writing the first n terms, finding the nth term, and evaluating summation formulas. Notation an. Rational Expressions 1 Complex Rationals 2 Rational Expressions (Review) Simplify Radicals Simplify Radicals 3 Rational Exponents Radical Expressions (Review) Geometric Sequences Sequence and Series (Review) 7 7 October 20-28 October 29 – November 7 AII.3 AII.4a The student will perform operations on complex numbers, express the results in simplest form using patterns of the powers of i, and identify field properties that are valid for the complex numbers. The student will solve, algebraically and graphically, a) absolute value equations and inequalities; Common Assessment CA AII.2,3,4a b) quadratic equations over the set of complex numbers; c) equations containing rational algebraic expressions; and d) equations containing radical expressions. Graphing calculators will be used for solving and for confirming the algebraic solutions. Imaginary Numbers Imaginary Numbers (Review) Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities Absolute Value (Review) 5 November 10-14 AII.4b 5 7 November 17-21 November 24 – December 4 AII.4c AII.4d 1 December 5 10 December 8-19 6 January 7-14 AII.5 6 January 15-23 AII.9 The student will collect and analyze data, determine the equation of the curve of best fit, make predictions, and solve real-world problems, using mathematical models. Mathematical models will include polynomial, exponential, and logarithmic functions. Line/Curve of Best Fit Data and Best Fit (Review) 6 January 26 – February 2 AII.10 The student will identify, create, and solve real-world problems involving inverse variation, joint variation, and a combination of direct and inverse variations. Inverse/Joint Variation Variation (Review) 1 February 3 AII.5 AII.9 AII.2 AII.3 AII.4 a,b,c,d Quadratic Equations 1 Quadratics (Review) Radical Equations Radical/Rational Eq (Review) Common Assessment CA AII.4 b,c,d Unit Test Pacing Calibration Project Work Cumulative Review Midterm Exam The student will solve nonlinear systems of equations, including linear-quadratic and quadratic-quadratic, algebraically and graphically. Graphing calculators will be used as a tool to visualize graphs and predict the number of solutions. Common Assessment CA AII.5,9,10 Unit Test Linear/Non-linear Systems Linear Quadratic Systems (Review) AII.10 AII.7 g,h 7 February 4-12 7 February 16-24 AII.7 a,b,c,d,e,f 8 February 25 – March 6 AII.8 4 March 9-12 AII.6 6 March 16-23 AII.6,7,8 1 March 24 7 March 25 – April 2 AII.6 AII.7 AII.8 AII.12 1 April 3 25 April 13 – May 15 The student will investigate and analyze functions algebraically and graphically. Key concepts include g) inverse of a function; and h) composition of multiple functions Evaluate/Compose Function The student will investigate and analyze functions algebraically and graphically. Key concepts include a) domain and range, including limited and discontinuous domains and ranges; b) zeros; c) x- and y-intercepts; d) intervals in which a function is increasing or decreasing; e) asymptotes; f) end behavior The student will investigate and describe the relationships among solutions of an equation, zeros of a function, x-intercepts of a graph, and factors of a polynomial expression. Domain and Range End Behavior Functions (Review) Common Assessment CA AII.7,8 The student will recognize the general shape of function (absolute value, square root, cube root, rational, polynomial, exponential, and logarithmic) families and will convert between graphic and symbolic forms of functions. A transformational approach to graphing will be employed. Graphing calculators will be used as a tool to investigate the shapes and behaviors of these functions. Polynomial Functions 2 Zeros (Review) Transformational Graphing Rational Functions Exponential and Logarithmic Rational Functions (Review) Transformations and Poly (Review) Common Assessment CA AII.6 Review and relate these 3 standards. Unit Test The student will compute and distinguish between permutations and combinations and use technology for applications. Common Assessment CA AII.12 Post – Test SOL Review/Testing Combinations Permutations and Combo (Review)