420:153g Physiology of Exercise
advertisement
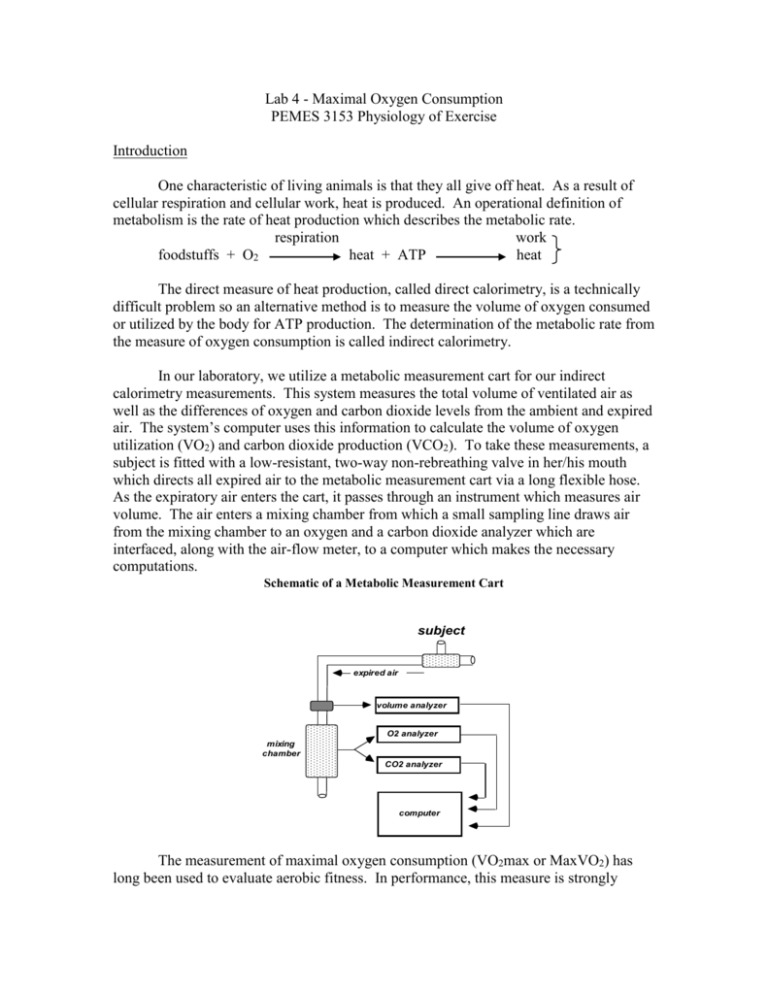
Lab 4 - Maximal Oxygen Consumption PEMES 3153 Physiology of Exercise Introduction One characteristic of living animals is that they all give off heat. As a result of cellular respiration and cellular work, heat is produced. An operational definition of metabolism is the rate of heat production which describes the metabolic rate. respiration work foodstuffs + O2 heat + ATP heat The direct measure of heat production, called direct calorimetry, is a technically difficult problem so an alternative method is to measure the volume of oxygen consumed or utilized by the body for ATP production. The determination of the metabolic rate from the measure of oxygen consumption is called indirect calorimetry. In our laboratory, we utilize a metabolic measurement cart for our indirect calorimetry measurements. This system measures the total volume of ventilated air as well as the differences of oxygen and carbon dioxide levels from the ambient and expired air. The system’s computer uses this information to calculate the volume of oxygen utilization (VO2) and carbon dioxide production (VCO2). To take these measurements, a subject is fitted with a low-resistant, two-way non-rebreathing valve in her/his mouth which directs all expired air to the metabolic measurement cart via a long flexible hose. As the expiratory air enters the cart, it passes through an instrument which measures air volume. The air enters a mixing chamber from which a small sampling line draws air from the mixing chamber to an oxygen and a carbon dioxide analyzer which are interfaced, along with the air-flow meter, to a computer which makes the necessary computations. Schematic of a Metabolic Measurement Cart subject expired air volume analyzer O2 analyzer mixing chamber CO2 analyzer computer The measurement of maximal oxygen consumption (VO2max or MaxVO2) has long been used to evaluate aerobic fitness. In performance, this measure is strongly related to endurance activities of short duration (one mile run) and moderately related to longer endurance (10K run and longer) tasks. In health, this measure has been linked to cardiorespiratory function as well as skeletal muscle oxygen consumption capabilities. Thus it has been viewed as the measure that reflects cardiorespiratory endurance, one of the health-related fitness components. Directly measuring VO2max requires laboratory instrumentation (metabolic cart), a mode of exercise that utilizes a lot of muscle (running for instance), an appropriate test protocol that minimizes oxygen deficit, and a motivated subject to perform a continuous test until exhaustion. While this is possible in an Exercise Physiology Laboratory, it is less practical in most wellness centers, sports medicine rehabilitative centers, and schools. Therefore many times tests are used to indirectly evaluate VO2max based upon performance to maximal efforts (time to fatigue on a progressive treadmill test), time in an aerobic task (1.5 mile test), or using the submaximal response to exercise and estimating the VO2max (heart rate response during a walking test). The purpose of this laboratory is to demonstrate a VO2max test using a direct measurement and learn the criteria for assessing whether a "true" VO2max value was obtained. Differences in VO2max between males and females will also be evaluated. Measurements 1. Two volunteer subjects, one male and one female will be solicited. Each will be subjected to a protocol using the treadmill and metabolic cart to measure the highest rate of oxygen consumption (VO2). A Polar heart rate transmitter will be used to monitor heart rate during the test. 2. For this laboratory experience, a protocol that starts with a warm-up of 3.5 mph for two minutes, 5.5 mph for two minutes, and increases the speed 0.5 mph every one minute until a running velocity comfortable for the subject is reached. Then the grade will be increased 1% every minute until reaching volitional exhaustion. It is important in this type of maximal effort to provide verbal encouragement for the subject to motivate him/her during the latter stages of the test. 3. The following variables will be determined each minute of the test: VO2 in ml.kg1. min-1, VO2 in ml.min-1, VE in L.min-1 , RER, and heart rate. Analysis 1. Using the article provided (“Criteria for VO2 max” on the website), determine if each subject reached a true VO2max and identify the criteria you used to make that decision. 2. Normally you expect and average male to have a higher VO2max than an average female of the same age and training level. What are three reasons the average male has a higher VO2max than the average female? 3. If all you knew was the data collected on each subject and that the subjects were equally trained in running and cycling and were the same age, which subject would do better in a 5 mile running race on a track? Which would do better on a 10 mile bicycle race over flat terrain? Explain your answers using physiological principles and rationale.