VO max Measurement and Analysis
advertisement
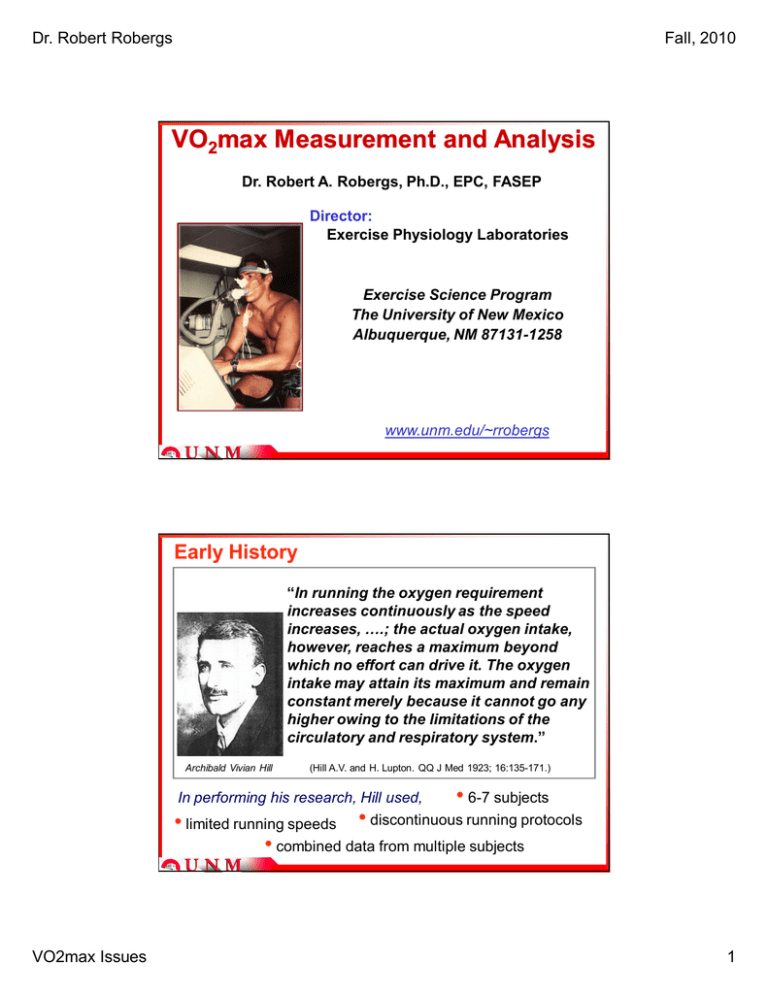
Dr. Robert Robergs Fall, 2010 VO2max Measurement and Analysis Dr. Robert A. Robergs, Ph.D., EPC, FASEP Director: Exercise Physiology Laboratories Exercise Science Program The University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM 87131-1258 www.unm.edu/~rrobergs Early History “In running the oxygen requirement increases continuously as the speed increases, ….; the actual oxygen intake, however, reaches a maximum beyond which no effort can drive it. The oxygen intake may attain its maximum and remain constant merely because it cannot go any higher owing to the limitations of the circulatory and respiratory system.” Archibald Vivian Hill (Hill A.V. and H. Lupton. QQ J Med 1923; 16:135-171.) In performing his research, Hill used, • 6-7 subjects • limited running speeds • discontinuous running protocols • combined data from multiple subjects VO2max Issues 1 Dr. Robert Robergs Fall, 2010 What is VO2max VO2 VO2max Cardiorespiratory limitations Duration should be ~8-10 min Time or Intensity Definitions: • The maximum rate oxygen can be taken in (pulmonary), transported (circulatory), and utilized (peripheral) for energy production. • The maximal rate at which the body can consume oxygen during exercise. Other “less correct” terms! “aerobic capacity” “aerobic power” “maximal cardiorespiratory capacity” VO2max Issues 2 Dr. Robert Robergs Fall, 2010 Powers and Howley, 1997, p: 50 “VO2max represents the physiological ceiling for the ability of the oxygen transport system to deliver O2 to contracting muscles.” Wilmore and Costill, 1994, p: 11 “…. Oxygen consumption peaks and remains constant or drops slightly, even though work intensity continues to increase…. The best single measurement of cardiorespiratory endurance and aerobic fitness.” VO2max Issues 3 Dr. Robert Robergs Fall, 2010 Robergs and Roberts, 1998, p: 227 “… the maximal rate that the body can consume oxygen during exercise… detected as a plateau despite further increases in exercise intensity...” VO2max Issues 4 Dr. Robert Robergs Fall, 2010 Determinants of VO2max CENTRAL HR x SV Cardiac Output PERIPHERAL A-aPO2 SaO2 [Hb] oxygen delivery PO2 gradients VO2max = Qmax x a-vO2max capillary density muscle mass fiber dimensions O2 supply demand relationships Peripheral Oxygen Diffusion VO2max Issues 5 Dr. Robert Robergs Fall, 2010 Plateau??? 2800 2400 VO2 (mL/min) Clear plateau Subject #2 Subject #3 2000 1600 1200 800 400 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Time (min) For 34 subjects, breath-by-breath data with an 11 breath average, and based on VO2 50 mL/min for VO2max and closest neighboring data point. VO plateau incidence = 86% 2 Background • No universally recommended procedures for processing VO2 data from breath-by-breath indirect calorimetry, or from time averaged systems. • No standardized criteria or recommended methods for detecting either of a VO2 plateau, the maximal rate of oxygen consumption (VO2max), or a peak VO2 in the absence of a VO2 plateau (VO2peak). • Increasing use of breath-by-breath indirect calorimetry in education, research and professional practice • The lack of any objective criteria to follow when processing decreases the validity of measurement. VO2max Issues 6 Dr. Robert Robergs Fall, 2010 Challenges • How do researchers in exercise physiology currently collect and process data? • How long should the protocol be? • What type of protocol should be used? • What causes the “noise” in breath-by-breath VO2 data? • Should this “noise” be reduced? If so, how? • What is a VO2 plateau? • How can a VO2 plateau be objectively determined? • What is VO2max vs. VO2peak? • How can VO2max and VO2peak be objectively determined? VO2 (L/min) What causes the “noise” in breath-by-breath VO2 data? 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 VE STPD (L/min) 2.17 0.3 L/min, with a range of 1.4 – 3.3 L/min 70 55 40 25 10 VO2max Issues 7 Fall, 2010 Variability 96 % explained by a twofactor model of VE and FEO2 Predicted VO2 (L/min) Dr. Robert Robergs 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 0.0 3.5 Pred VO2 = 0.9572(Meas VO2) + 0.0898 R2 = 0.9572 SEE = 0.059 L/min) 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 Measured VO2 (L/min) VO2 (L/min) 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 Measured Predicted 0.5 0.0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Time (min) Variability Remaining VO2 (L/min) 2.5 5%error 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Time (min) VO2max Issues 8 Dr. Robert Robergs Fall, 2010 Should this “noise” be reduced? YES How should this “noise” be reduced? 4.5 3.5 VO2 (L/min) VO2 (L/min) 4 a=bb 4.0 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 Time Averaging b=15 s 3 2 40 e 1 1.0 0.5 60 s 0 5 10 15 0 20 0 Time (min) 4 5 10 15 20 Time (min) Breaths 30 0.0 20 30 s 4 c=30 s d=60 s 10 VO2 (L/min) VO2 (L/min) 15 s 3 2 1 0 0 2 5 10 15 20 Time (min) 1 0 0 5 10 15 Time (min) VO2max Issues 3 20 0 0 5 10 15 20 Time (min) 9 Dr. Robert Robergs Fall, 2010 4.5 Breath Averaging b=5 bre aths 4 3.5 VO2 (L/min) 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 3 2 1.75 1.0 1 0.5 0.0 0 0 5 10 15 20 0 5 Time (min) 15 20 Time (min) 4 c=11 breaths d=21 bre aths 3 VO2 (L/min) VO2 (L/min) 4 10 2 1 Time Interval (min) VO2 (L/min) 5 a=bb 4.0 1.50 1.25 21 breaths 1.00 0.75 11 breaths 0.50 5 breaths 0.25 3 bb 0.00 0 2 5 10 15 20 Time (min) 1 0 0 5 10 15 0 20 0 Time (min) 5 10 15 20 Time (min) 4 VO2 (L/min) a muscle Digital Filtering 3 2 1 4 d VO2 (L/min) 0 4 VO2 (L/min) b cardiovascular 3 3 2 1 2 1 0 0 4 e VO2 (L/min) c VO2 (L/min) ventilation 4 3 2 2 1 1 0 0 0 50 100 150 Data Points VO2max Issues 3 200 250 0 50 100 150 200 250 Data Points 10 Dr. Robert Robergs Fall, 2010 Digital Filter Example What is a VO2 plateau? linear regress ion 3750 VO2 (mL/min) 4000 VO2 (mL/min) 3500 3000 3500 3250 VO2 plateau at VO2max 3000 2500 2750 12 13 2000 14 15 16 17 18 Time (min) initial deviation from linearity 1500 1000 500 exercise rest 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Time (min) VO2max Issues 11 Dr. Robert Robergs Fall, 2010 What is VO2max or VO2peak? VO2 (L/min) 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Time (min) Data Example treadmill running VO2 (mL/min) 4000 3600 3200 2800 2400 2000 10 11 12 13 14 15 Time (min) VO2max Issues 12 Dr. Robert Robergs Fall, 2010 Conclusions • Clear rationale for processing breath-by-breath VO2 data to decrease “noise”. • Processing best done by digital filtering • Still formulating and debating criteria and methods to quantify VO2 plateau, VO2max, VO2peak • In the absence of a VO2 plateau, what are valid criteria to use to verify a “true” VO2max? VO2max Issues 13